This article explains how to use Linear Dimension to create length dimensions.
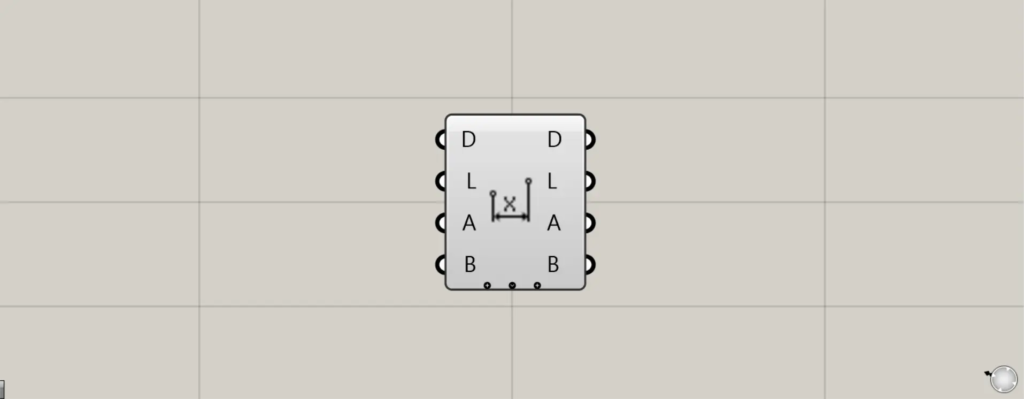
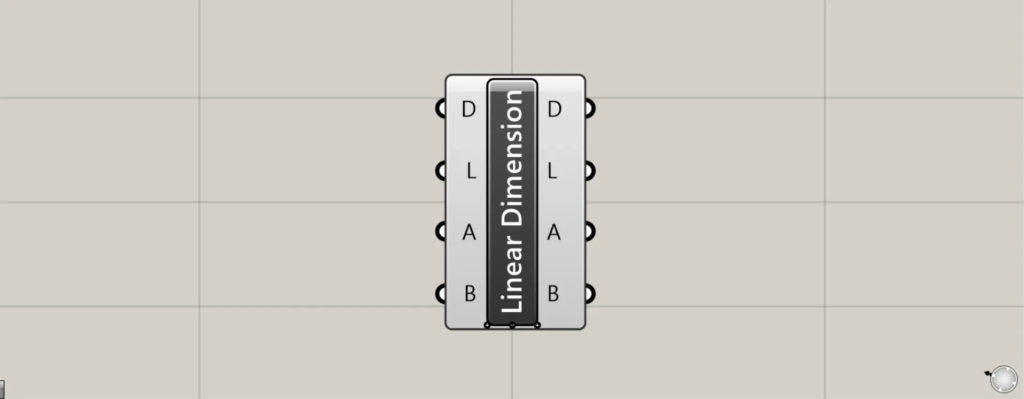
On the Grasshopper, it is represented by either of the two above.
Create length dimensions
Using Linear Dimension allows you to create length dimensions.

This time, we’ll explain using a line and two points on Rhino.
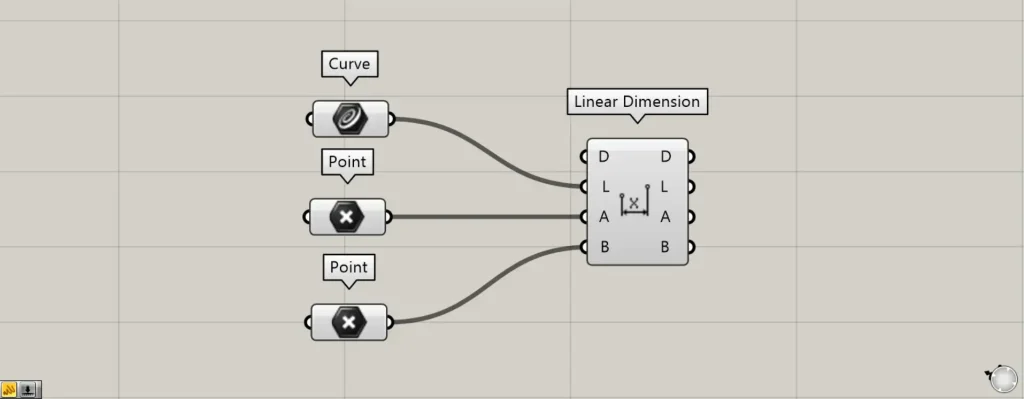
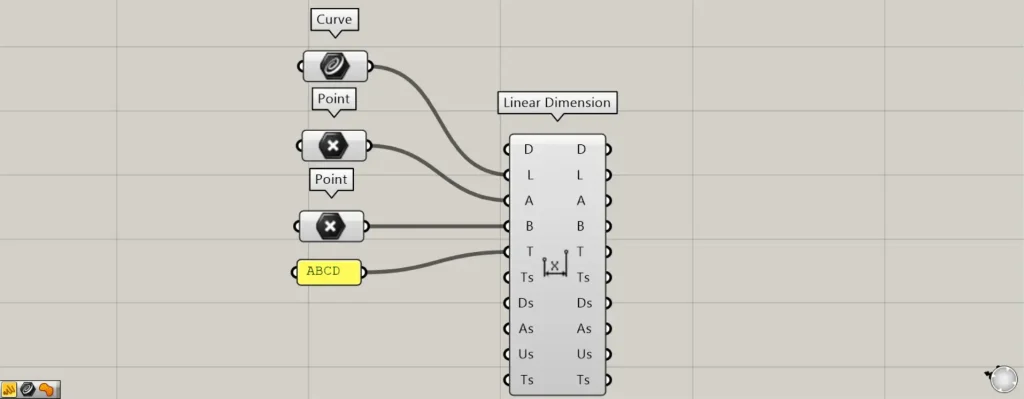
Components used: ①Curve ②Point ③Linear Dimension
Set a straight line on Rhino in Curve.
Set two points on Rhino in two Point.

Then connect Curve to the Linear Dimension(L).
Note that only straight lines can be set in Linear Dimension(L); curves and other shapes cannot be used.
Additionally, connect the two points to the Linear Dimension(A and B), respectively.
Then, as shown in the image above, the length dimension was created.
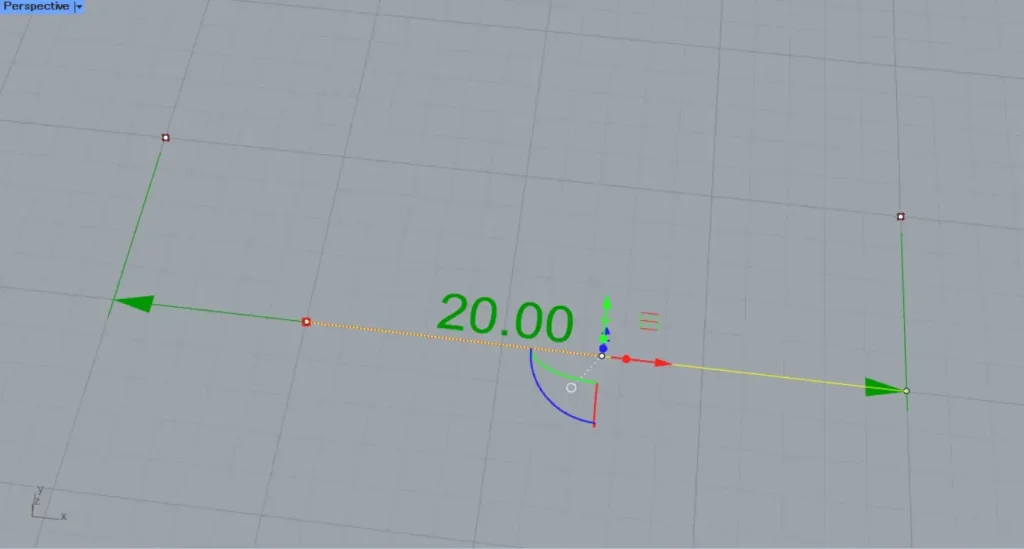
The displayed length value represents the numerical length between two points.
The line used will serve as the reference line for the length dimension.
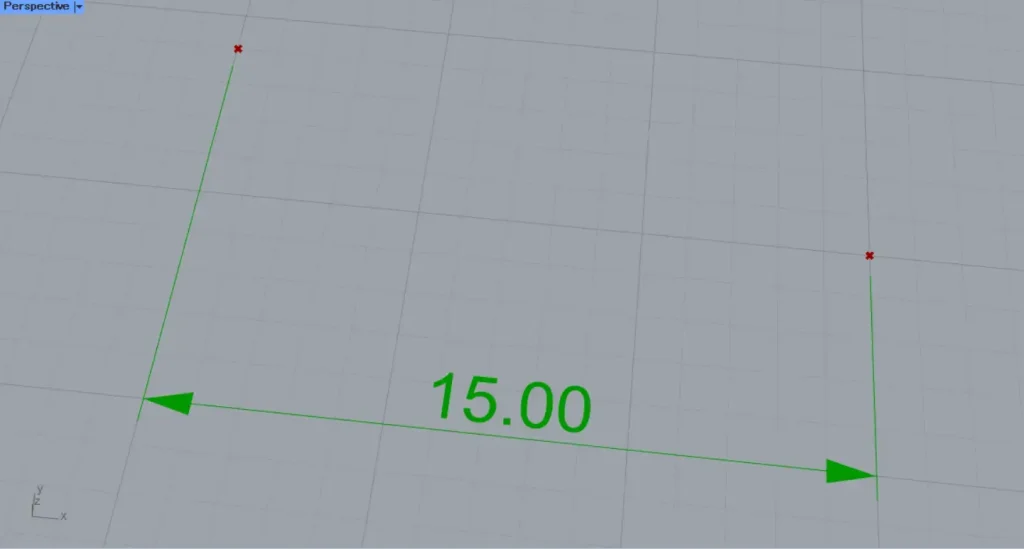
Changing the position of the point also changes the position of the edge line.
Therefore, you can freely adjust the length of the left and right lines.
Extract the existing length dimension components
You can also extract existing length dimension components.
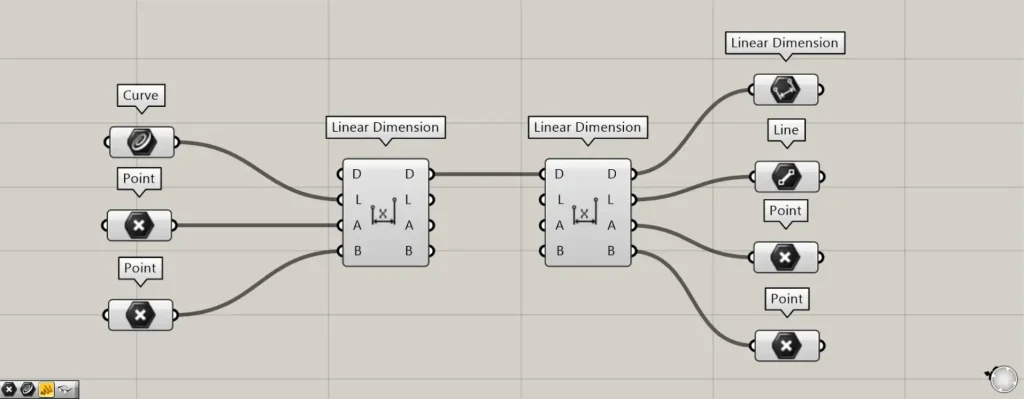
Additional Components: ①Linear Dimension ②Line
Connect the existing length dimension to the Linear Dimension(D).
Then, the existing length-dimensioned components are output from the right-hand terminal.
Length dimension data is output from the D terminal on the right side.
The L terminal on the right outputs the linear data used for the length dimension.
Point data used for length measurements is output from the A and B terminals on the right side.
Configure detailed length dimensions
You can also configure detailed length dimensions.
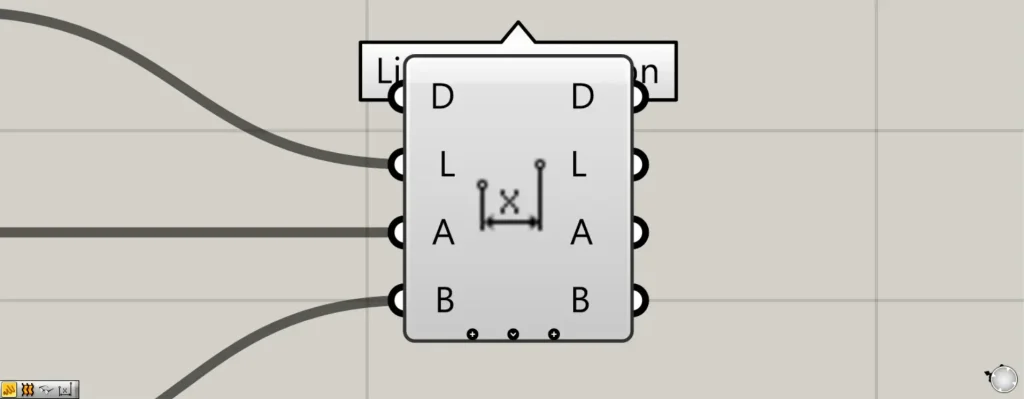
When you zoom toward the Linear Dimension component, a plus and arrow icon appears at the bottom.
Pressing these icons will display new terminals.
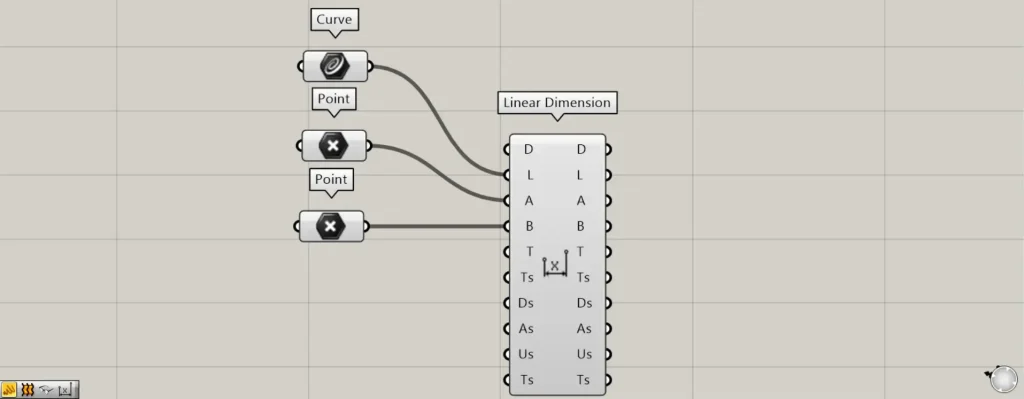
When all terminals are displayed, the T, Ts, Ds, As, Us, and Ts terminals will be displayed additionally.
You can set the values and texts displayed on the T terminal.
This time, we entered ABCD.

Then, the displayed numbers and characters changed.
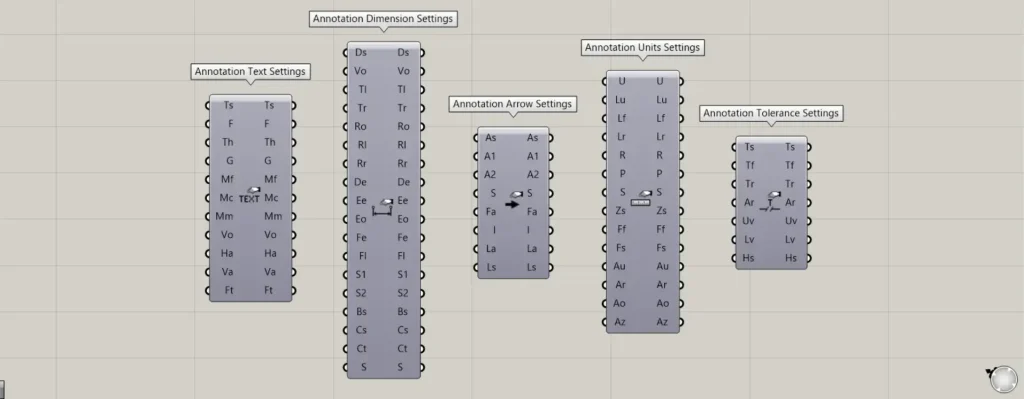
Components used for detailed settings: ① Annotation Text Settings ② Annotation Dimension Settings ③ Annotation Arrow Settings ④ Annotation Units Settings ⑤ Annotation Tolerance Settings
For the Ts, Ds, As, Us, and Ts terminals, use the components shown in the image above for each.
For the Ts terminal, use the Annotation Text Settings.
The Ts terminal allows you to configure text settings.
For the Ds terminal, use Annotation Dimension Settings.
The Ds terminal allows you to set dimensions.
For the As terminal, use Annotation Arrow Settings.
On the As terminal, you can configure the arrow settings.
For the Us terminal, use Annotation Units Settings.
The Us terminal allows you to set the unit.
For the Ts terminal, use the Annotation Tolerance Settings.
The Ts terminal allows you to set the tolerance.
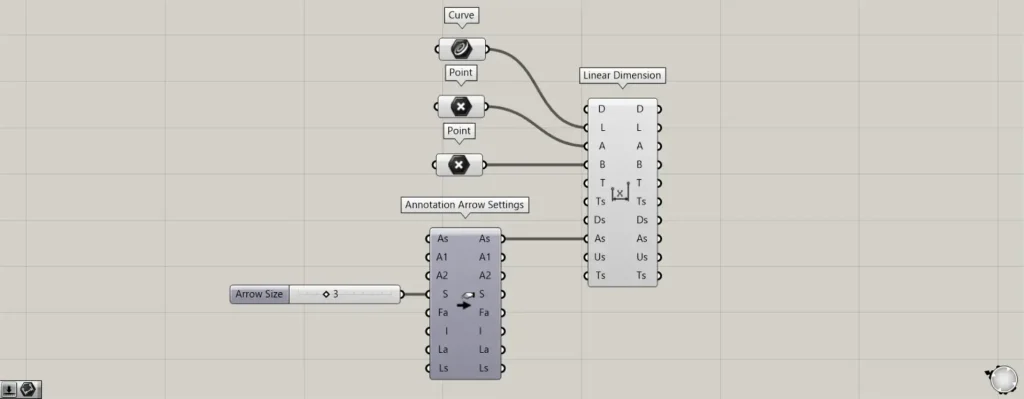
As an example of using advanced settings, we’ll configure the Annotation Arrow Settings for the As terminal to customize the arrow details.
In the Annotation Arrow Settings(S), you can set the arrow size by entering a numerical value.
This time, we entered 3.

Original arrow size.
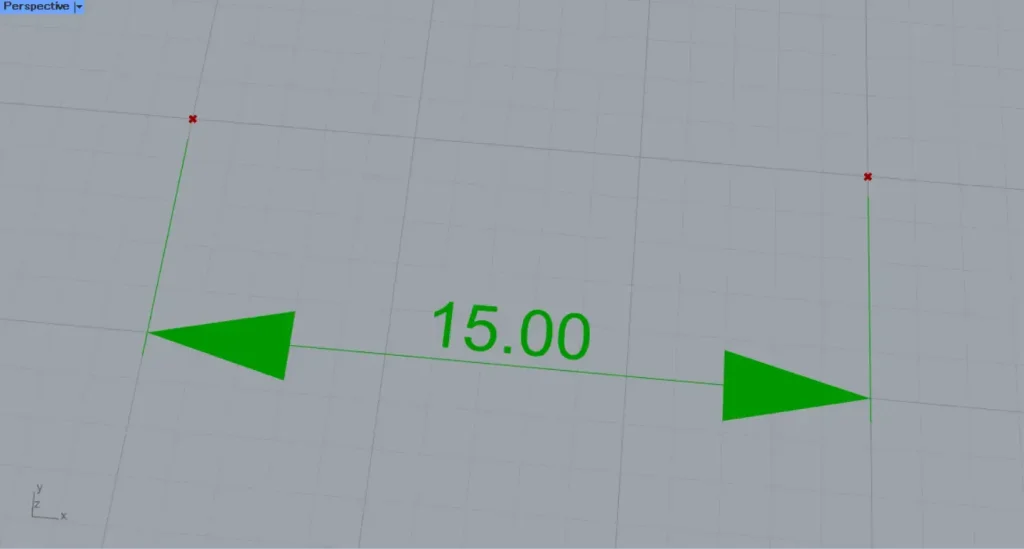
After setting the value, the arrow size changed.
In this way, you can configure detailed length dimensions using additional terminals.
List of Grasshopper articles using Linear Dimension component↓

![[Grasshopper] How to use Linear Dimension to create length dimensions](https://iarchway.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/01/Linear-Dimension-1.png)


Comment