This section explains how to use the Vector 2Pt component, which creates a vector from two points.
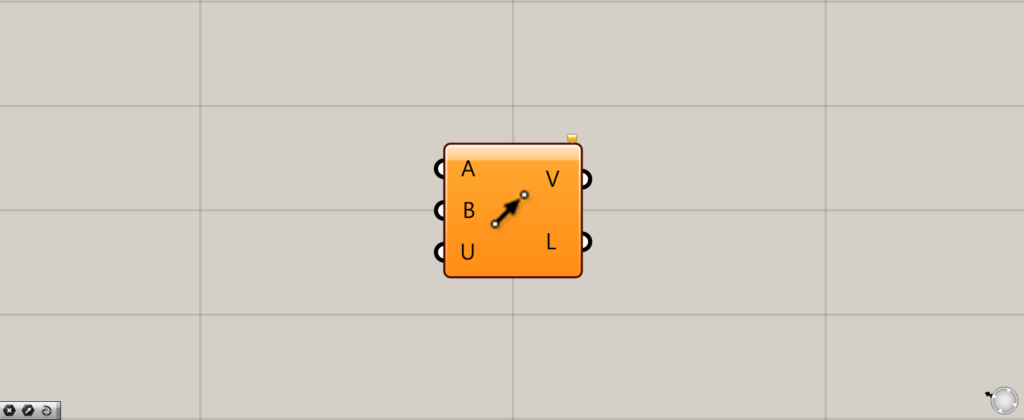
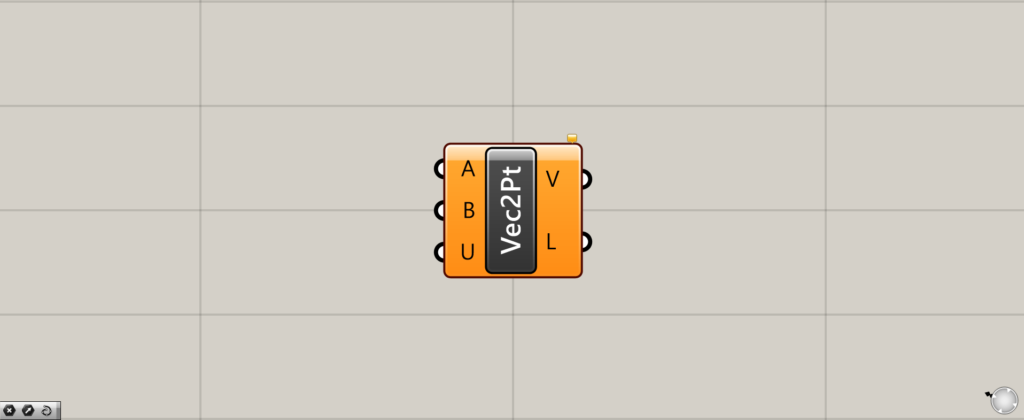
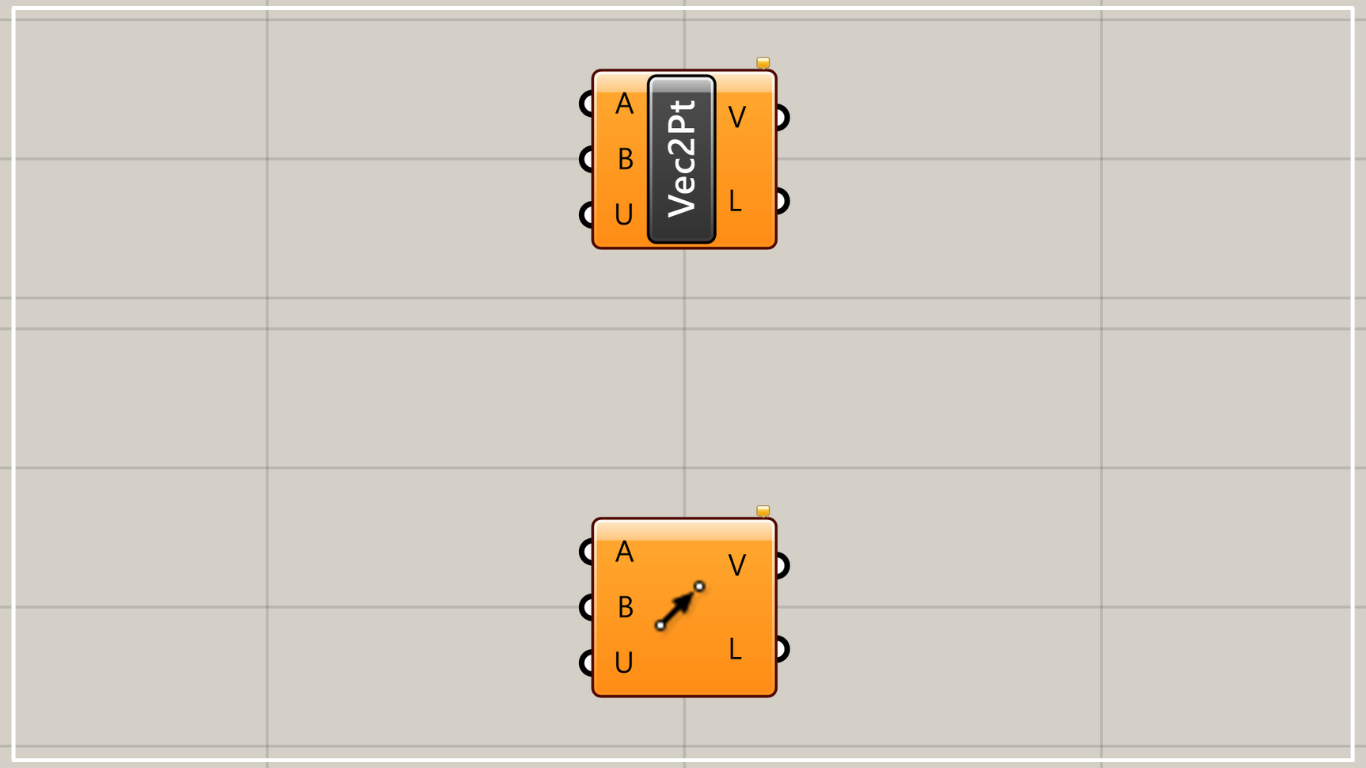
On the Grasshopper, it is represented by either of the two above.
Creating a vector from two points
Vector 2Pt allows you to create a vector from two points.
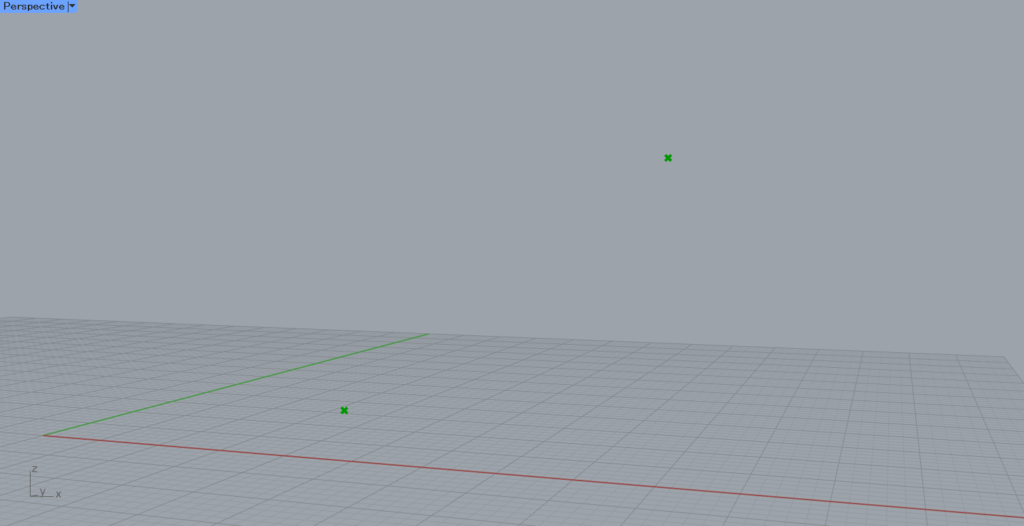
In this article, we will use the two points in the image above.
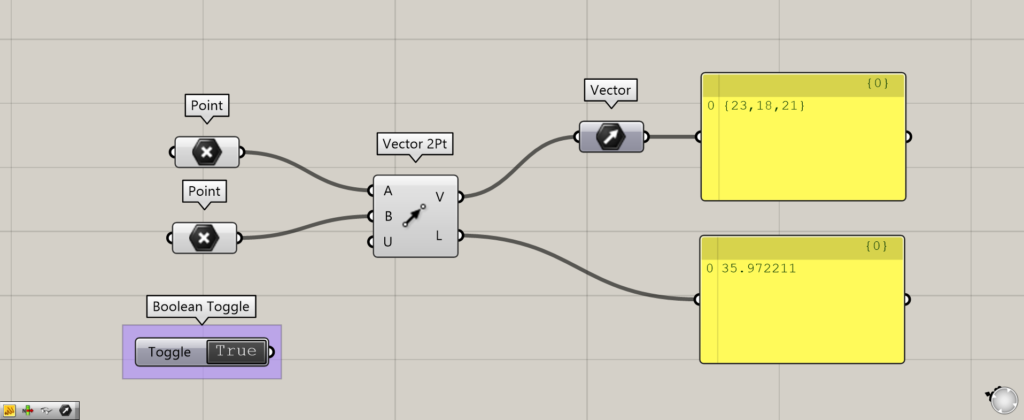
Components used: (1) Point (2) Vector 2Pt ( 3 ) Vector (4) Boolean Toggle
This time, the points are set in Point.
Connect two Points to the Vector 2Pt(A and B).
The point at the Vector 2Pt(A) is the starting point of the vector and the point at the Vector 2Pt(B) is the ending point of the vector.
The Vector 2Pt(V) then outputs the vector information.
The Vector 2Pt(L) outputs the numerical value of the distance between the two points.
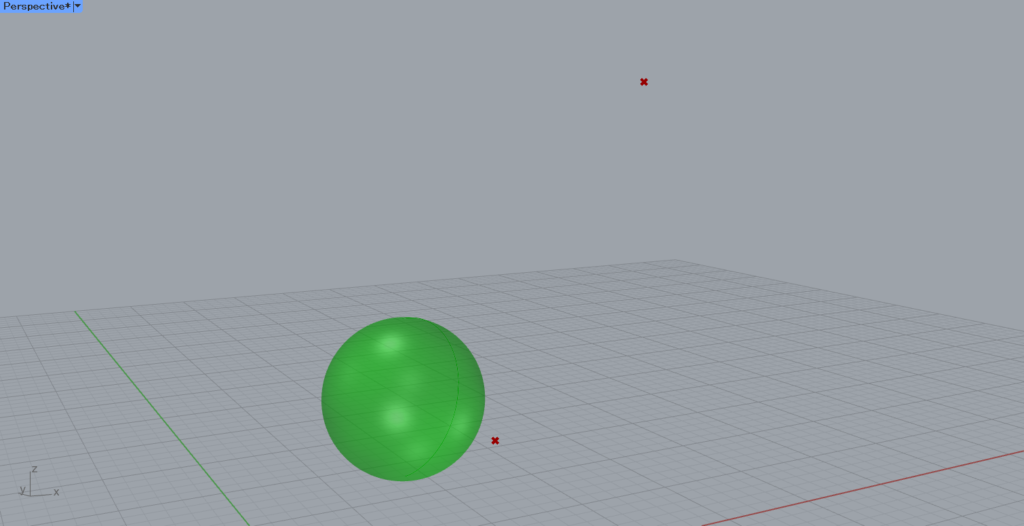
Let’s try to move the sphere in the image above using the vector we have created.
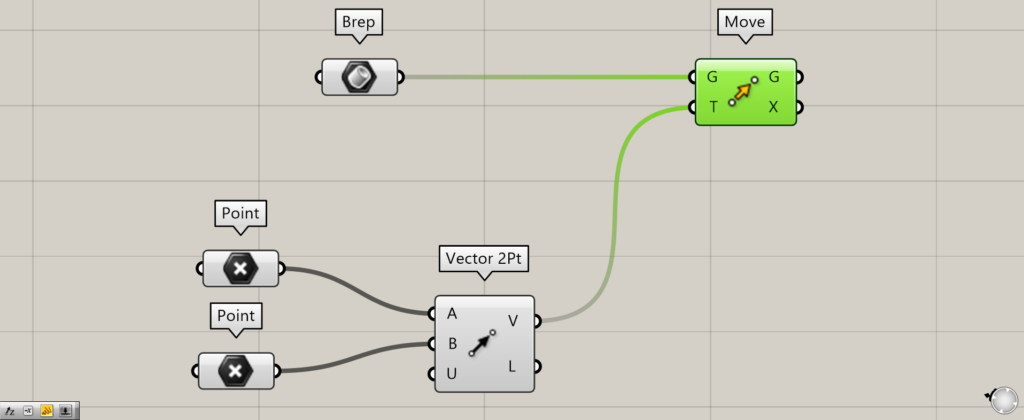
Components used: (1) Brep ( 2 ) Move (3) Point (4) Vector 2Pt
This time, the sphere created on Rhino is set in Brep.
Connect the Brep to the Move(G).
Connect the Vector 2Pt(V) to the Move(T).
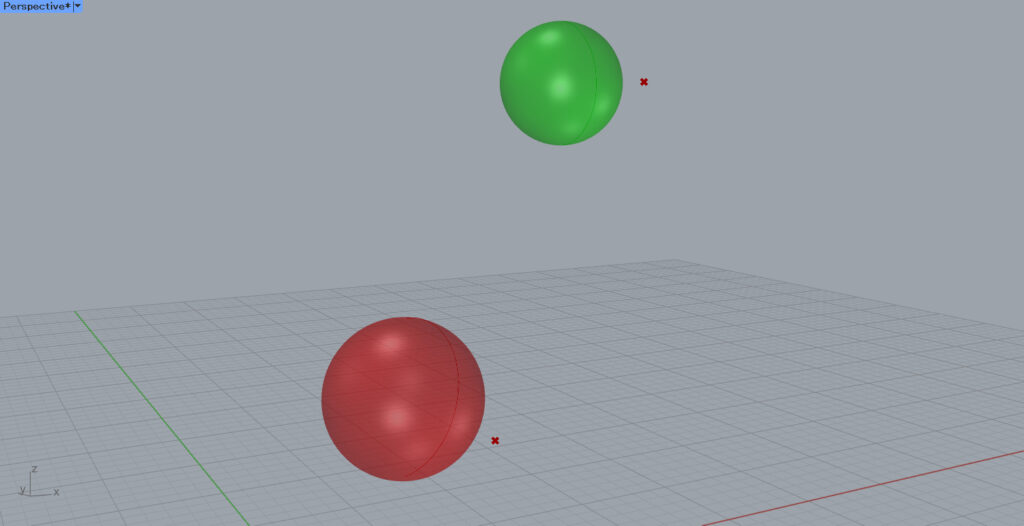
The sphere is now moved by the vector of the direction and distance from the first point to the second point.
Unitize
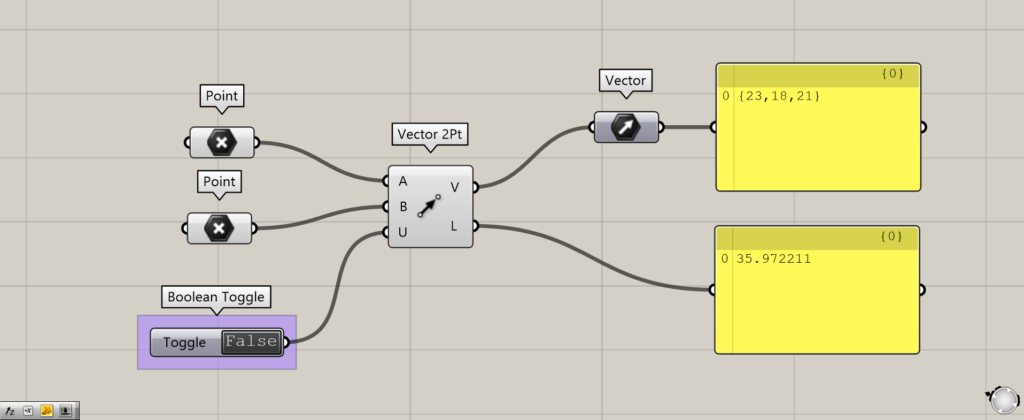
By setting the Vector 2Pt(U) to True or False, you can choose whether to unitize or not.
Unitize allows the output numerical data to be converted to a 0~1 value.
Initially, the Boolean Toggle is used to determine True or False.
If False, the numeric value remains the same as before.
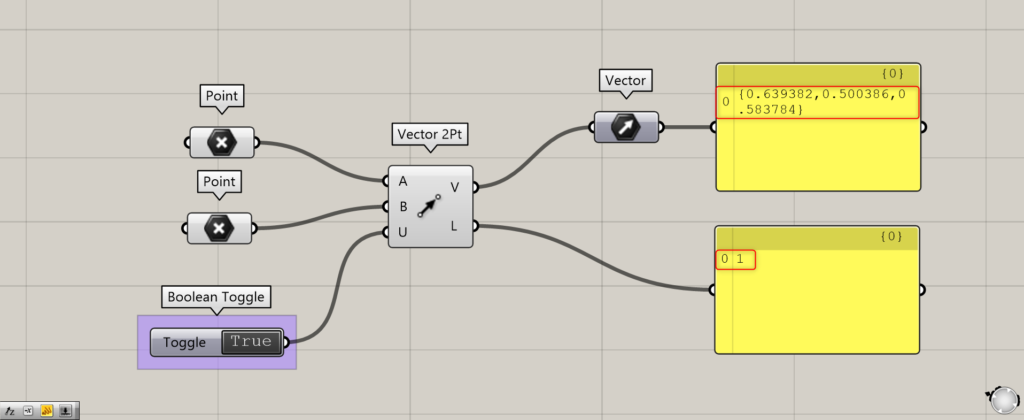
When True, the output number is now converted to 0~1.
The maximum value of 1 is the distance between two points.
You can also see that the x, y, and z directions of the vector are also converted to 0~1 values.
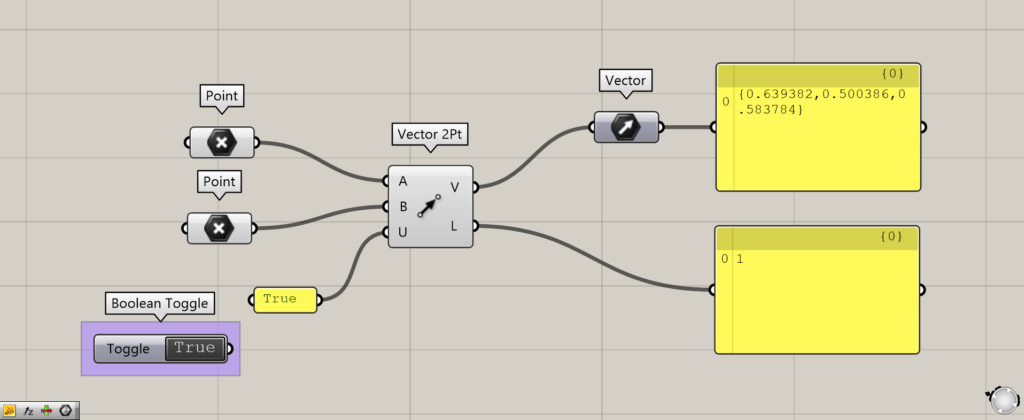
You can do the same thing without using the Boolean Toggle or by entering True or False in the panel.
List of Grasshopper articles using Vector 2Pt component↓

![[Grasshopper] How to use Vector 2Pt to create a vector from two points](https://iarchway.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/09/Vector-2Pt.png)


Comment