This guide explains how to use Clean Tree to remove and organize null, invalid, and empty data.

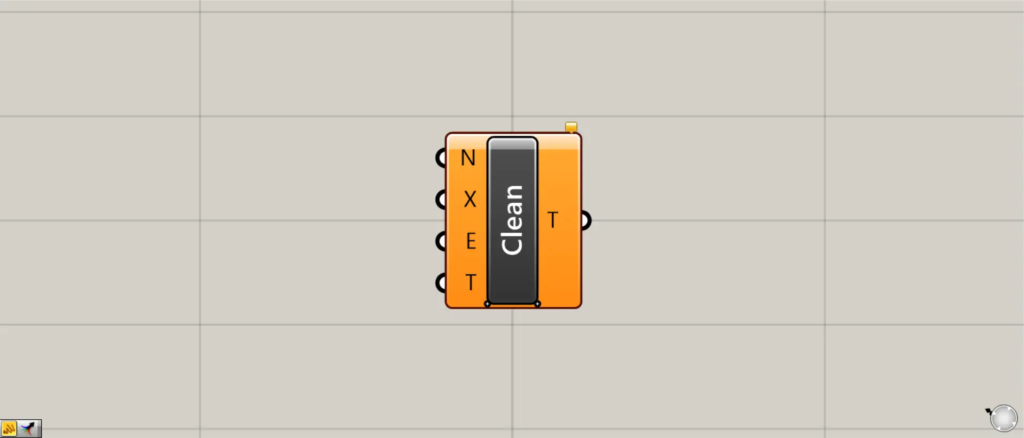
On the Grasshopper, it is represented by either of the two above.
Deleting and organizing null, invalid, and empty data
Using Clean Tree allows you to remove and organize Null, Invalid, and Empty data.
Therefore, in some cases, it is possible to resolve the error state.
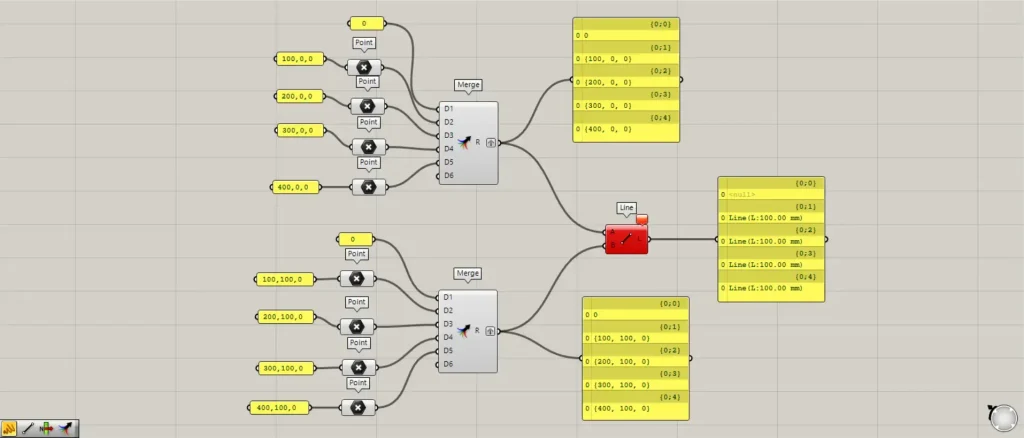
Components used: ①Point ②Merge ③Line
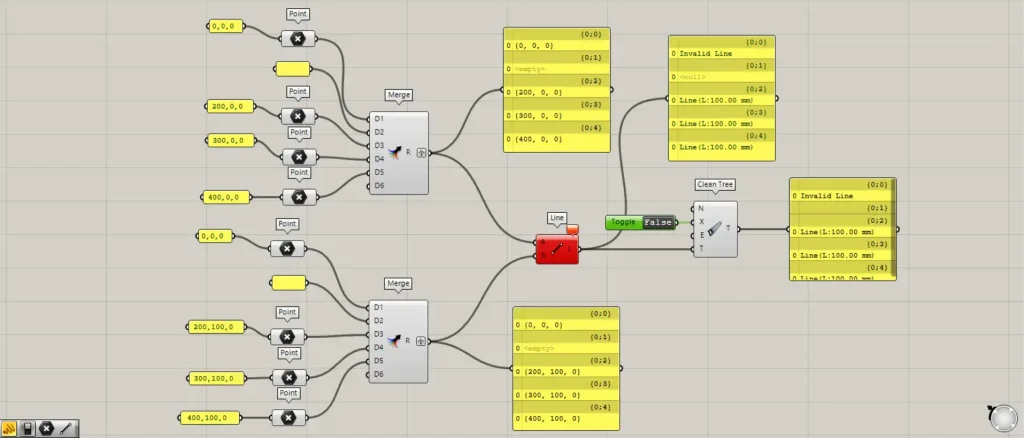
First, let’s create and examine a Null (when a value does not exist).
Enter the number 0 into the first terminal of the first Merge.
For the remaining four terminals of the first Merge, input the four coordinate data sets: 100,0,0, 200,0,0, 300,0,0, and 400,0,0.
Enter the number 0 into the first terminal of the second Merge as well.
For the remaining four terminals of the second Merge, input the four coordinate data sets: 100,100,0; 200,100,0; 300,100,0; 400,100,0.
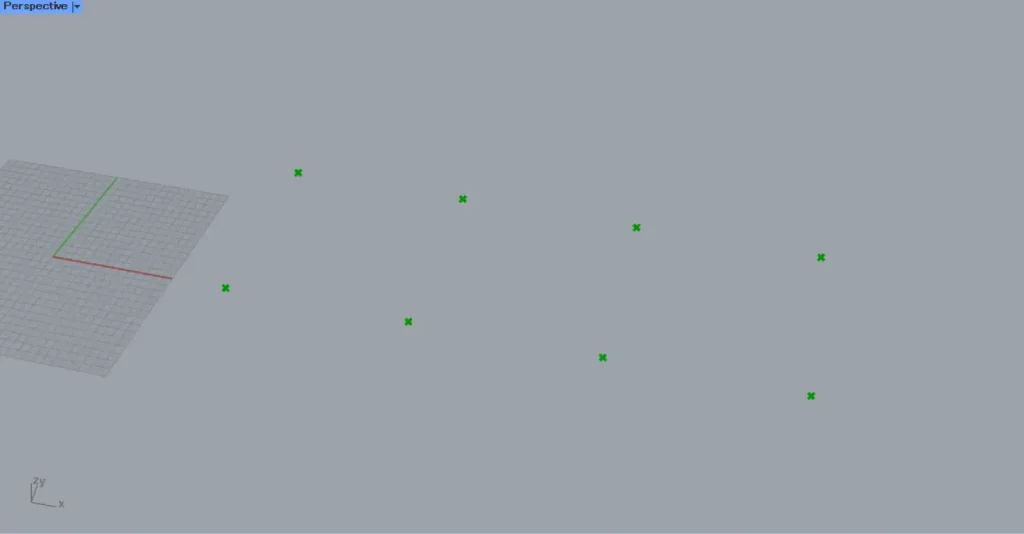

Then, connect the coordinate data to the Point.
Then, the coordinate data is converted into point data at that location.
In this way, eight points are created.
Since only a numerical value is entered into the first terminal of Merge, nothing happens.
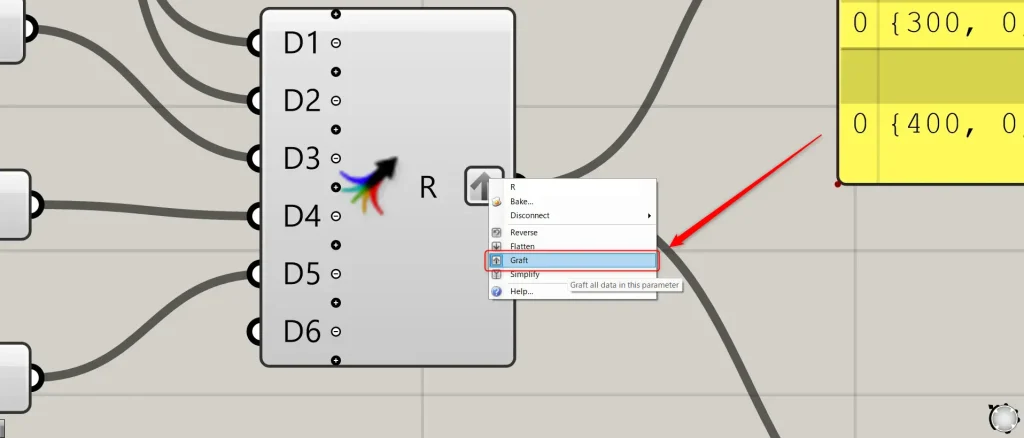
At this point, right-click the two Merge(R) and select “Graft“.
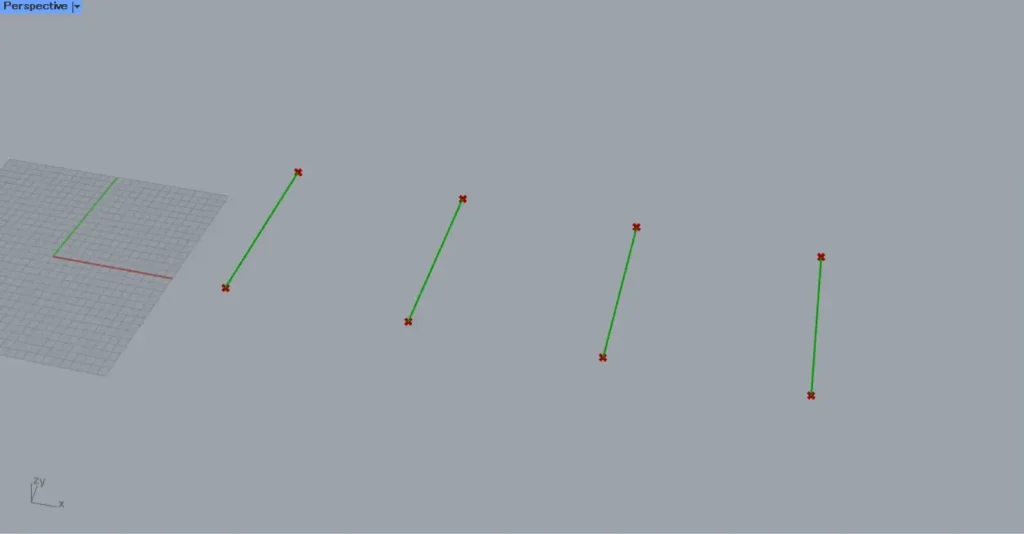

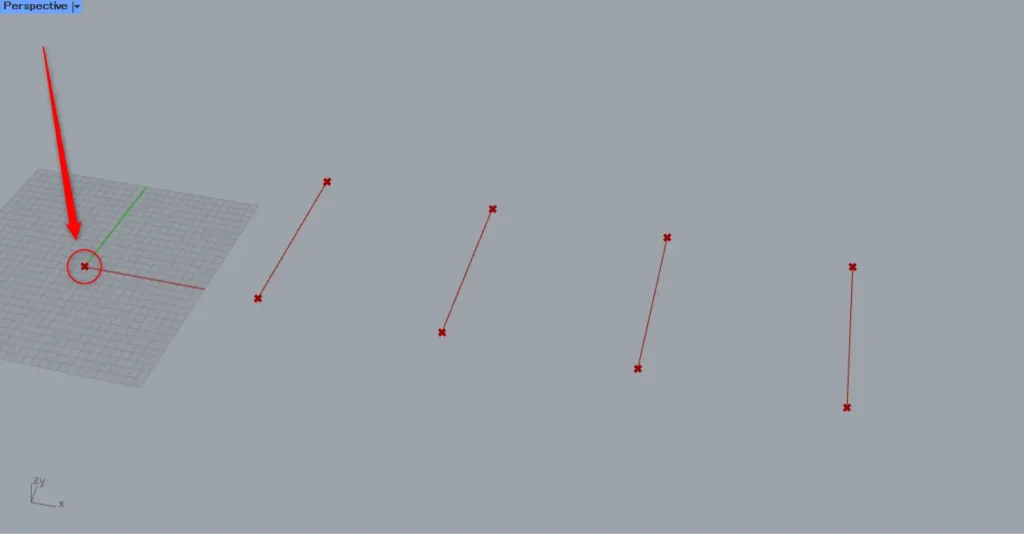
Then, connect the two Merge to the Line(A and B).
Then, as shown in the image above, a line is created by connecting the two points.
And a total of four lines were created.
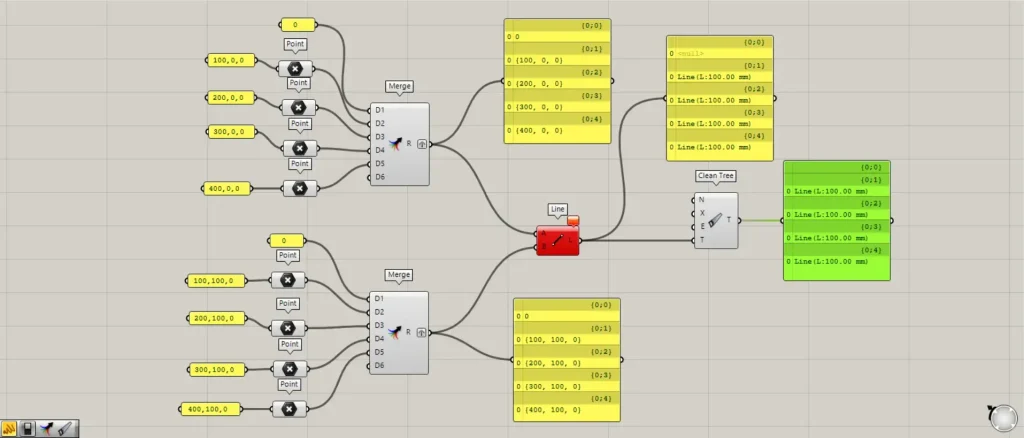
Additional Component: ①Clean Tree
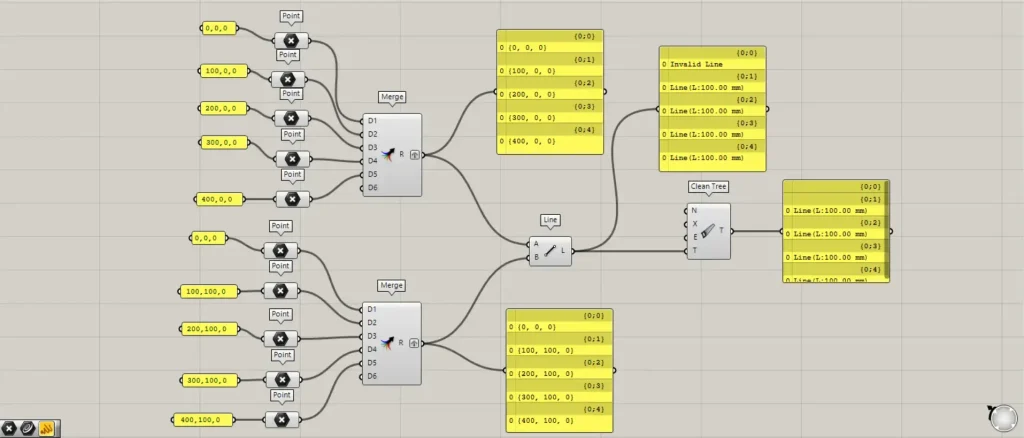
However, when we check Line, it shows an error message.
This is because you must input point data into Line, but since you are inputting numerical data, an error is occurring.
When we connect a Panel to the Line and examine the data, the first branch is null.
The remaining four are displayed correctly as “Line,” indicating that line data has been created.
In this state, connect the Line to the Clean Tree(T).
Then, the null in the first branch was deleted.
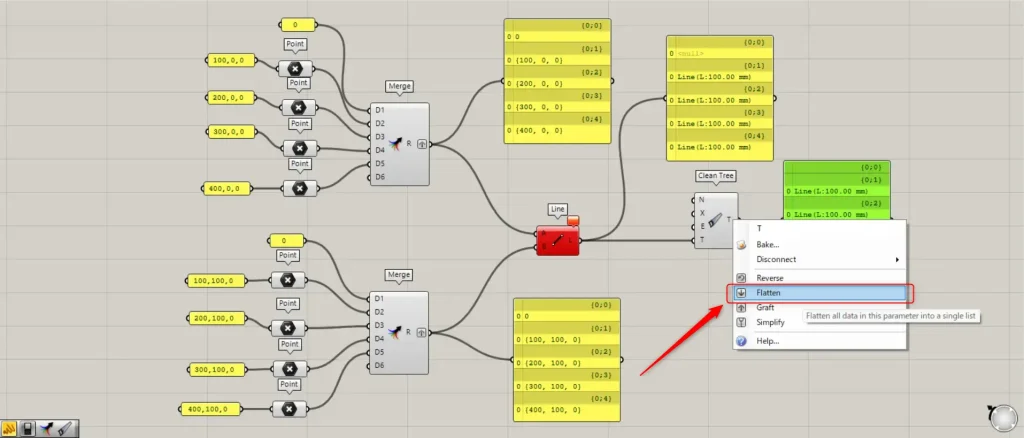
However, if we leave it as is, the {0;0} branch will remain.
By flattening the data into a single branch, you can eliminate empty layers.
Right-click the Clean Tree(T) and select “Flatten“.
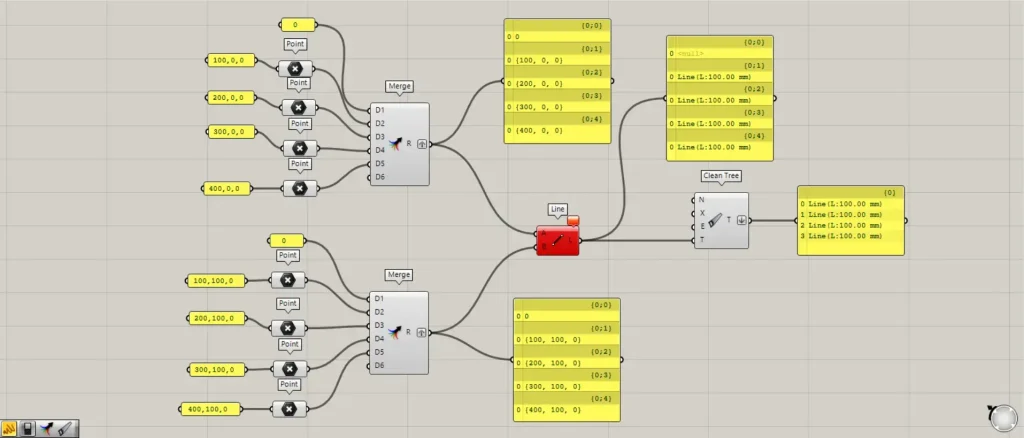
Then, the data was consolidated into a single branch, and the empty branch disappeared.
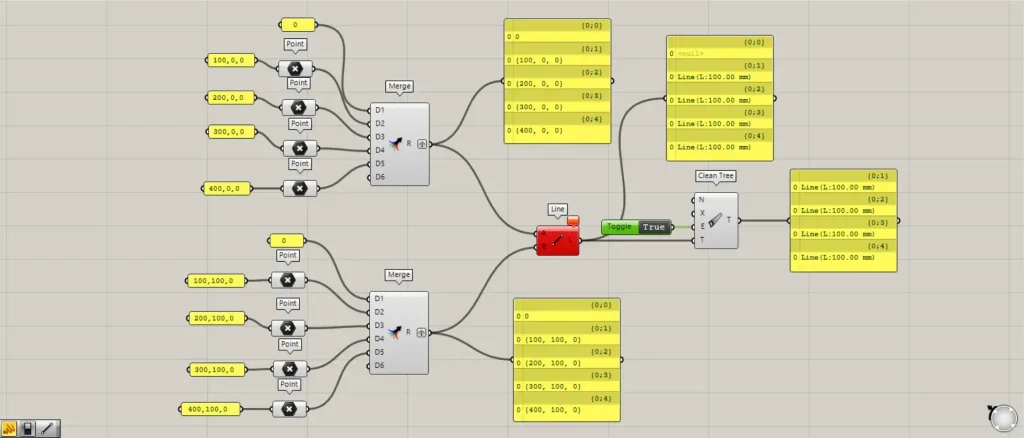
Additional Component: ① Boolean Toggle
To preserve the branch structure, input True into the Clean Tree(E).
This time, we were inputting the information for True using a Boolean Toggle.
Then, we were able to delete the empty branch while maintaining the branch structure.
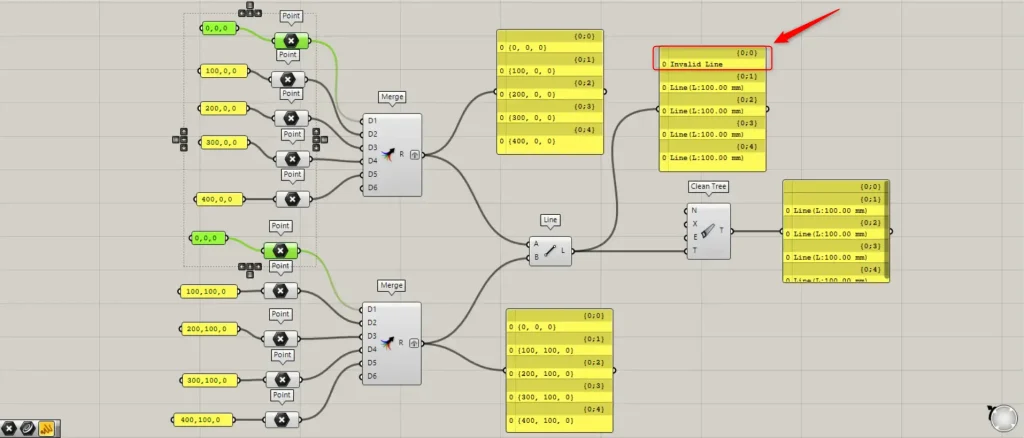
Next, let’s look at the Invalid state.
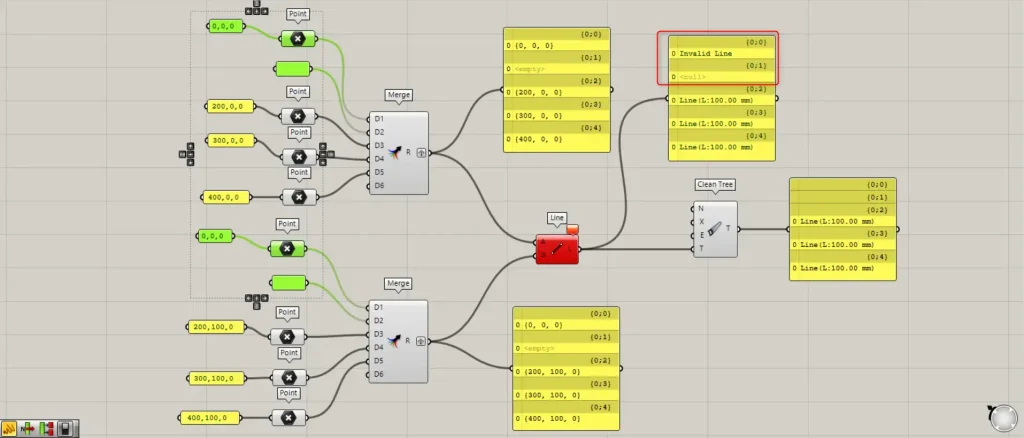
Set the coordinate data entered into the first Merge to the origin position of 0,0,0 for both.
A line connects two points to form a line, but if the points are at the same location, no line is created.
In such cases, “Invalid Line” will be displayed.
In this state, connecting the line to the Clean Tree will remove the invalid line.
Let’s consider the case where both null and Invalid exist.
In this case too, you can use Clean Tree to remove null and Invalid values in bulk.
However, in some cases, it may be necessary to leave null or invalid data.
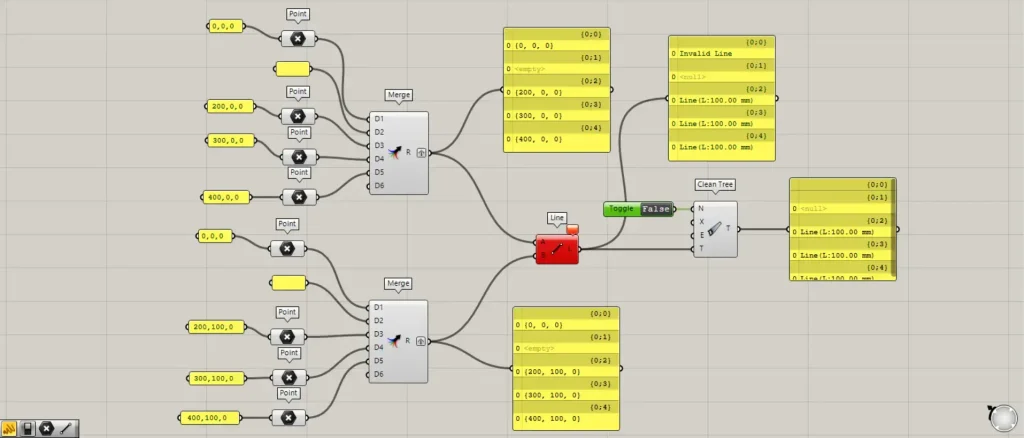
To retain null data, enter False into the Clean Tree(N).
This time, we are inputting False information using a Boolean Toggle.
Then, the invalid data was deleted, but the null data remained.
To retain invalid data, enter False into the Clean Tree(X).
Then, the null data was deleted, but the invalid data remained.
List of Grasshopper articles using Clean Tree component↓

![[Grasshopper] How to use Clean Tree to remove and organize null, invalid, and empty data](https://iarchway.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/01/Clean-Tree.png)



Comment