This article explains how to use Divide Domain to divide domain ranges.
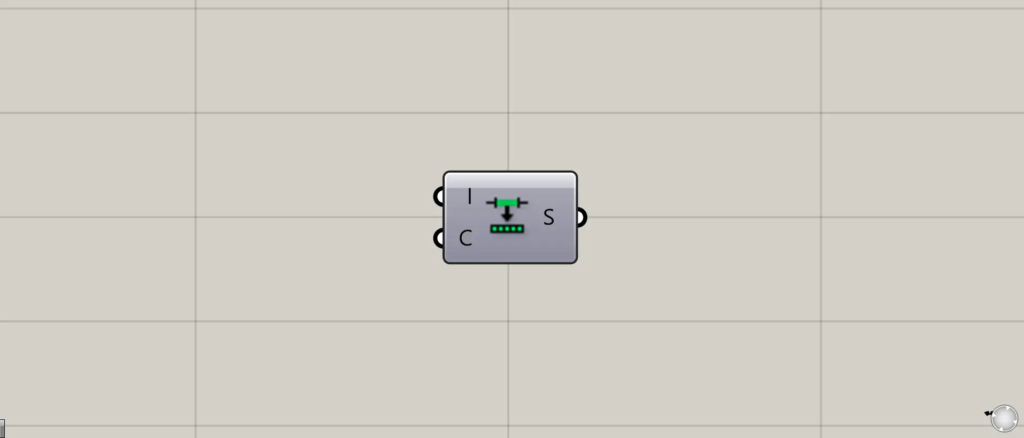

On the Grasshopper, it is represented by either of the two above.
Divide domain ranges
Using Divide Domain allows you to divide domain ranges.

For this example, we will use the surface shown in the image above.
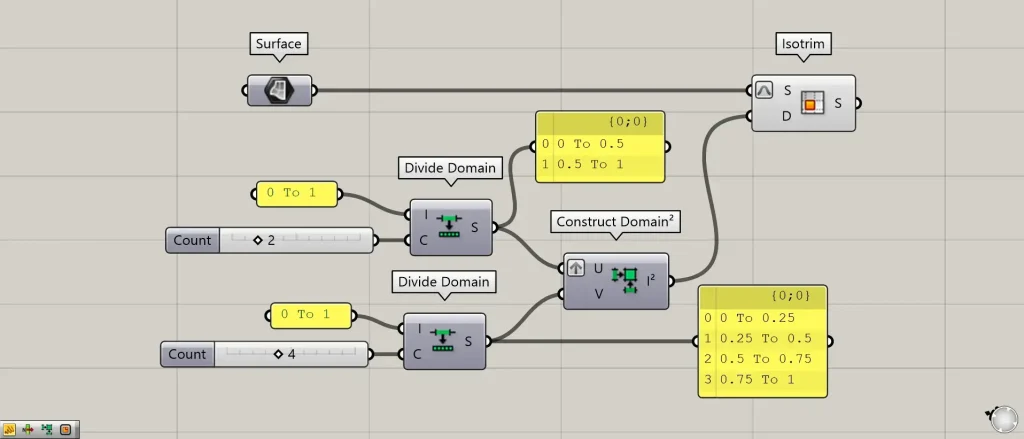
Components used: ①Surface ②Divide Domain ③Construct Domain² ④Isotrim
The surfaces created in Rhino are set in Surface.
This time, we’ll split the domain scope into two 0 To 1 segments.
Connect the domain range 0 to 1 to each Divide Domain(I).
Enter the number of divisions into the Divide Domain(C).
This time, we are connecting 2 to the first one and 4 to the second one.
Then, the one connecting 2 was divided into two domain ranges: 0 to 0.5 and 0.5 to 1.0.
Additionally, the data connected to 4 was divided into four domain ranges: 0 to 0.25, 0.25 to 0.5, 0.5 to 0.75, and 0.75 to 1.
In this way, using Divide Domain allows you to split the domain range.
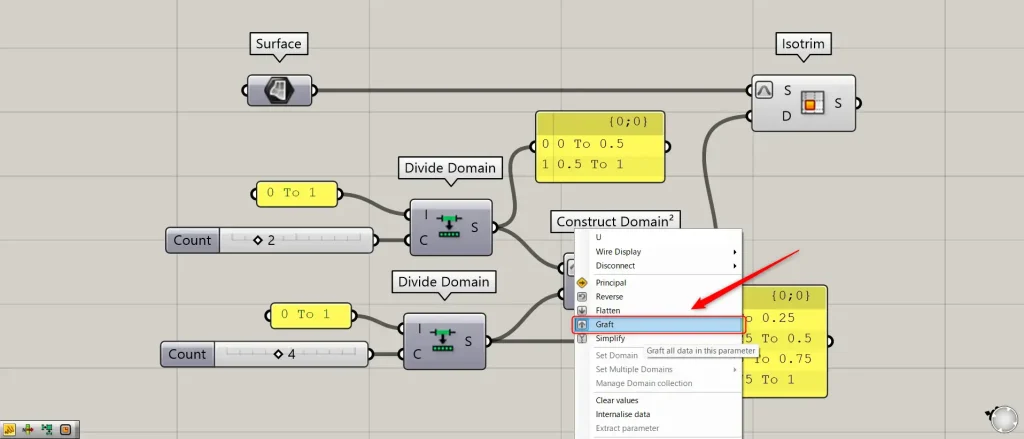
Let’s try splitting the surface using the partitioned domain range.
Connect the first Divide Domain to Construct Domain²(U).
At this point, right-click Construct Domain²(U) and set it to Graft.
Next, connect the second Divide Domain to the Construct Domain²(V).
Then, the U-direction and V-direction domain ranges required for surface subdivision are created.

Then connect the Surface to Isotrim(S).
At this point, right-click Isotrim(S) and set it to Reparameterize.
This allows you to specify a position on the surface using a value between 0 and 1.
Furthermore, connect Construct Domain² to Isotrim(D).

Then, as shown in the image above, we were able to split the surface using the divided domain ranges.
List of Grasshopper articles using Divide Domain component↓

![[Grasshopper] How to use Divide Domain to divide domain ranges](https://iarchway.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/01/eyecatch-40.png)



Comment