When using Grasshopper, you’ll often find yourself wanting to change the scale of your model.
So this time, we’ll introduce two methods anyone can easily use to change scales in Grasshopper.
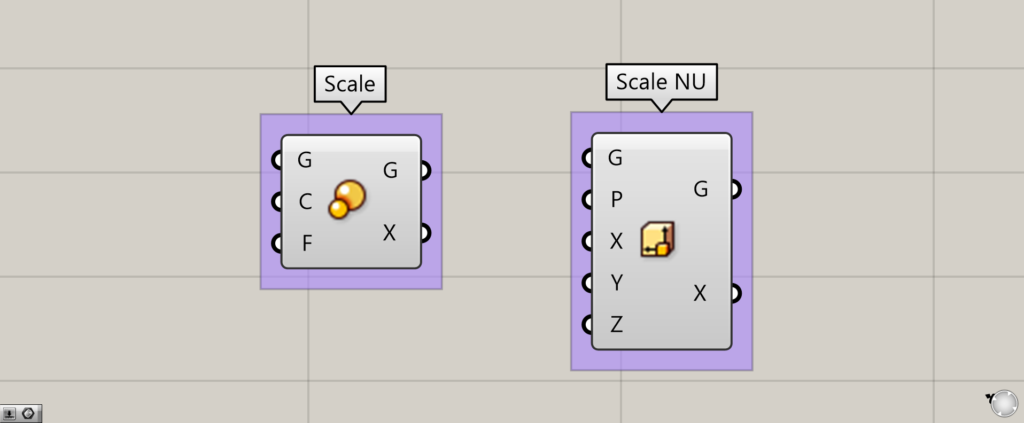
To put it simply, you can do it using Scale and Scale NU.
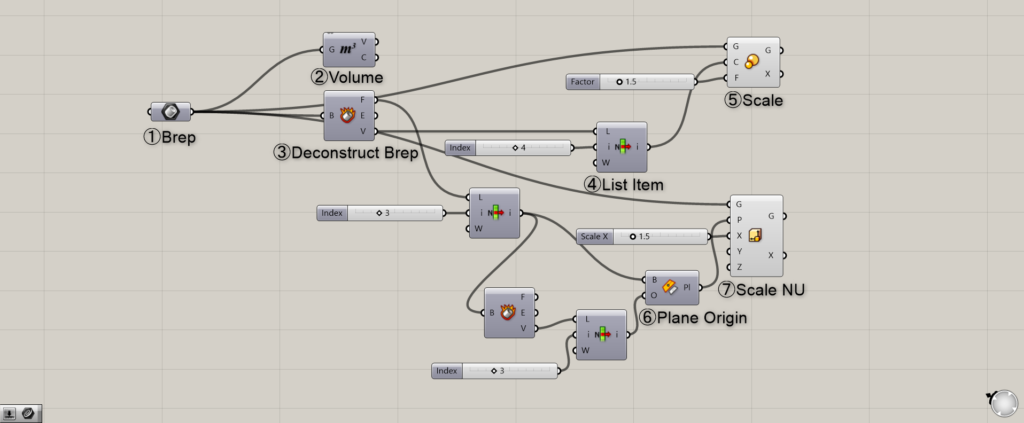
The overall components will look like this.
The Grasshopper and Rhino data for this session can be downloaded from the link below.
Data download for this Grasshopper and Rhino project is available here.
For information regarding the use of downloadable data, please refer to the Terms of Use.
Now, I’ll explain them in order.
Scale Component
Overall Component
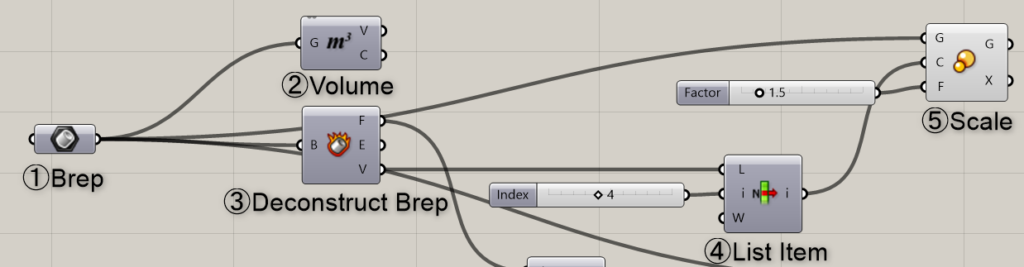
Components used: ① Brep ② Volume ③ Deconstruct Brep ④ List Item ⑤ Scale
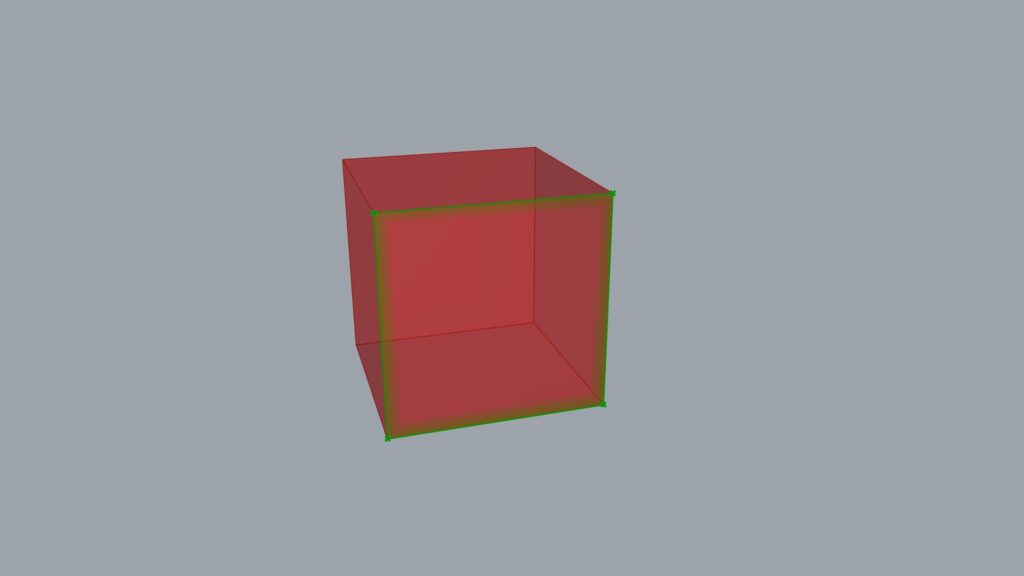
The model we will be using this time is this cube.
As a preparatory step, store the model you wish to use in Rhino in Brep.
Create a reference point for changing the scale
To run the Scale component, we will create several reference points.
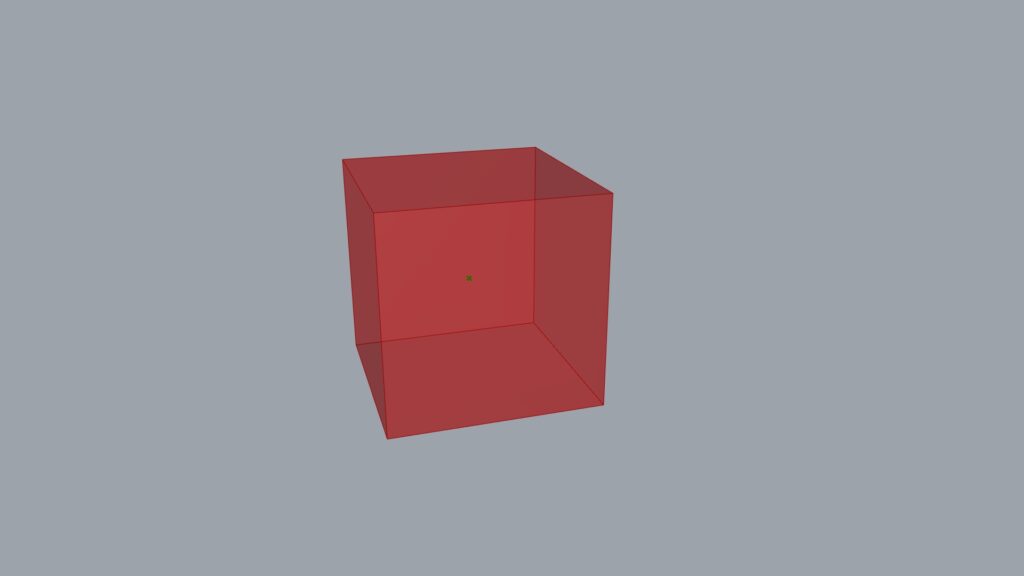
First, use Volume to extract the center point of the cube, as shown in the image above.
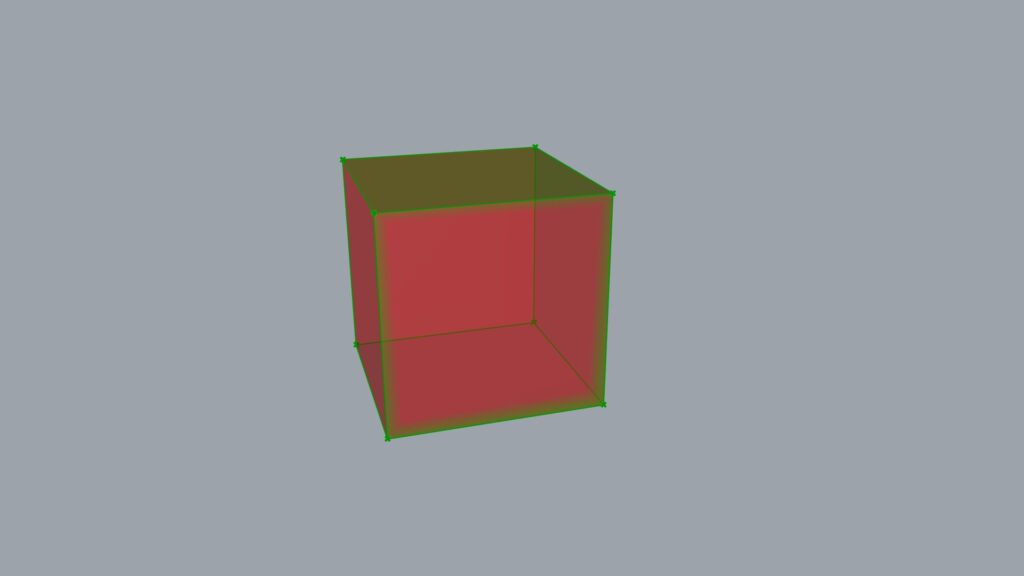
Next, we will extract each vertex of the cube.
First, using Deconstruct Brep breaks the model down into three components: surfaces, curves, and points.
Here, only points will be used to create reference points.
Point data can be extracted from the V terminal.
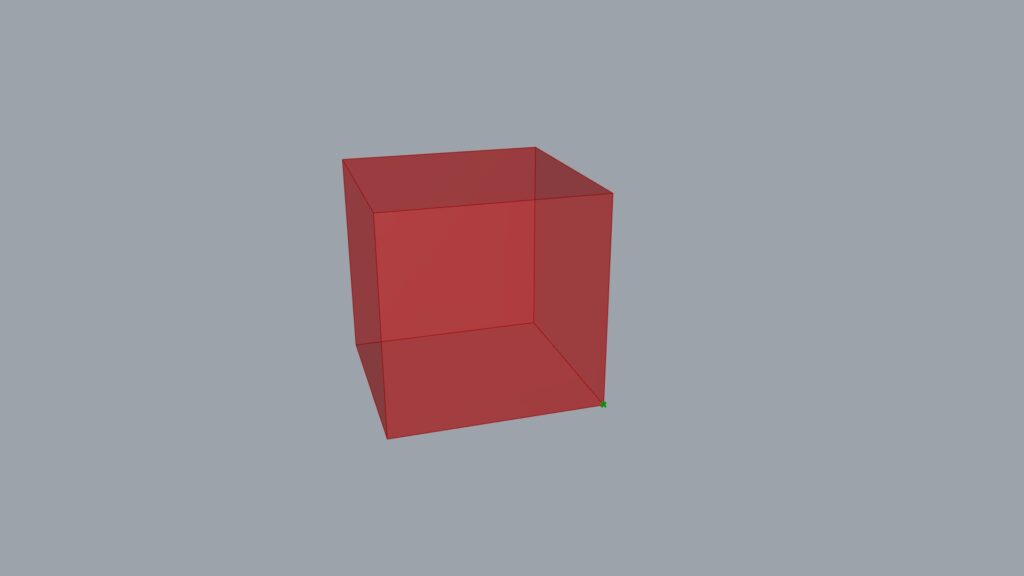
And by using List Item, you can retrieve only one point from among multiple vertices.
By changing the value of the i terminal in the List Item, you can change the point that can be acquired.
This time, we extracted the point in the lower right corner.
Now you can use both the center point and the vertex points of the cube.
Set the ratio using the Scale component
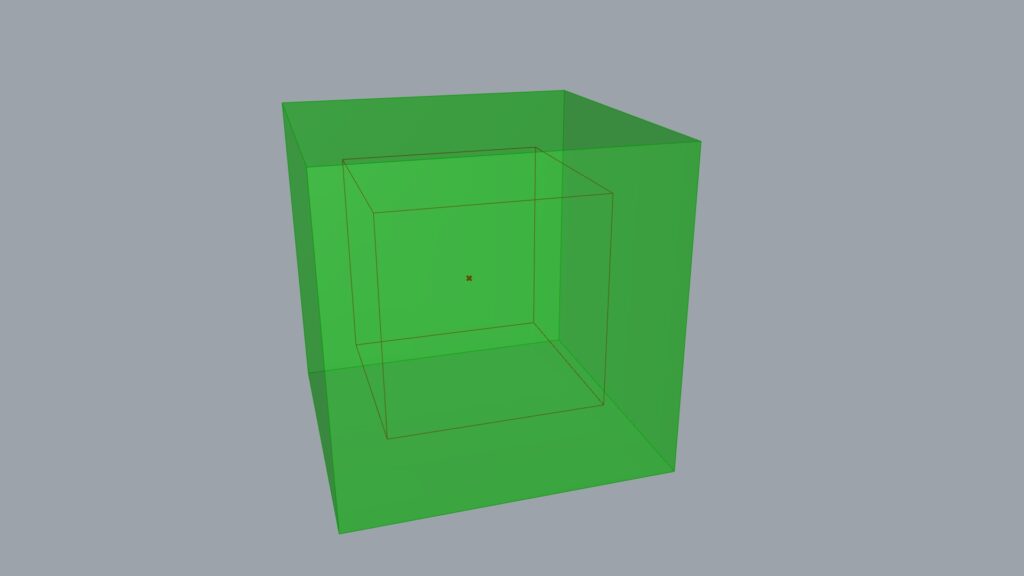
Here we use Scale.
Enter the desired reference point for the Scale(C) and the magnification value for the Scale(F).
Initially, we connect the center point obtained from Volume with the value 1.5 to multiply it by 1.5.
As shown in the image above, the cube’s size is changing around the reference point.
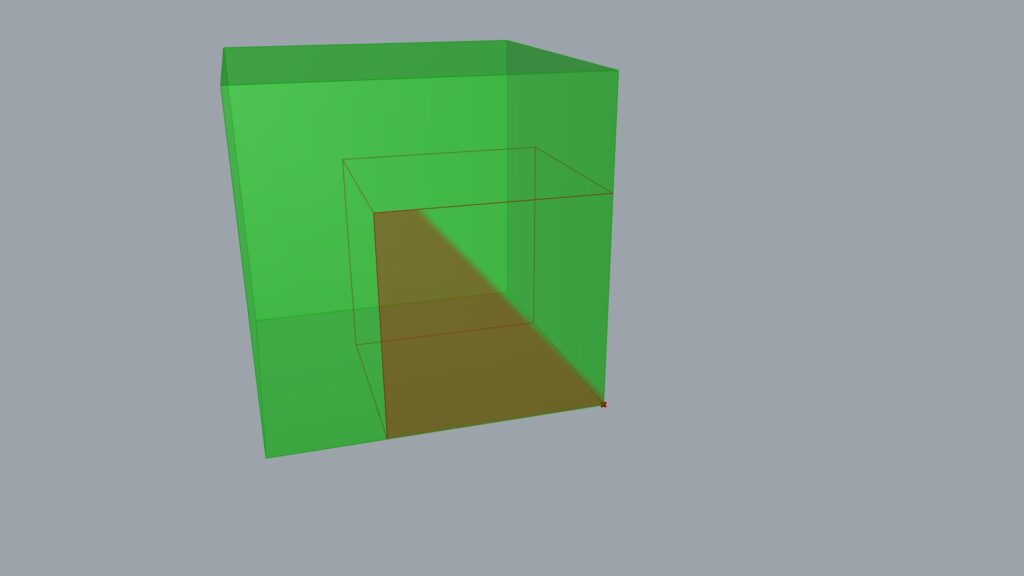
Next, we connected the vertex obtained from the List Item to the Scale(C).
The size has changed to 1.5 times larger, using the point at the bottom right as the reference.
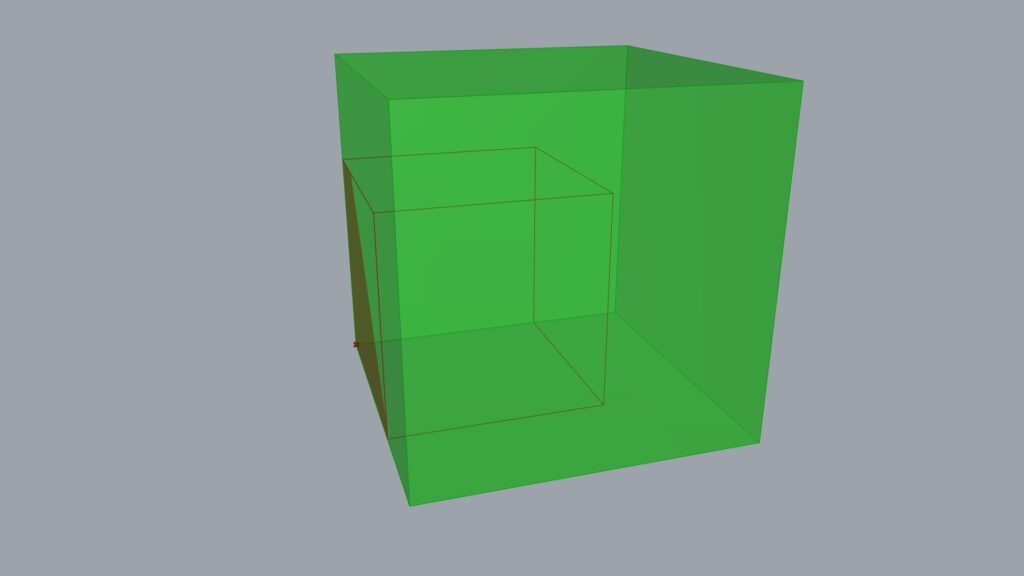
Changing the reference point’s position further altered the scale’s behavior like this.
This concludes the explanation of the Scale component.
List of Grasshopper articles using Scale component↓
Scale NU Component
Overall Component
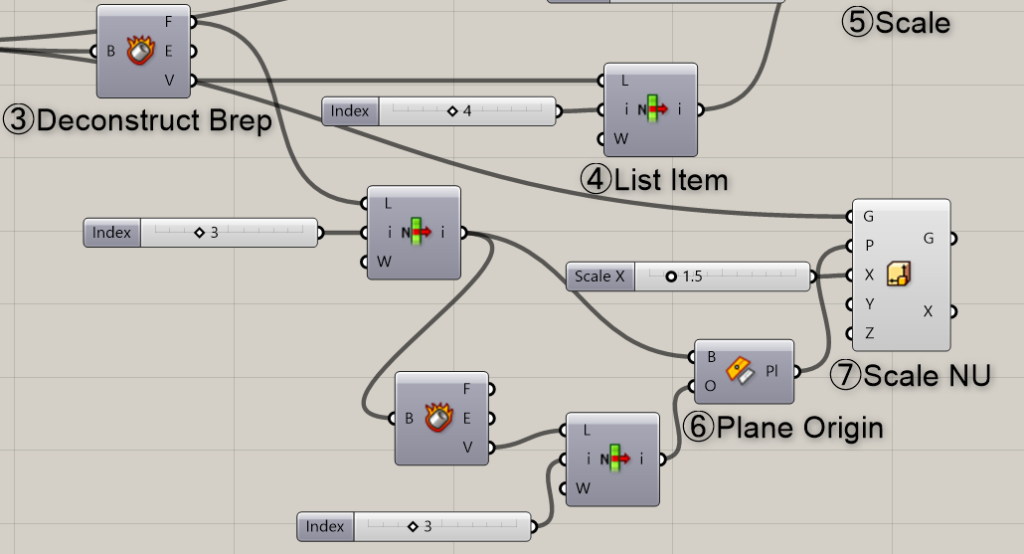
Components Used: ③ Deconstruct Brep ④ List Item ⑥ Plane Origin ⑦ Scale NU
Create a plane and origin
To use Scale NU, you must create a plane and its origin.
First, extract the cube’s surface from the F terminal the Deconstruct Brep used earlier.
Here, we also use List Item and input a numerical value into the i terminal to obtain only one surface.
Then, use Deconstruct Brep to break down the acquired surface once more.
Then, once again, retrieve one vertex using List Item.
Later, you can determine the scale direction by changing the value of this List Item.
Next, use the Plane Origin.
This component can create a plane and its origin by combining a surface and a point.
Output the surface to Plane Origin(B) and the point to Plane Origin(O).
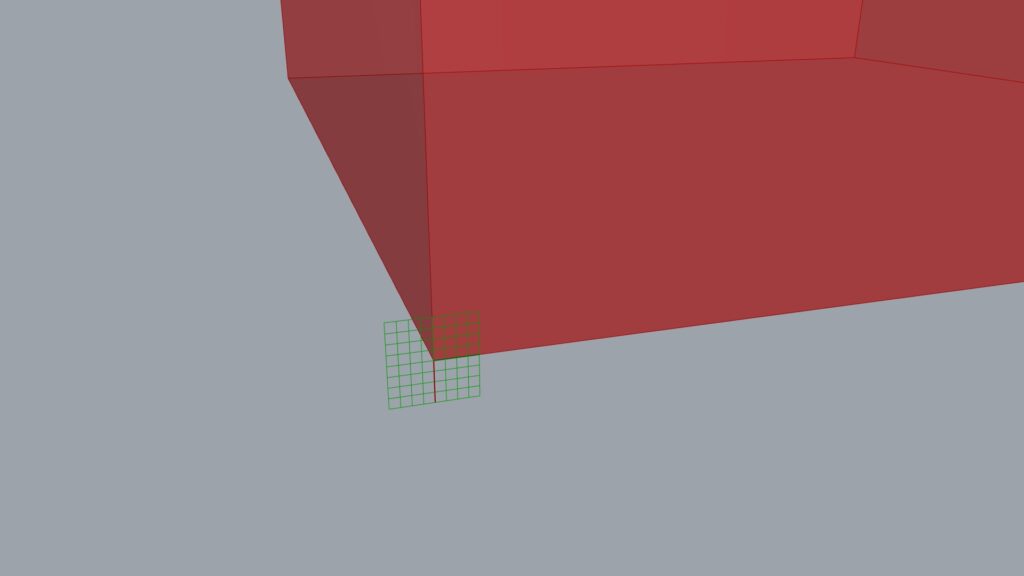
In this way, the plane has been created with the previously defined reference point as its origin.
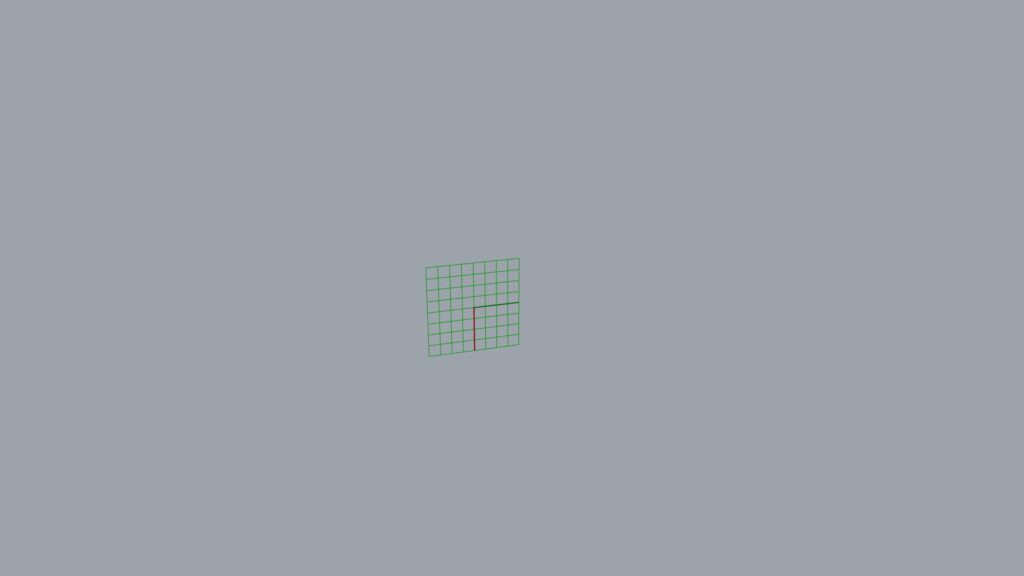
There’s something we want you to be careful about here.
In this case, the X-axis points downward and the Y-axis points horizontally, which is the opposite of the usual orientation.
Therefore, if you wish to extend the scale horizontally later, adjust the Y-axis.
Use the Scale NU component to determine the ratio and direction of scaling
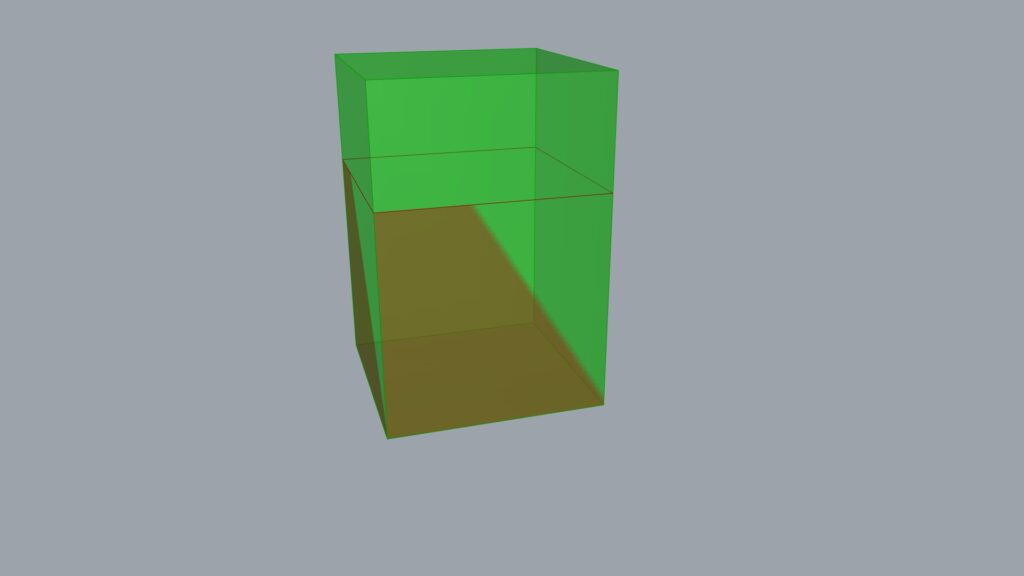
Here, we use Scale NU.
Enter the model you wish to scale into the Scale NU(G), the plane into the Scale NU(P), and the numerical values into the XYZ terminals.
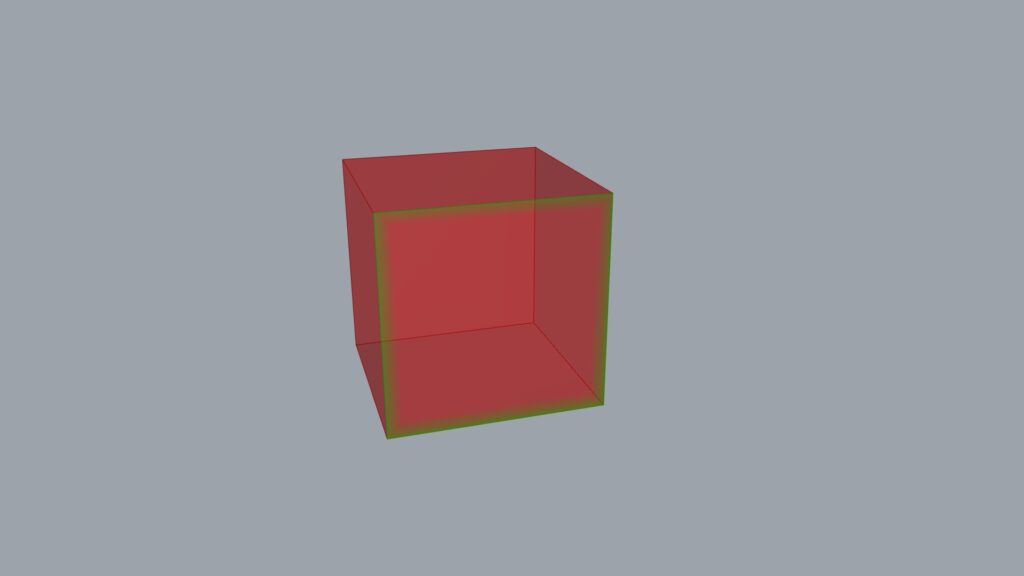
In the case of the image above, only the X terminal has a value of 1.5 entered.
As mentioned earlier, the XY axes are reversed, so the upward direction is scaled by a factor of 1.5.
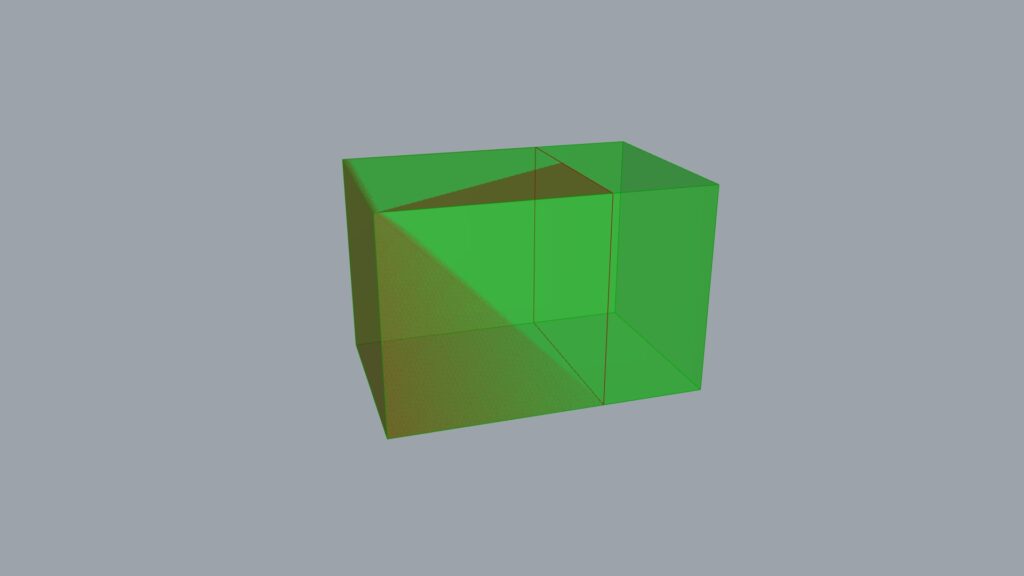
The result input into the Y terminal stretched horizontally.
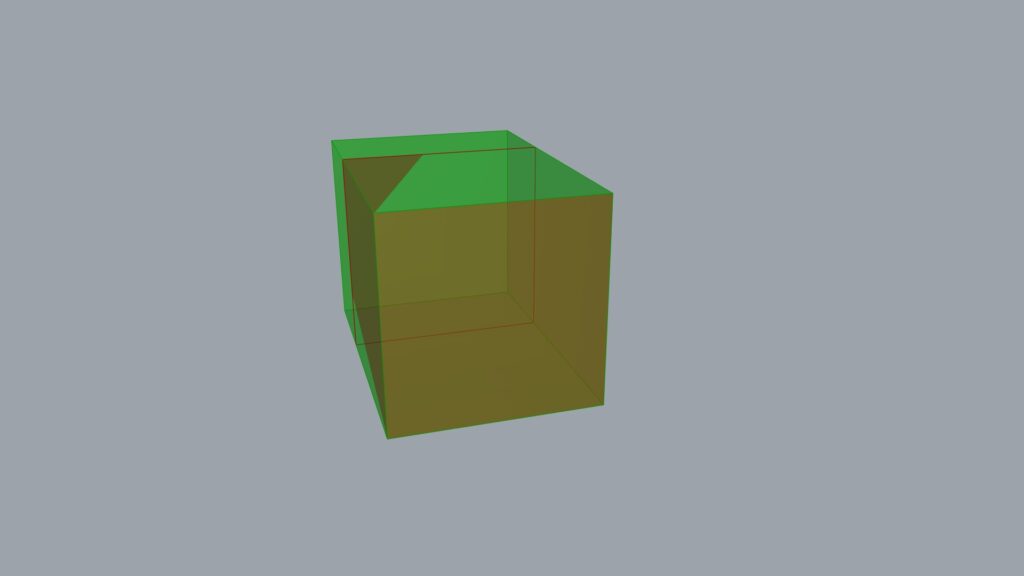
The result of inputting into the Z terminal extended inward.
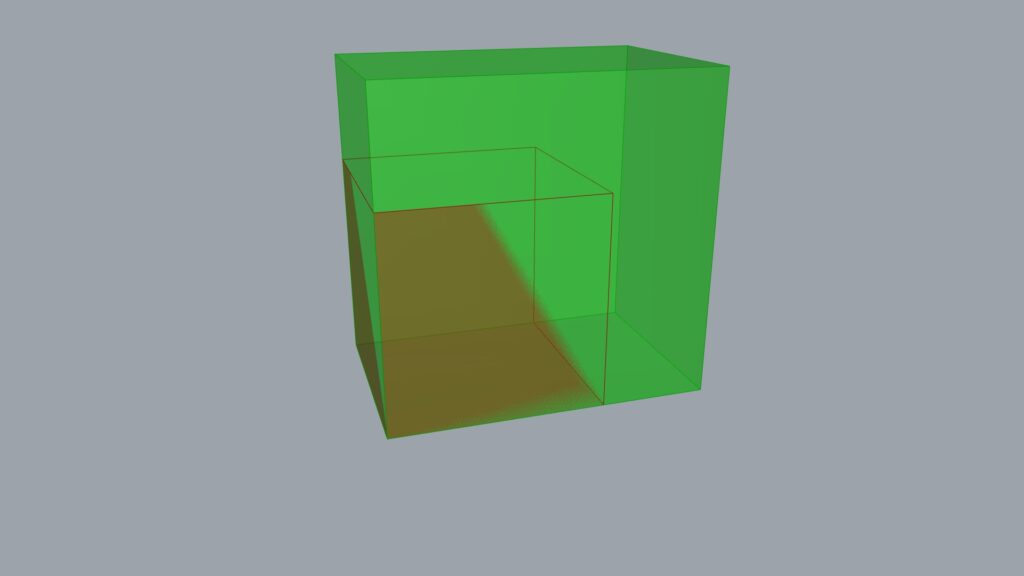
Of course, you can enter values into multiple terminals.
When connected to the XY terminals, the scale changed both horizontally and vertically.
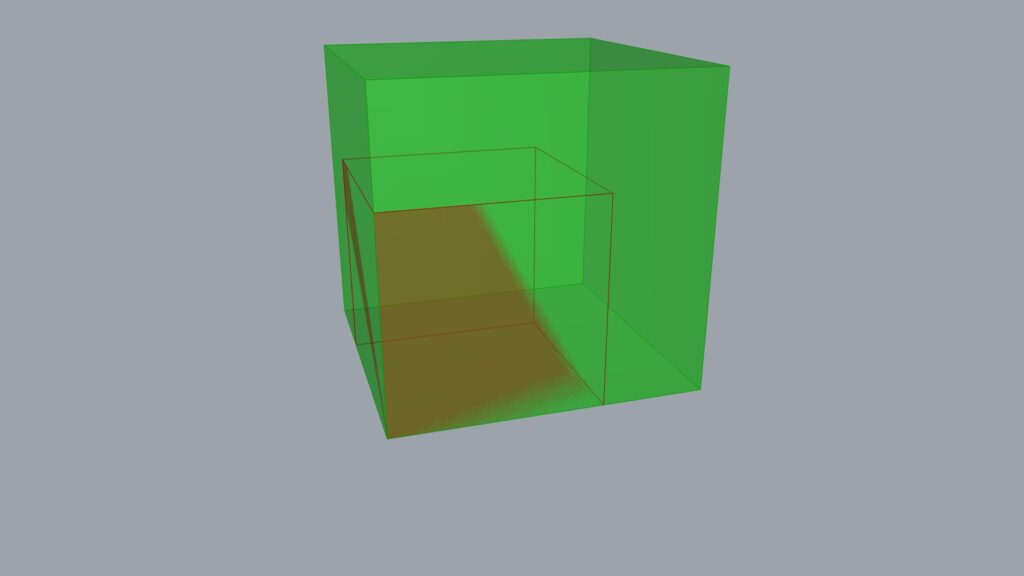
After inputting to all XYZ terminals, all three directions changed.
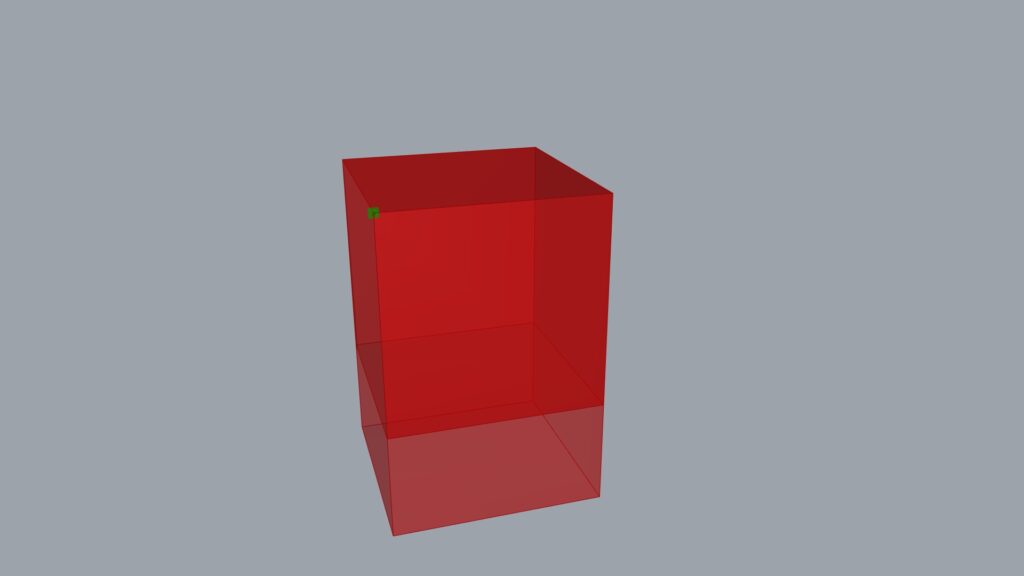
To reverse the scaling direction, modify the value of the last List Item used and extract the vertex on the opposite side.
In this case, while we previously extracted the lower vertex, this time we obtained the upper vertex.
This allowed us to reverse the direction.
List of Grasshopper articles using Scale NU component↓




Comment