This article explains how to use Surface | Line to find intersection points between surfaces and lines.
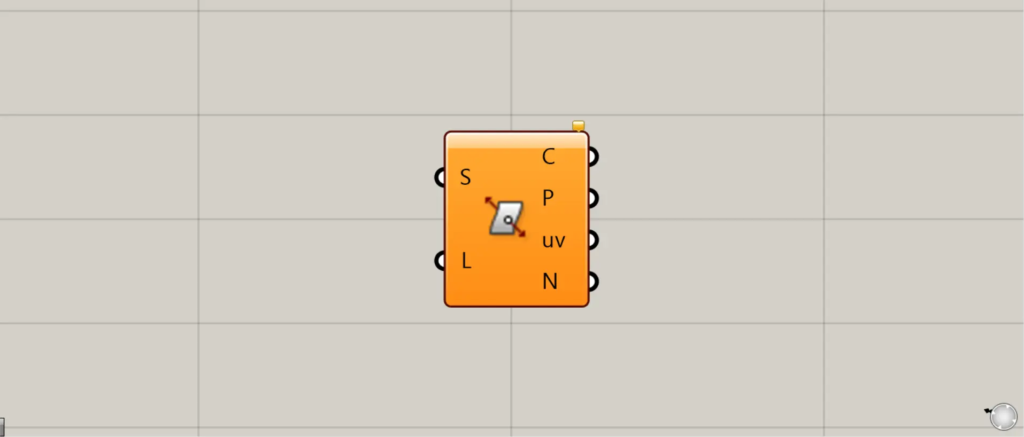
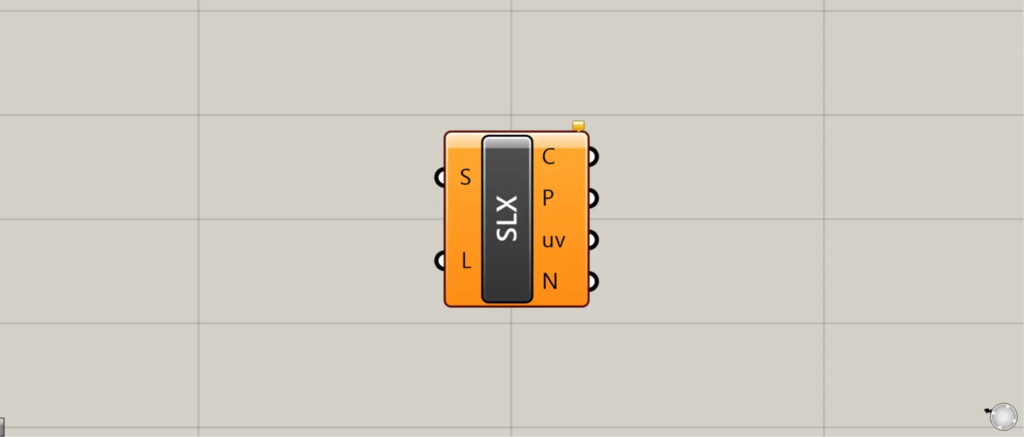
On the Grasshopper, it is represented by either of the two above.
Find intersection points between a surface and a line
Using Surface | Line, you can obtain intersection points between a surface and a line.
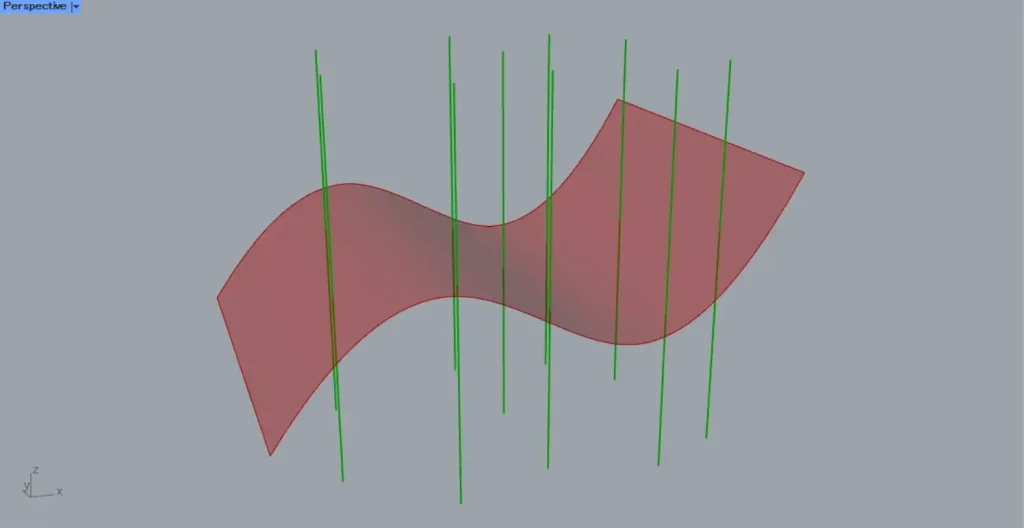
As a first example, we will use the surface and line from the image above.
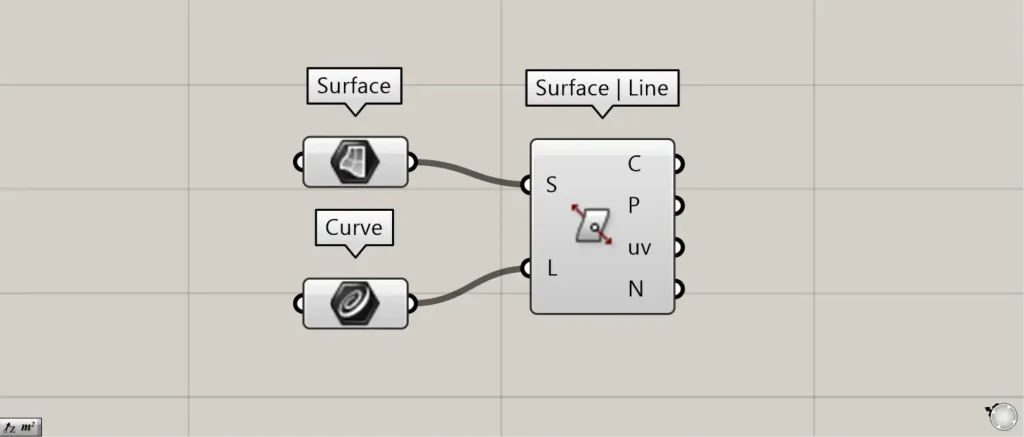
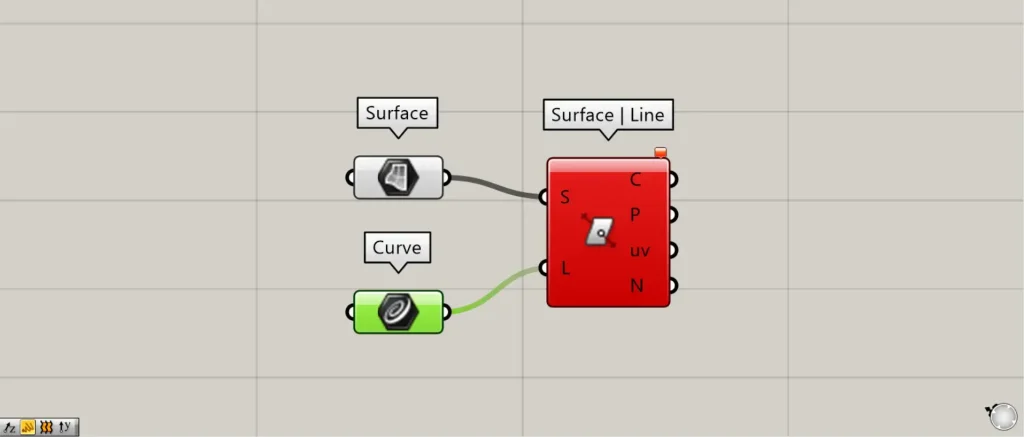
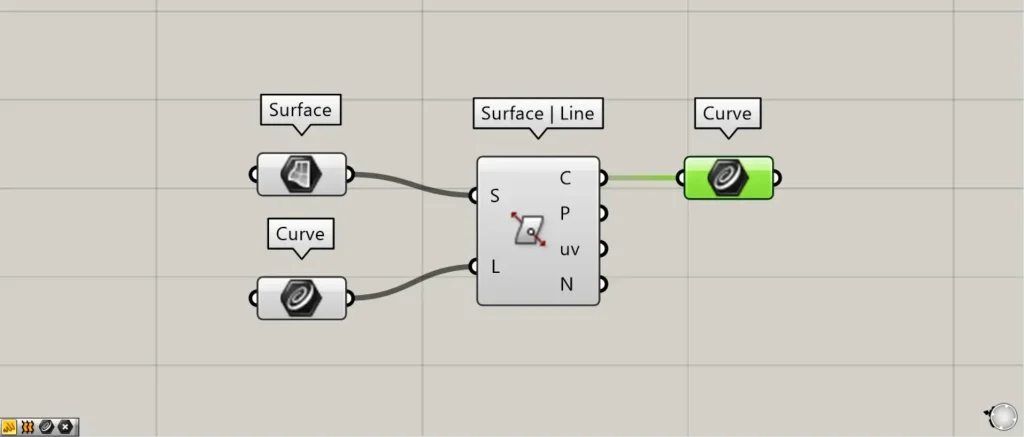
Components used: ①Surface ②Curve ③Surface | Line
Connect any surface to Surface | Line(S).
This time, we are connecting the surfaces set in the Surface.
Connect any straight line to Surface | Line(L).
This time, we are connecting multiple straight lines set in Curve.
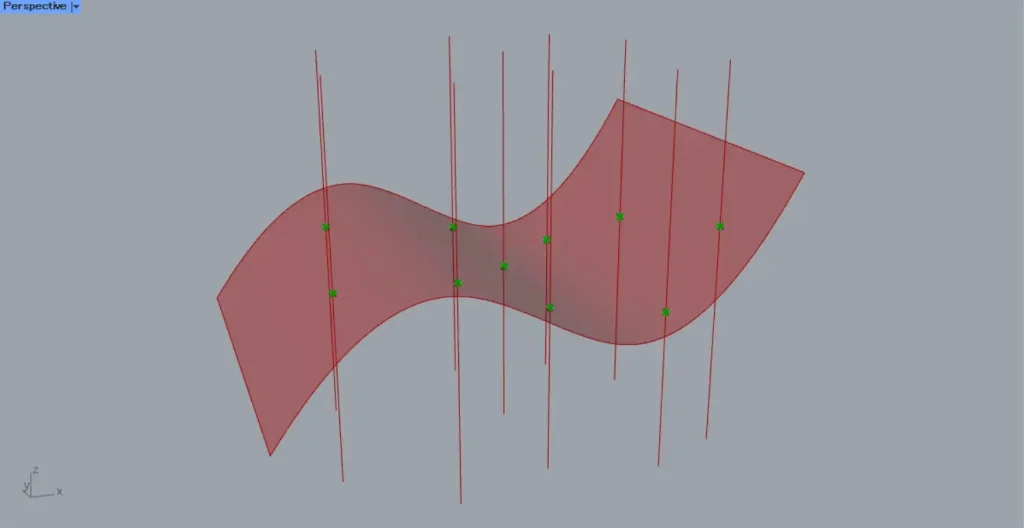
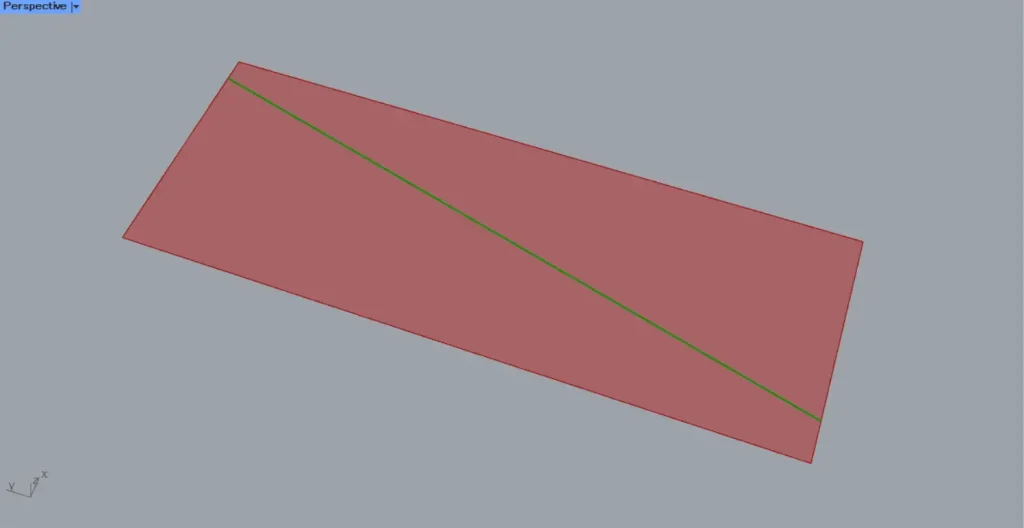
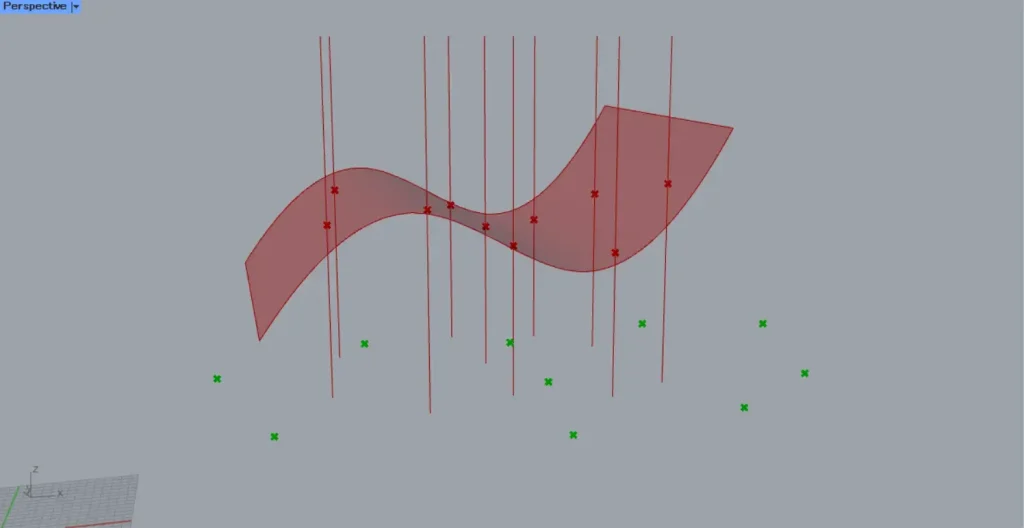
Then, as shown in the image above, we were able to obtain the intersection points between the surface and the straight lines.
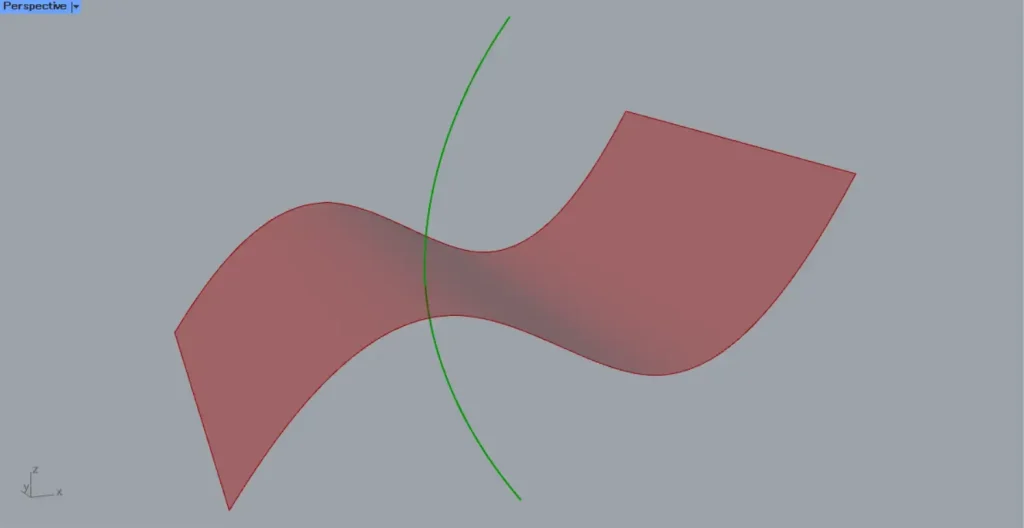
We’ll try it with a curve.
Testing with curves resulted in an error.
In Surface | Line, you cannot use curves; only straight lines can be used.
Output data
Let’s take a look at the output data.
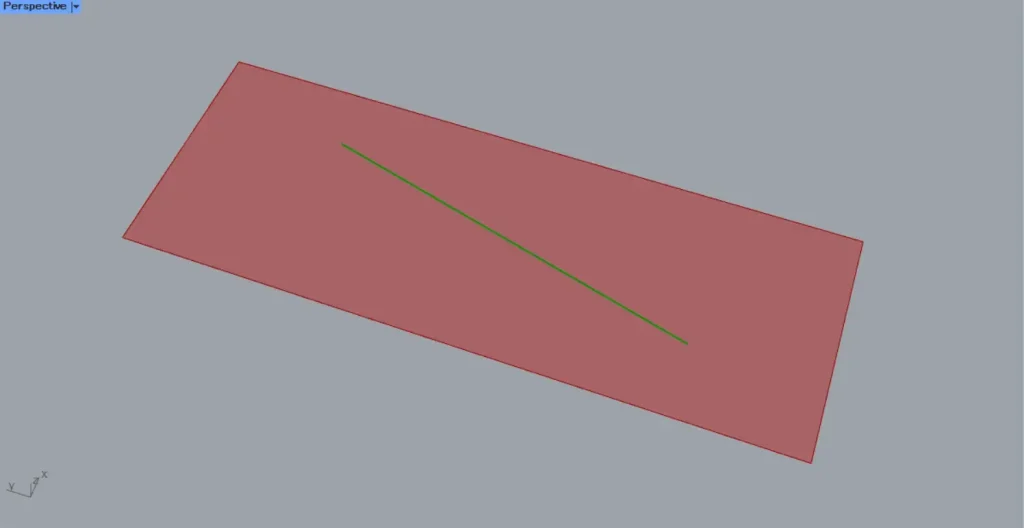
As shown in the image above, let’s consider the case where a straight line exists on the surface.
When a line exists on a surface, the Surface | Line(C) outputs the line data for the intersection point between the surface and the line.
In this case, the output lines will be extended to the edges of the surface.
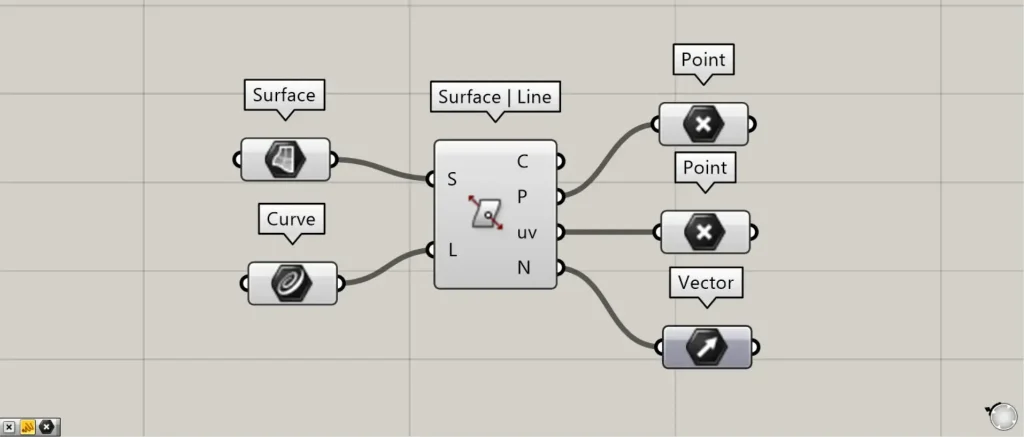
Additional Components: ①Point ②Vector
Surface | Line(P) outputs the intersection point between the surface and the line.
Surface | Line(uv) outputs point data representing the surface when flattened.
In this case, point data is created on the plane formed by the X and Y axes.
Surface | Line(uv) is extremely important when acquiring surface information.
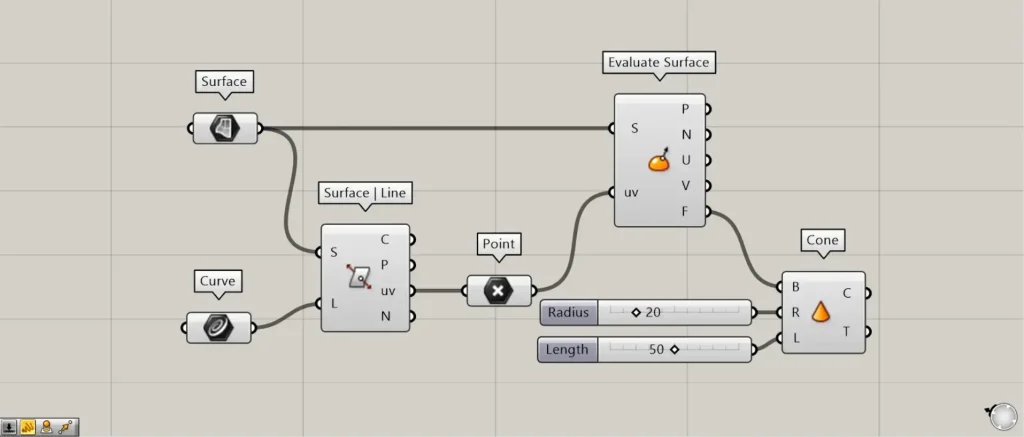
Additional Components: ①Evaluate Surface ②Cone
As an example using Surface | Line(uv), we introduce Evaluate Surface.
Connect the Surface | Line(uv) to Evaluate Surface(uv).
Next, connect the Surface to the Evaluate Surface(S).
Then, you can obtain the surface information at the intersection point.
As an example this time, we will use the data for the plane at the intersection point output from Evaluate Surface(F).
Connect the Evaluate Surface(F) to the Cone(B).
Furthermore, connect the radius value to Cone(R).
This time, we’re connecting 20.
Furthermore, connect the height value to Cone(L).
This time, we’re connecting 50.
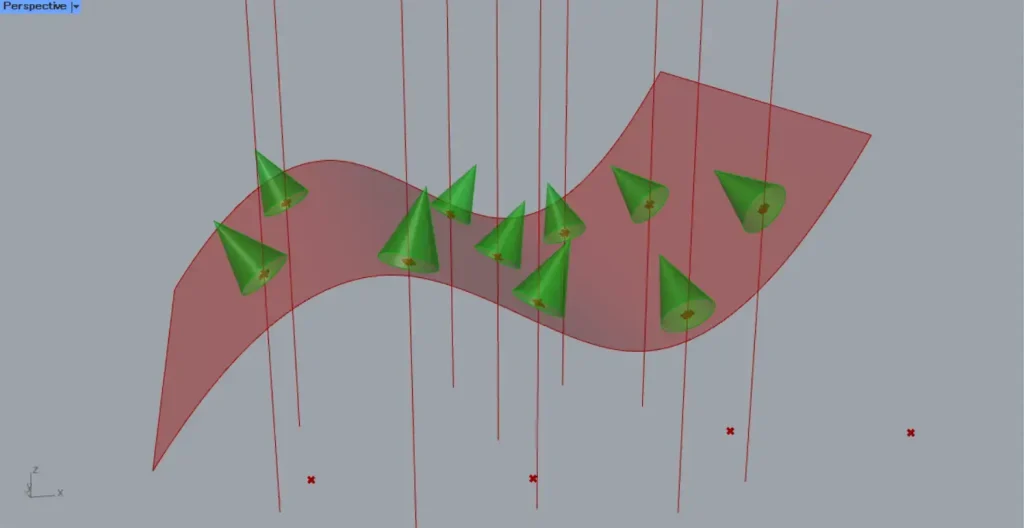
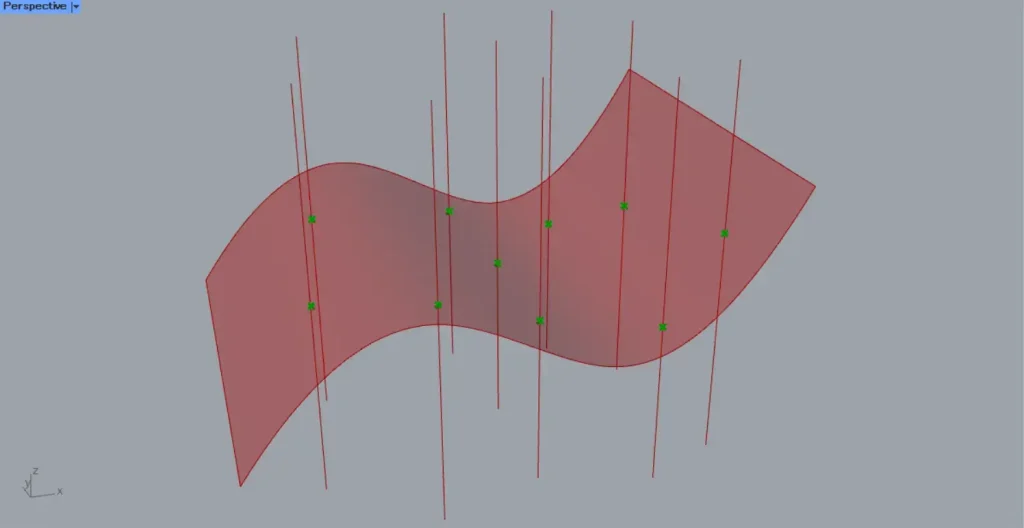
Then, as shown in the image above, we were able to create a cone on the plane created at the intersection point.
In this way, using Surface | Line(uv) allows you to obtain surface information at the intersection point.
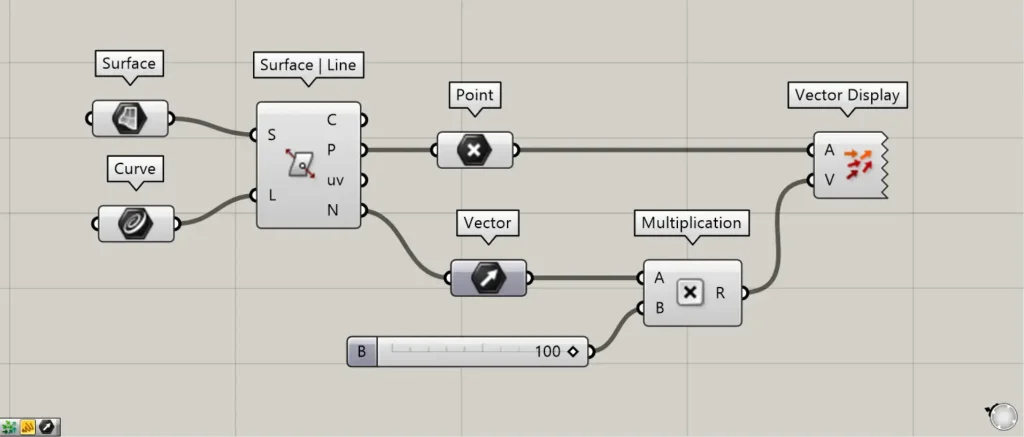
Additional Components: ① Vector ② Multiplication ③ Vector Display
Surface | Line(N) returns the normal vector at the intersection point on the surface.
The image above shows programming that visualizes the acquired vectors by assigning distances to them.
Connect Surface | Line(N) to Multiplication(A).
Furthermore, connect the distance value to Multiplication(B).
Then you can specify a distance for the vector.
Next, connect the Multiplication to the Vector Display(V).
Furthermore, connect the Surface | Line(P) containing the intersection information to the Vector Display(A).
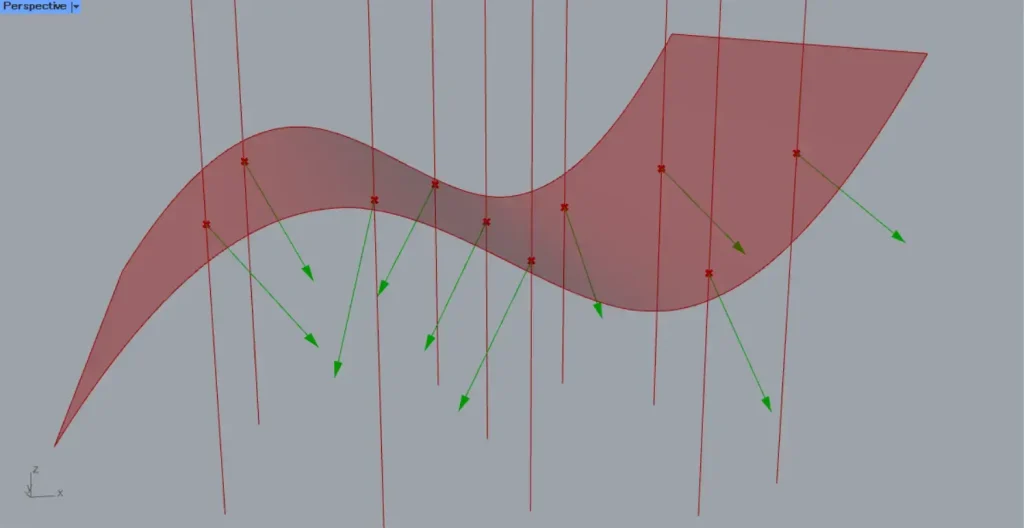
Then, as shown in the image above, the vectors were visualized.
The acquired vector is determined to be the normal direction at the intersection point of the surface.
List of Grasshopper articles using Surface | Line component↓

![[Grasshopper] How to use Surface | Line to find intersection points between surfaces and lines](https://iarchway.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/01/eyecatch-15.png)


Comment