This article explains how to use Linear Array to arrange models at equal intervals.
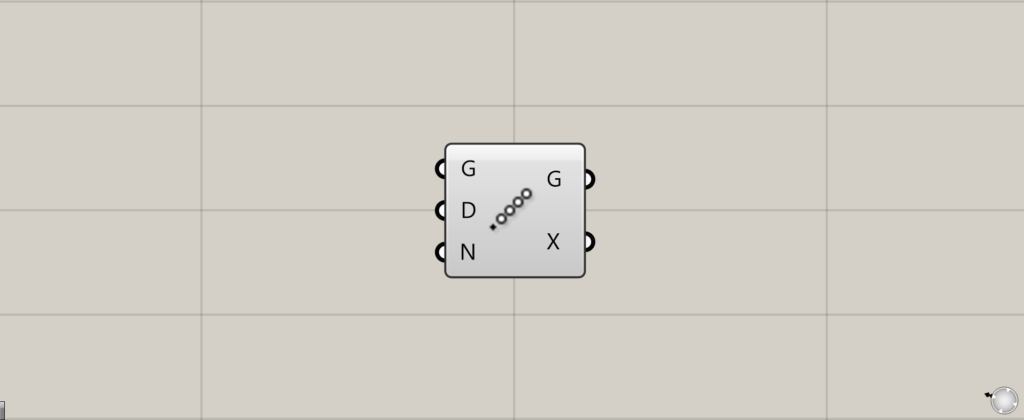
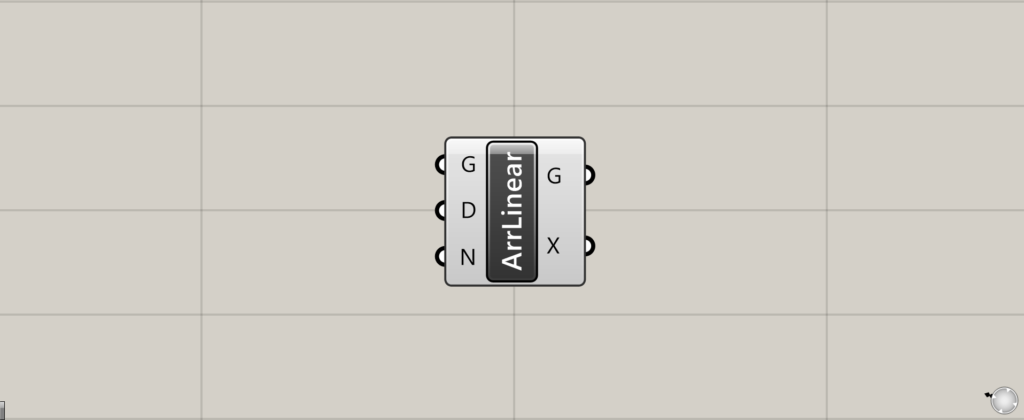
On the Grasshopper, it is represented by either of the two above.
Copying an array of objects equally spaced in a single direction
Linear Array allows you to copy an array of objects in a single direction at equal intervals.
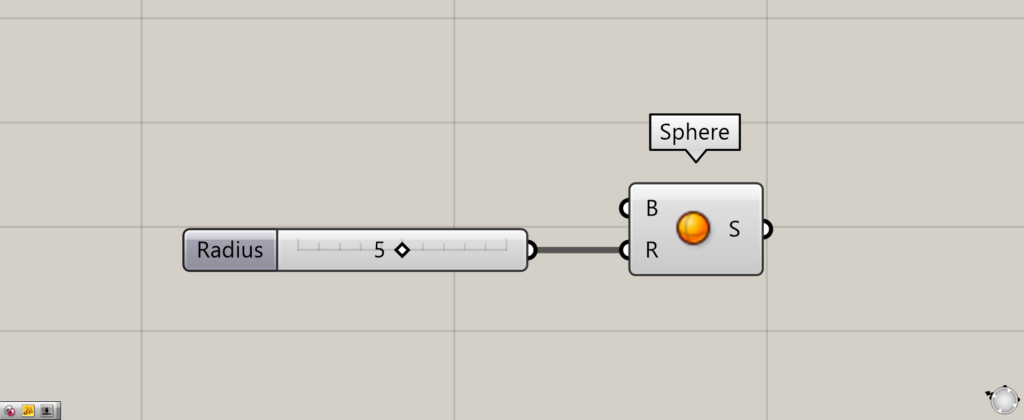
In this case, we will create a sphere with Sphere, and then use a Linear Array to copy the sphere into a single direction of equally spaced arrays.
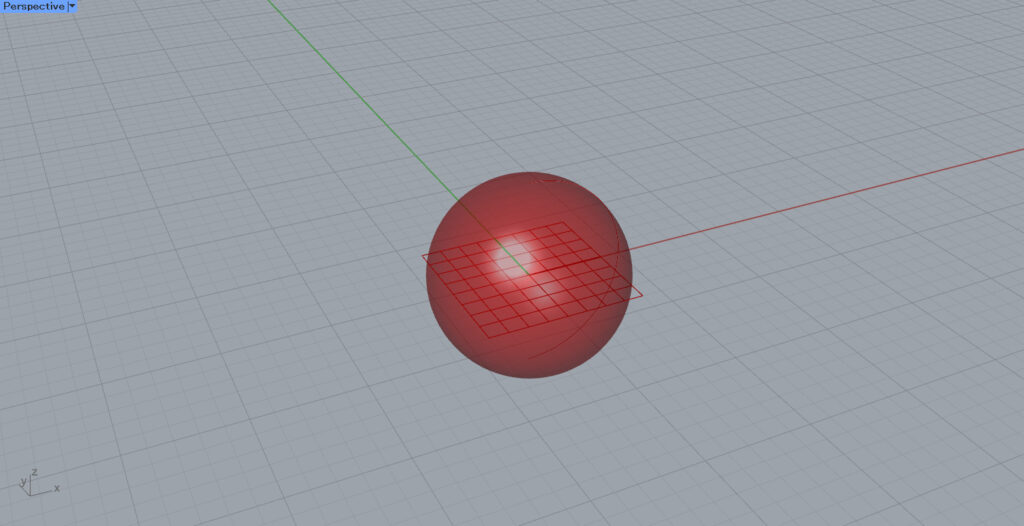
A sphere like this is created.
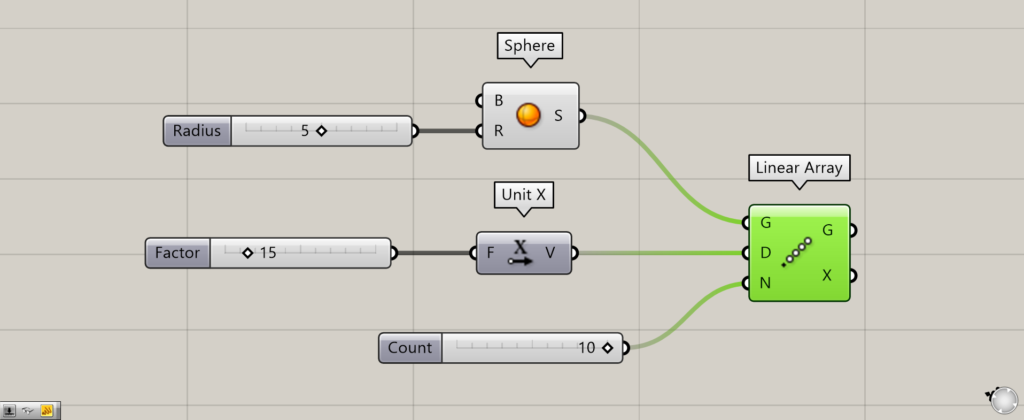
Components used: (1) Sphere (2) Unit X (3) Linear Array
Connect the objects to be copied in a single direction at equal intervals to the Linear Array(G).
This time, connect Sphere.
Connect the vector direction to be moved and distance data to the Linear Array(D).
This time, we connect the value 15 to Unit X and connect the Unit X to the Linear Array(D).
Now, we can copy an array of 15 values in the X direction at equal intervals.
Finally, enter the number of items into the Linear Array(N).
This time, we entered 10, so the number of spheres after execution will be 10.
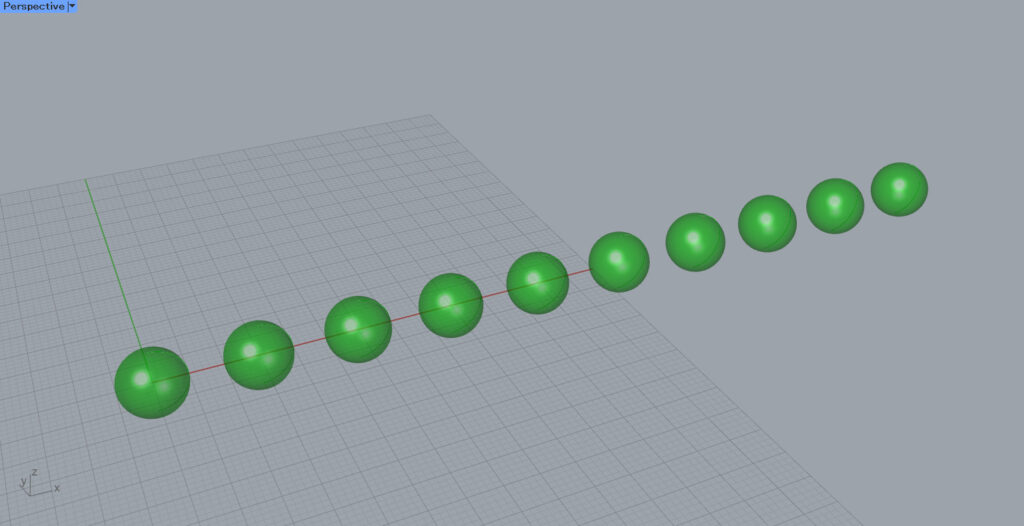
Then, as you can see, the array was copied in a single direction at equal intervals.
As specified, 10 spheres are created with an interval of 15 in the X direction.
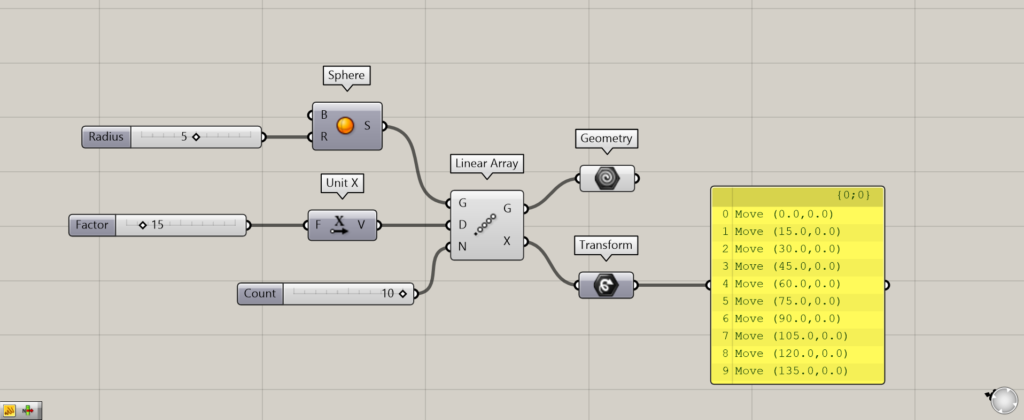
Additional components: (1) Geometry (2) Transform
Let’s look at the data output from the Linear Array.
The Linear Array(G) outputs an array of objects copied at equal intervals.
The Linear Array(X) outputs Transform data, which contains information on how the object was deformed or moved.
List of Grasshopper articles using Linear Array component↓

![[Grasshopper] How to use Linear Array to arrange models at equal intervals](https://iarchway.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/09/Linear-Array.png)


Comment