This article explains how to use Expression to use mathematical expressions, formulas, and functions.
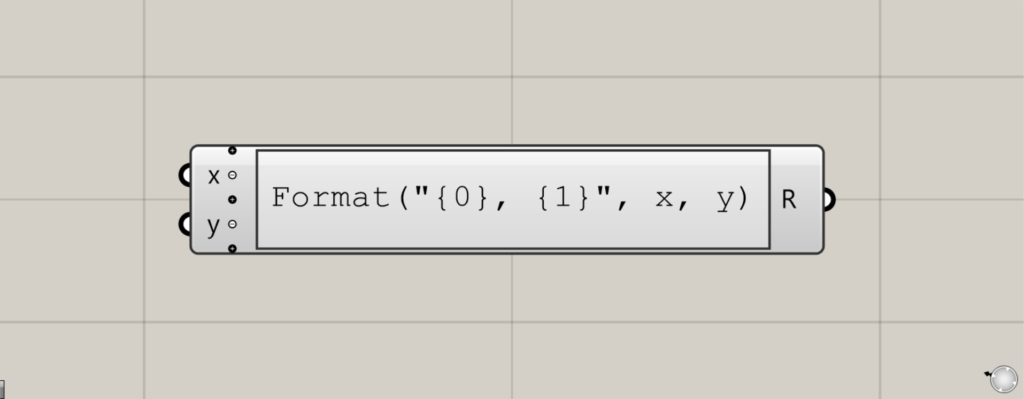
On the Grasshopper, Expression is represented as above.
Using mathematical expressions and formulas
Expression allows you to use mathematical expressions and formulas.
Expression Settings Screen
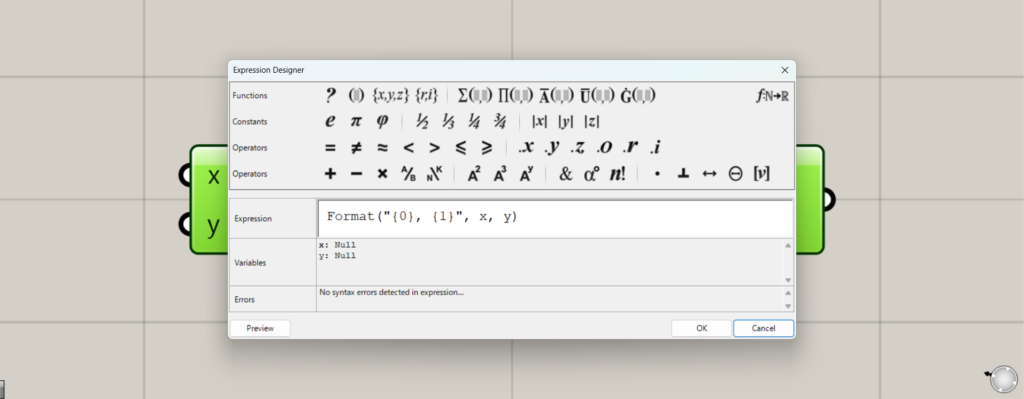
Double-click on an Expression to display the Expression settings screen.
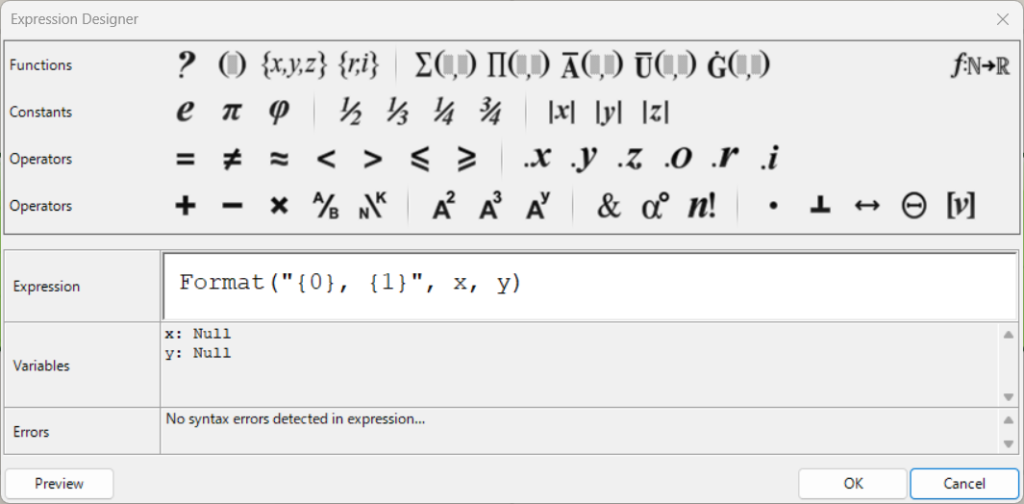
This is the Expression settings screen.
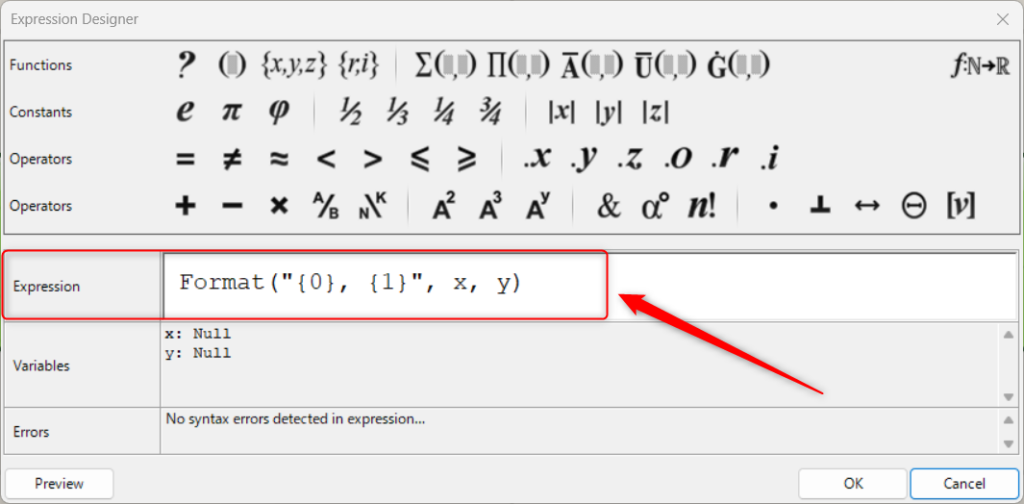
By changing the Expression part, you can create any formula or calculation expression.
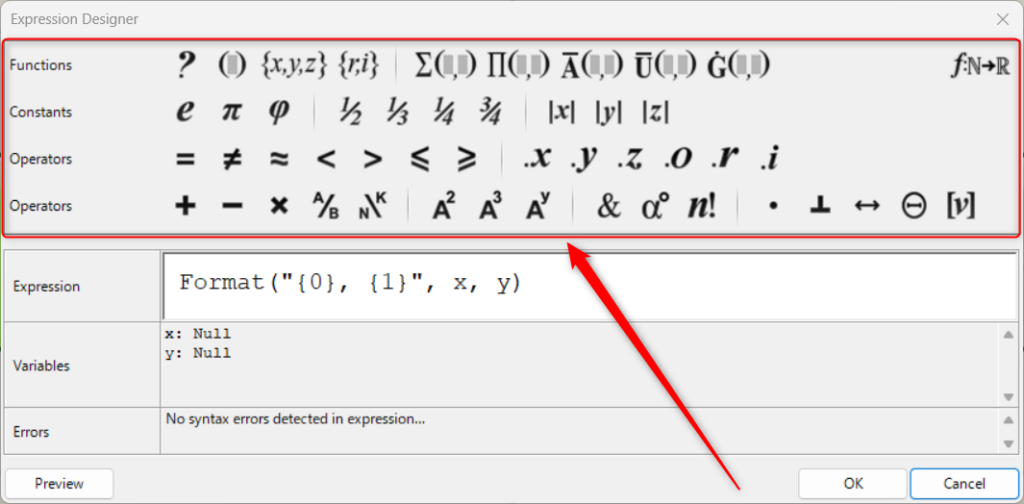
You can also add symbols and functions to formulas and formulas by clicking the icons above.
Creating a formula or calculation
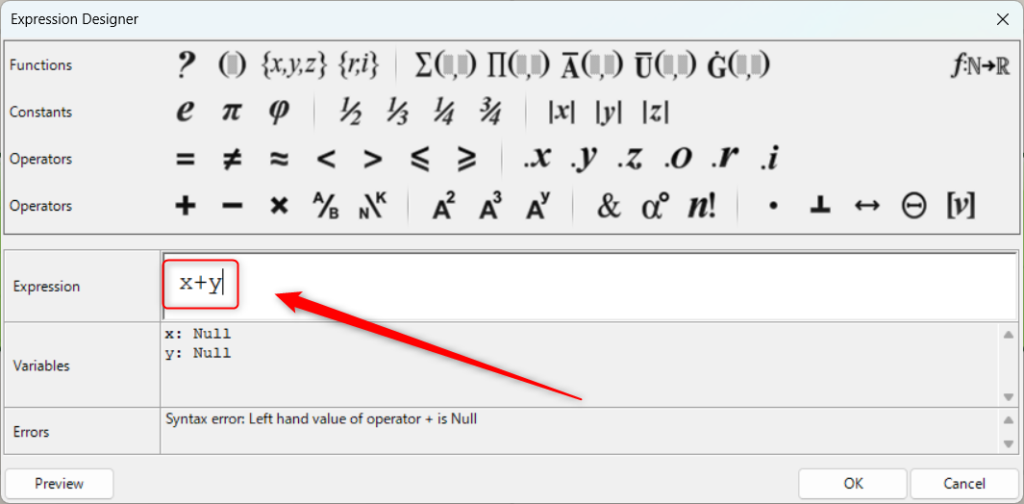
Let’s start with a simple calculation.
First, we entered x y in Expression.
Then press OK in the lower right corner.
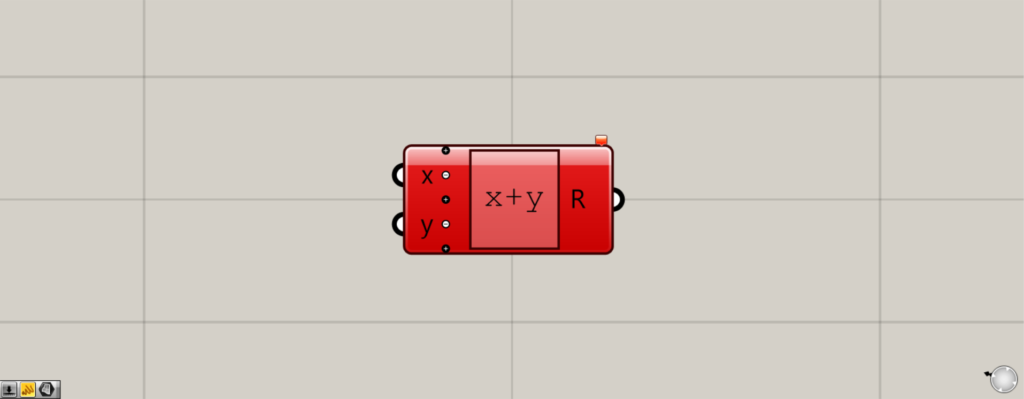
Then an error message appears in red as shown in the image above.
However, there is no problem as it is.
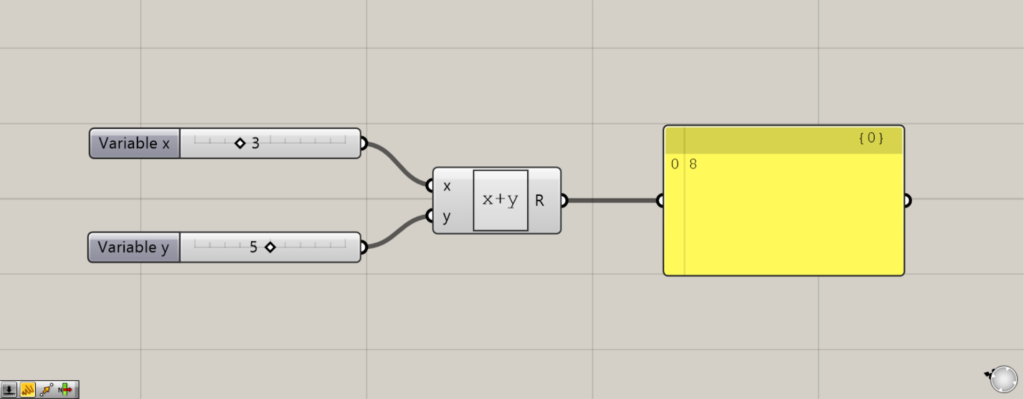
Enter information into the terminals on the left.
By default, there are x and y terminals.
In this case, we input 3 to the x terminal and 5 to the y terminal.
Then 3 5 was added and 8 was output from the R terminal.
Thus, the left terminal is used to input variables.
Increasing the number of terminals and variables
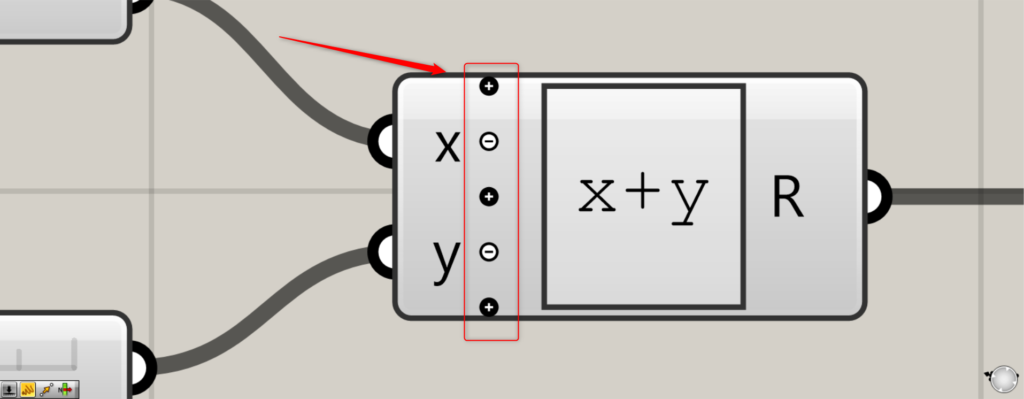
The number of terminals on the left side can also be changed.
Zoom in on Expression and you will see the and – icons.
icon to add a terminal at that location.
-icon will remove the terminal in that area.
In this case, I pressed under the y terminal.
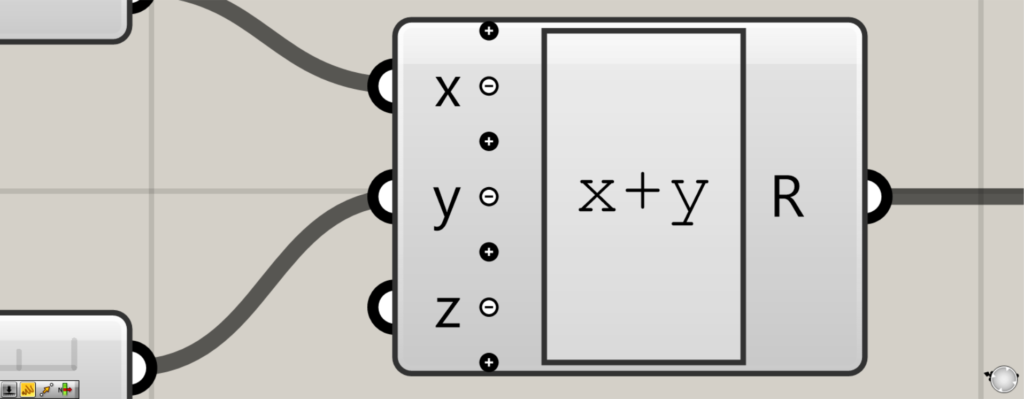
Now a new terminal z is added.
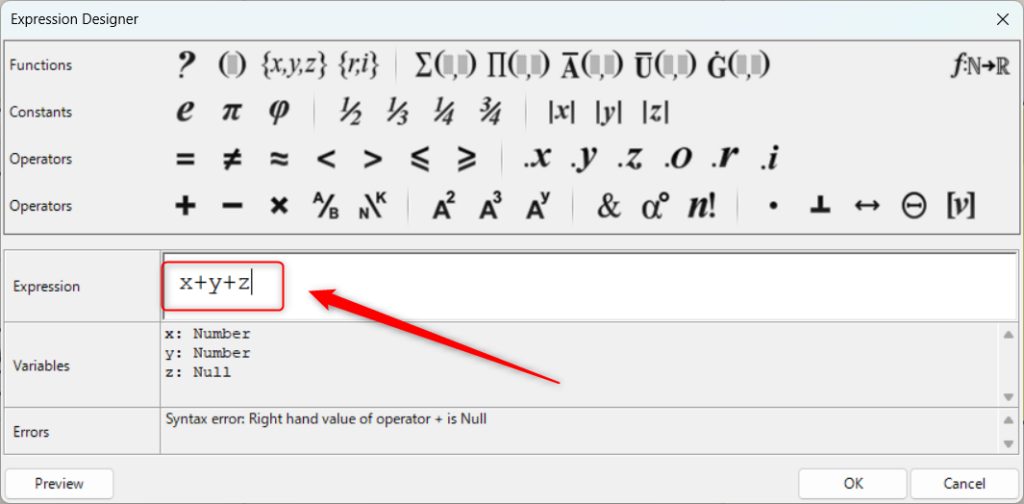
Now that we have a z terminal, we changed the formula to x+y+z.
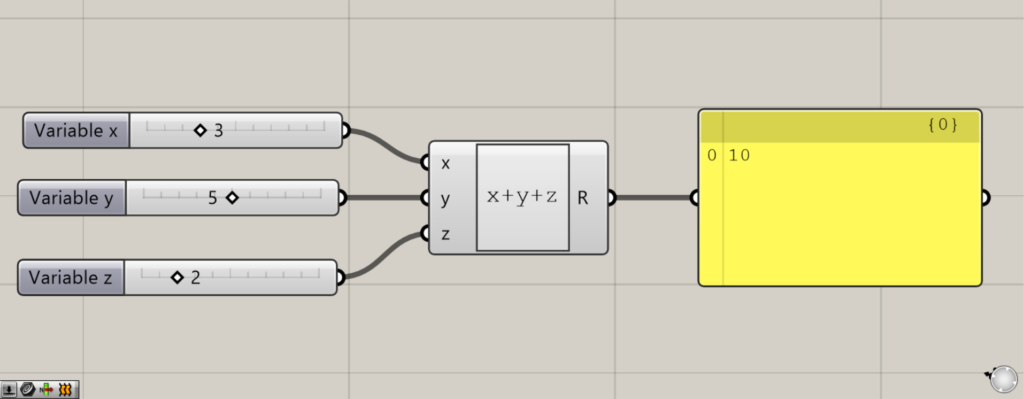
Now we have a calculation with three terminals.
As you can see, the calculation can be done with multiple terminals.
Changing terminal/variable names
By changing the name of a terminal, you can also change the name of a variable.
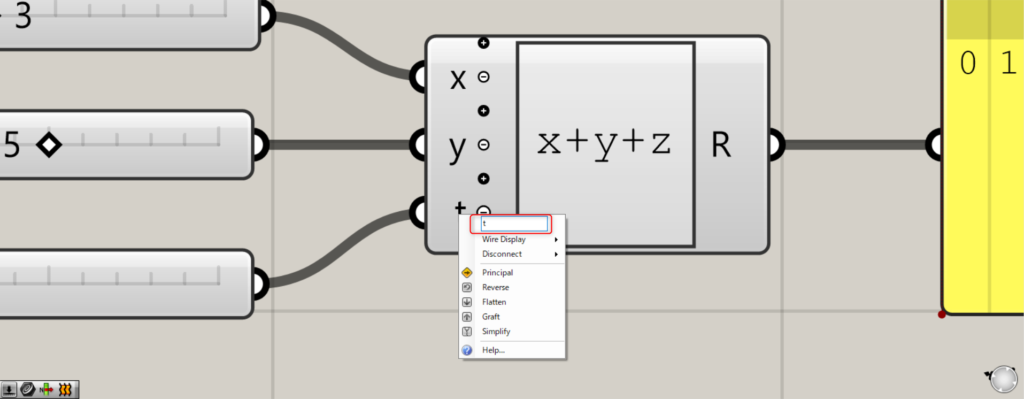
To do so, right-click on the terminal you wish to change.
Then change the name of the terminal.
In this case, the terminal name is set to “t”.
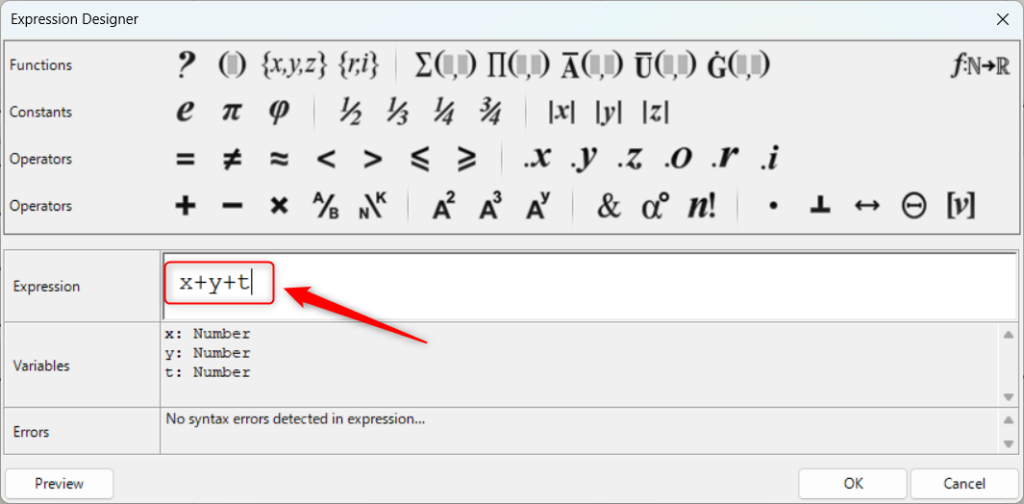
In this case, the variable name of the formula is also changed.
This time, the terminal name is set to “t”, so we set it to “x+y+t”.
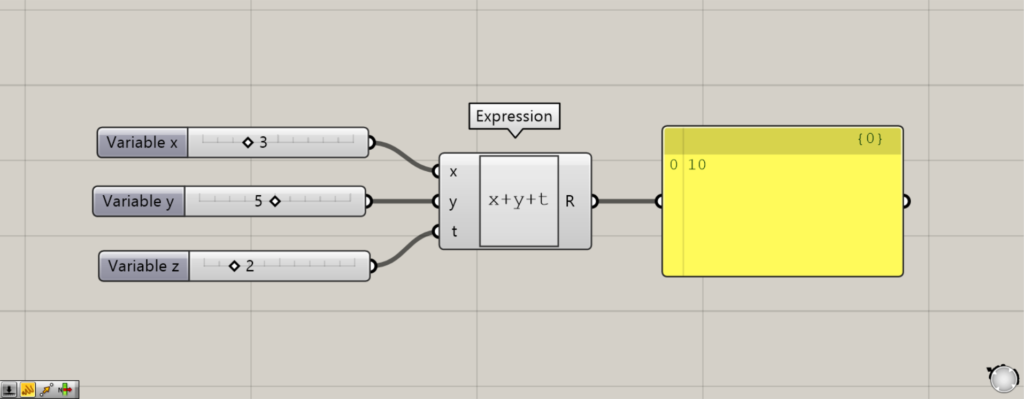
Then, the calculation was completed with the variable name changed as shown here.
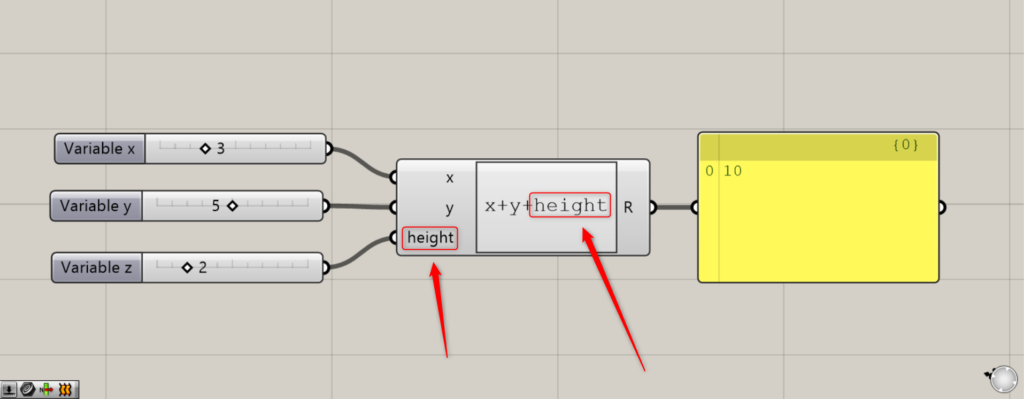
Long variable names can also be made longer, as in the image above.
Combining as a String
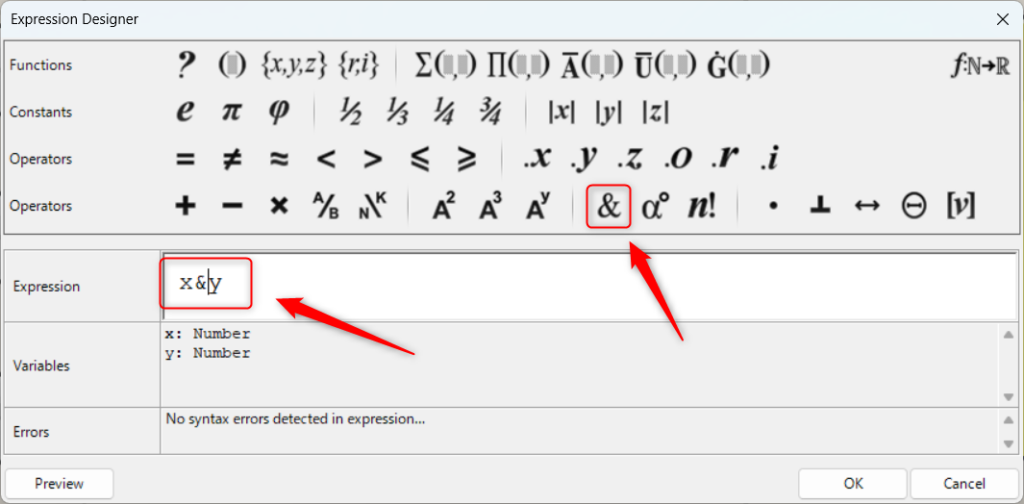
By using &&, you can also combine the input information as a string.
In this case, x&y was entered into Expression.
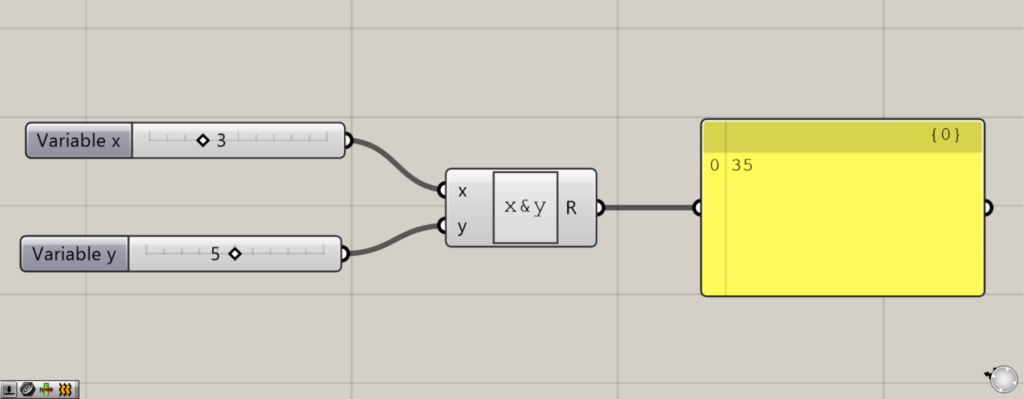
Then enter the information in the left terminal.
At first, I entered 3 in the x terminal and 5 in the y terminal.
Then, as shown in the image above, 35 was displayed.
This is not the numerical value 35, but 3 and 5 next to each other as letters.
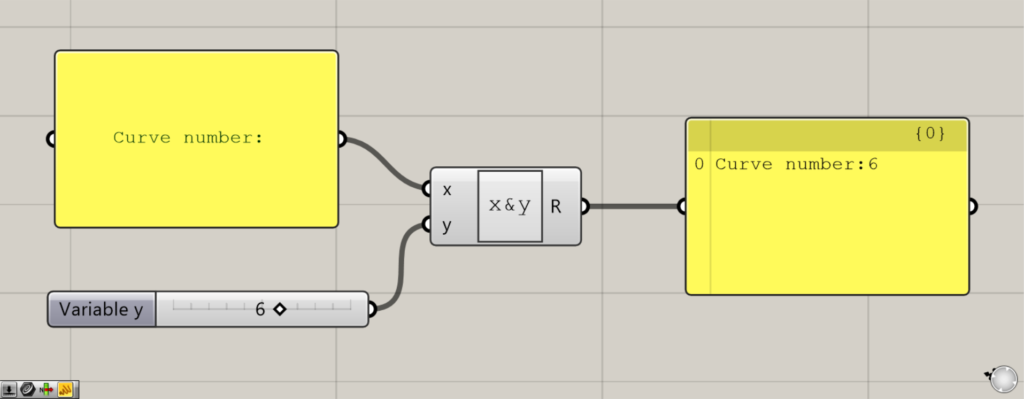
Since they are treated as letters, they can also be used as shown in the image above, such as the number of lines: 6.
Creating Coordinates
Coordinates can also be created.
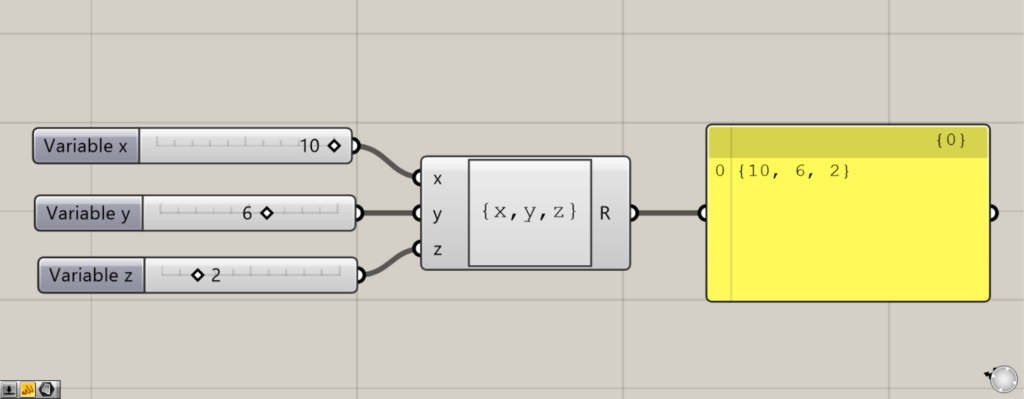
To do so, enter {x,y,z} in the Expression field.
Then, enter the numerical values of the x, y, and z coordinates in the left terminal.
Coordinate data is then created.
Looking on Rhino, we can see that a point has been created at the specified coordinates.
Using Functions
Next, we will explain how to use functions.
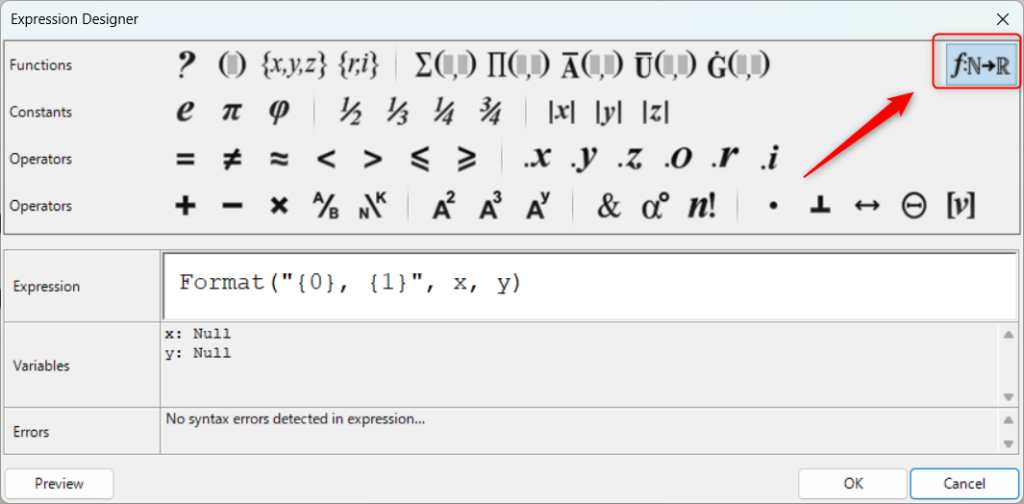
In the Expression settings screen, click on the top right corner to see the available functions.
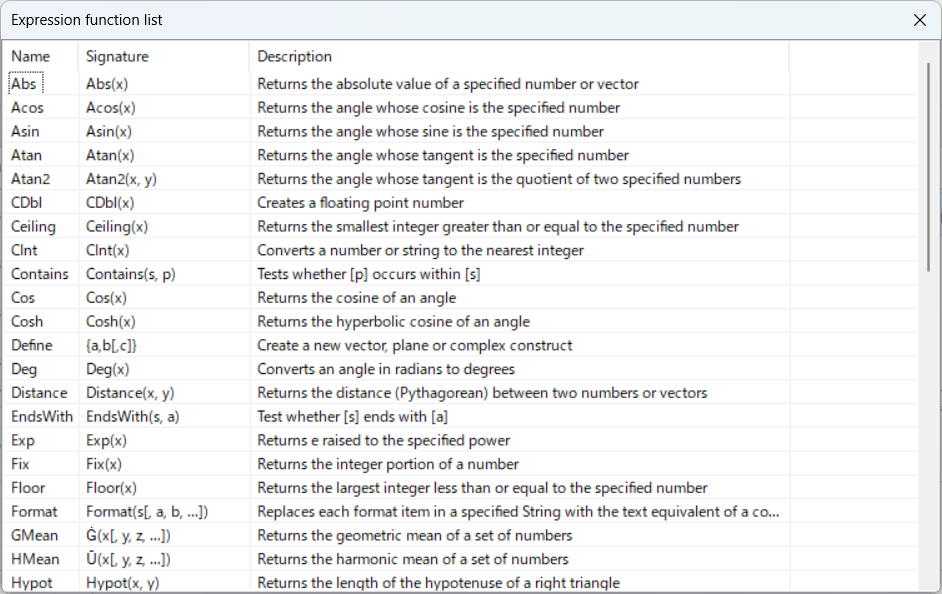
As you can see, a list of functions is displayed.
The following is a list of available functions.
The leftmost Name is the function name.
Signature in the middle is how to enter the function in Expression.
Description is a description of the function (in English).
| Name | Signature | Description |
| Abs | Abs(x) | Returns the absolute value of a specified number or vector |
| Acos | Acos(x) | Returns the angle whose cosine is the specified number |
| Asin | Asin(x) | Returns the angle whose sine is the specified number |
| Atan | Atan(x) | Returns the angle whose tangent is the specified number |
| Atan2 | Atan2(x, y) | Returns the angle whose tangent is the quotient of two specified numbers |
| CDbl | CDbl(x) | Creates a floating point number |
| Ceiling | Ceiling(x) | Returns the smallest integer greater than or equal to the specified number |
| Clnt | Clnt(x) | Converts a number or string to the nearest integer |
| Contains | Contains(s, p) | Tests whether [p] occurs within |
| Cos | Cos(x) | Returns the cosine of an angle |
| Cosh | Cosh(x) | Returns the hyperbolic cosine of an angle |
| Define | {Define | Create a new vector, plane or complex construct |
| Deg(x) | Deg(x) | Converts an angle in radians to degrees |
| Distance | Distance(x, y) | Returns the distance (Pythagorean) between two numbers or vectors |
| EndsWith | EndsWith(s, a) | Test whether |
| Exp | Exp(x) | Returns e raised to the specified power |
| Fix | Fix(x) | Returns the integer portion of a number |
| Floor | Floor(x) | Returns the largest integer less than or equal to the specified number |
| Format | Format(s[, a, b, …]) | Replaces each format item in a specified String with the text equivalent of a corresponding value |
| GMean | Ġ(x[ y, z , …]) | Returns the geometric mean of a set of numbers |
| HMean | Ū(x[ y, z , …]) | Returns the harmonic mean of a set of numbers |
| Hypot | Hypot(x, y) | Returns the length of the hypotenuse of a right triangle |
| If | If(test, A, B) | Returns A if test is True, B if test is false |
| IndexOf | IndexOf(s, a[, i]) | Find the first character position of |
| Int | Int(x) | Returns the integer portion of a number |
| LCase | LCase(s) | Converts all characters in a string to their lower case equivalent |
| Left | Left(s, i) | Returns the |
| Length | Length(x) | Returns the magnitude of a vector or the number of characters in a string |
| Ln | Ln(x) | Returns the natural (base e) logarithm of a specified number |
| Log | Log(x[,b]) | Returns the base |
| Log10 | Log10(x) | Returns the base 10 logarithm of a specified number |
| Max(x[ Z, …]) | Max(x[ Z, …]) | Returns the maximum value in a set of numbers |
| Mean | A(x[, Z, …]) | Returns the mean (average) of a set of numbers, vectors or planes |
| Min | Min(x[, y, Z, …]) | Returns the minimum value in a set of numbers |
| MinkowskiDistance | MinkowskiDistance(x, y, p) | Returns the p-order Minkowski distance between two numbers or vectors |
| Pow | Pow(x, y) | Returns a specified number or vector raised to the specified power |
| Prod | Π(x[, y, z, …]) | Returns the product of a set of numbers |
| Rad | Rad(x) | Converts an angle in degrees to radians |
| Replace | Replace(s, a, b) | Replaces all occurrences of |
| Right | Right(s) i) | Returns the |
| Round | Round(x[, d]) | Rounds a floating point number to the specific decimal places |
| Sin | Sin(x) | Returns the sine of an angle |
| Sinh | Sinh(x) | Returns the hyperbolic sine of an angle |
| Sqrt | Sqrt(x) | Returns the square root of a specified number |
| StartsWith | StartsWith(s, a) | Test whether |
| SubString | SubString(s, i[ I]) | Returns a substring based on start char index and length |
| Sum | ∑Sum(x[, y, z, …]) | Returns the sum of a set of numbers or vectors |
| Tan | Tan(x) | Returns the tangent of an angle |
| Tanh | Tanh(x) | Returns the hyperbolic cosine of an angle |
| UCase | UCase(s) | Converts all characters in a string to their upper case equivalent |
| Unitize | [v] Returns a unit length vector | Returns a unit length vector |
Function Usage Examples
Let’s look at some examples of function usage.
Usage Example 1
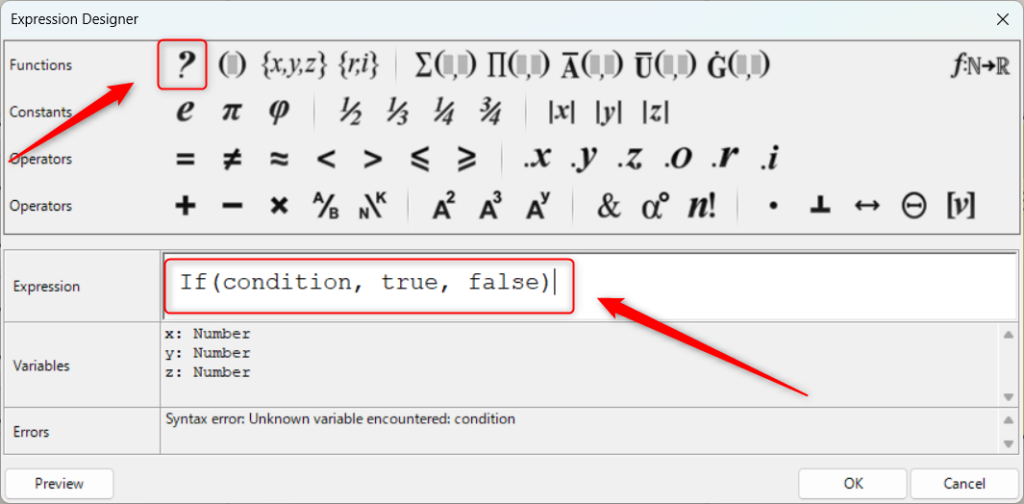
The first example is the If function.
The If function can also be done by clicking on the icon in the upper left corner of Expression.
To use the If function, type something like If(condition, if true, if false).
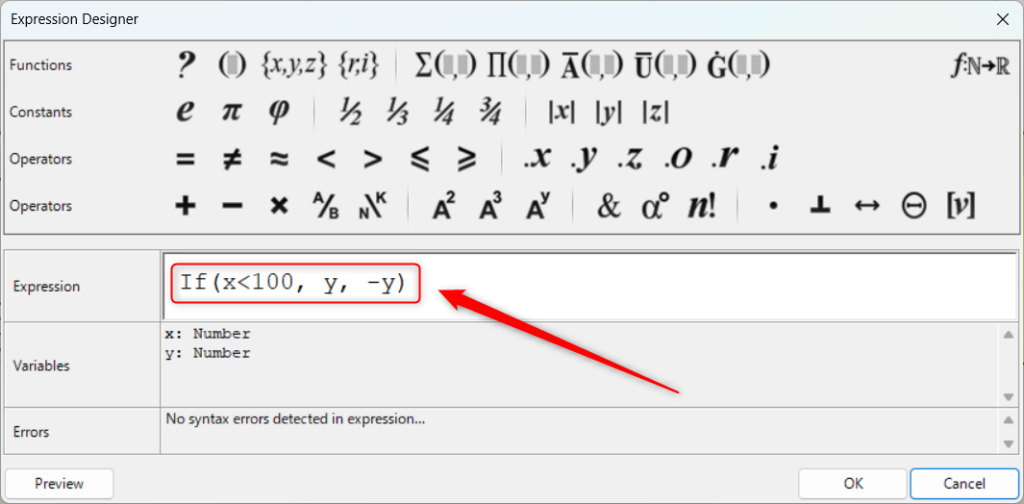
In this case, we typed If(x<100, y, -y).
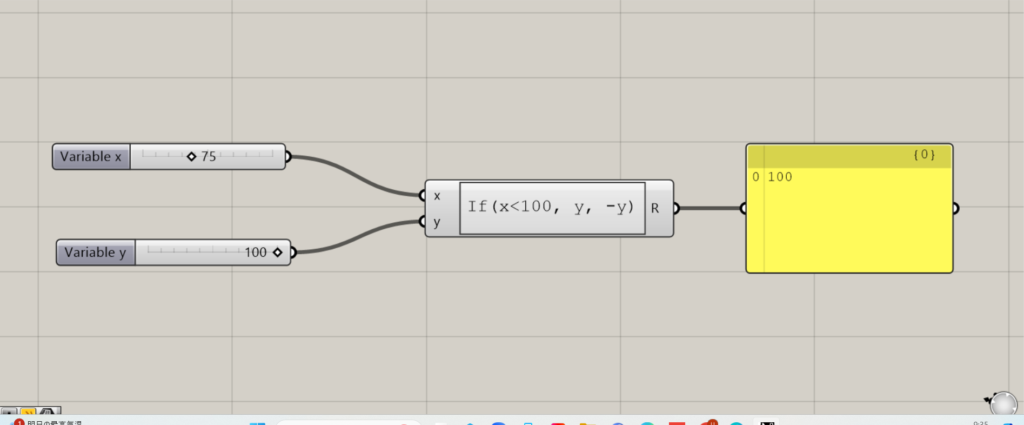
In this case, if x is less than 100, y will be negative.
In this case, the number entered for x is 75, which is less than 100, so the output value is positive.
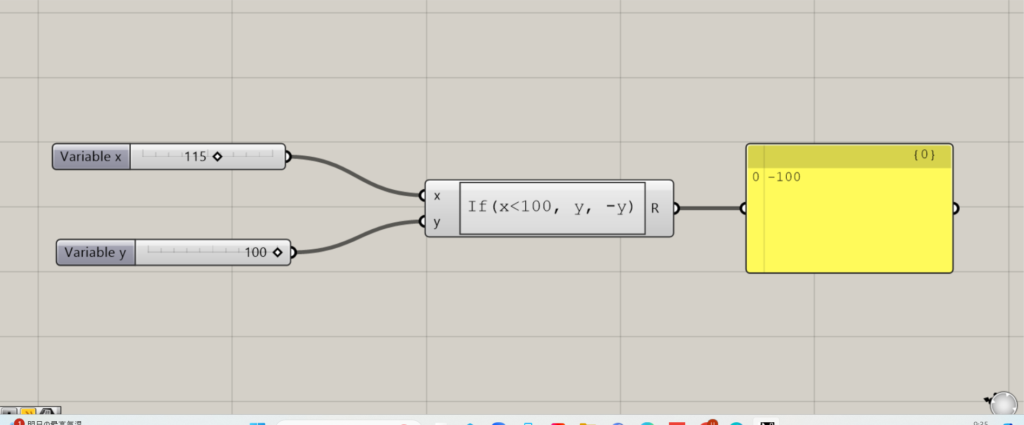
Conversely, when x is greater than 100, y is positive.
In this case, the value entered for x is 115, which is greater than 100, so the output value is negative.
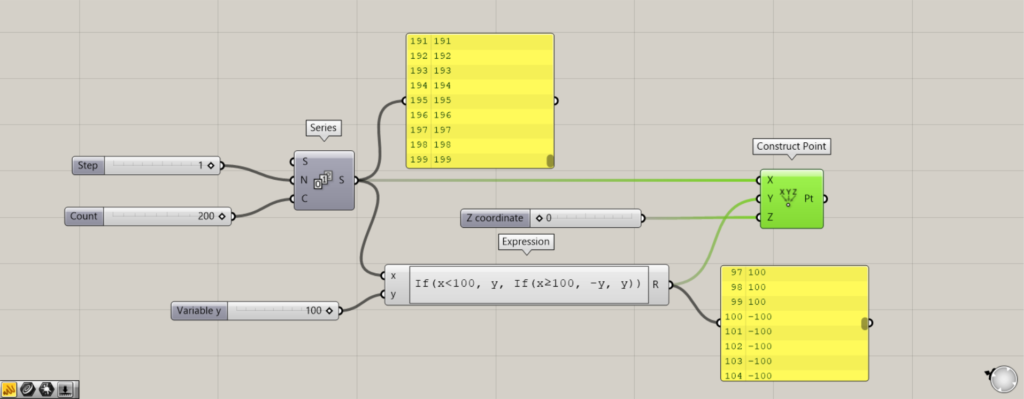
Components used: (1) Series (2) Expression (3) Construct Point
The above example shows how to create multiple points.
Applying the previous method, if x exceeds a certain number, the position of the point changes because it becomes a negative number.
Enter an incremental number, 1, at the Series(N).
Enter 200, the number of numbers to be created, in the Series(C).
This will create a number from 0 to 199.
Connect that number to the x terminal of Expression.
Then, connect the Series to the Construct Point(X).
Connect the R terminal of Expression to the Construct Point(Y).
Connect 0 to the Construct Point(Z).
Now, when the X coordinate is 100, the Y coordinate of the generated point is negative.
Usage Example 2
The next use case is the Sin function.
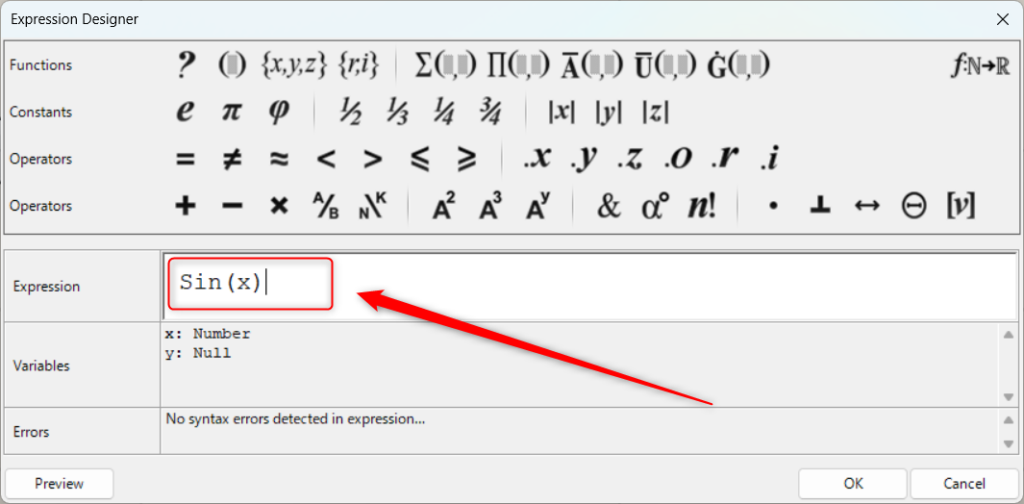
To use the Sin function, type Sin(x) in Expression.
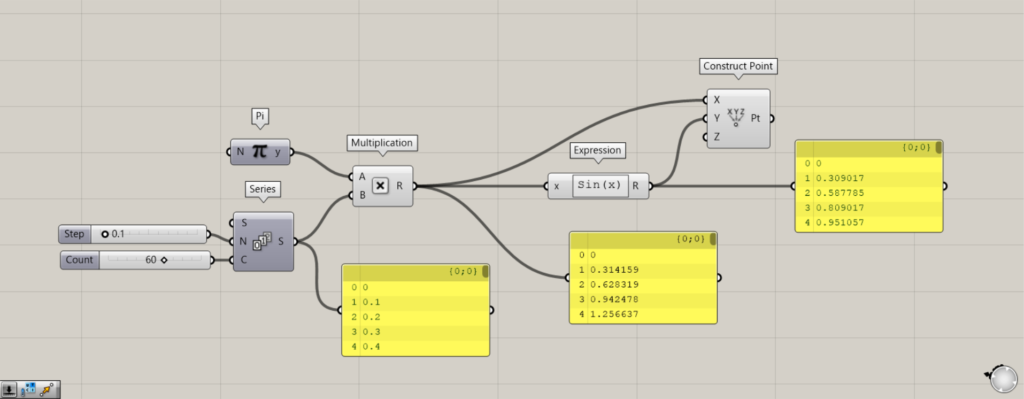
Components used: (1) Pi (2) Series (3) Multiplication (4) Expression (5) Construct Point
Using Pi allows us to use pi.
Connect 0.1 to the Series(N).
Enter the number of numbers to be created in the Series(C).
Then connect Pi and Series to Multiplication.
Further, connect Multiplication to Expression.
Connect Multiplication to the Construct Point(X).
Connect Expression to the Construct Point(Y).
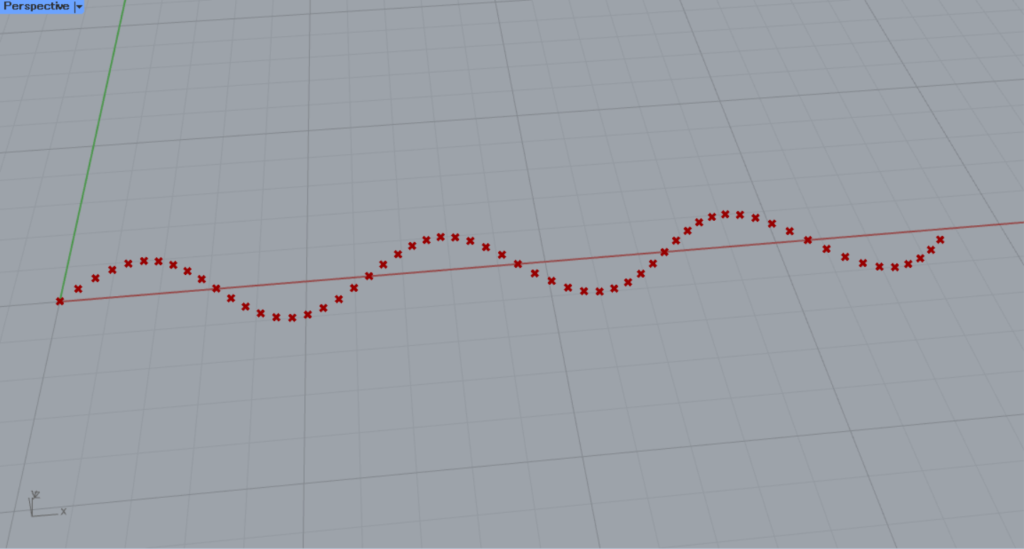
As you can see, a point is created as if drawing a sinusoidal wave.
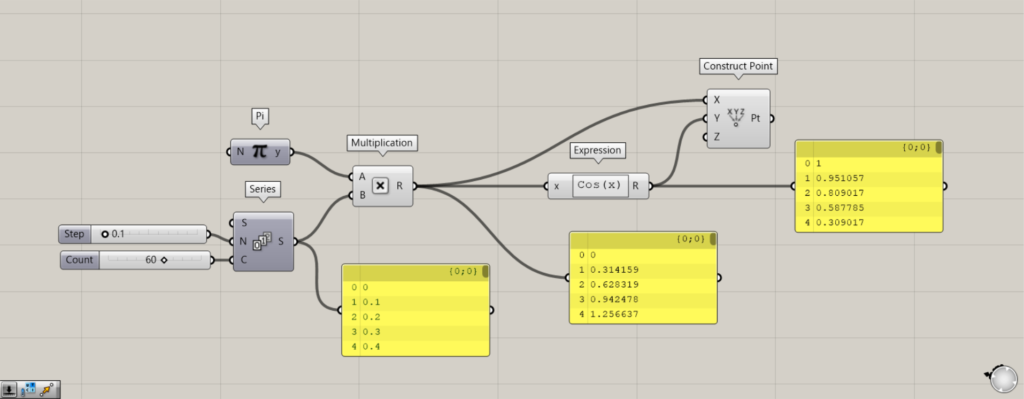
Let’s change to the Cos function.
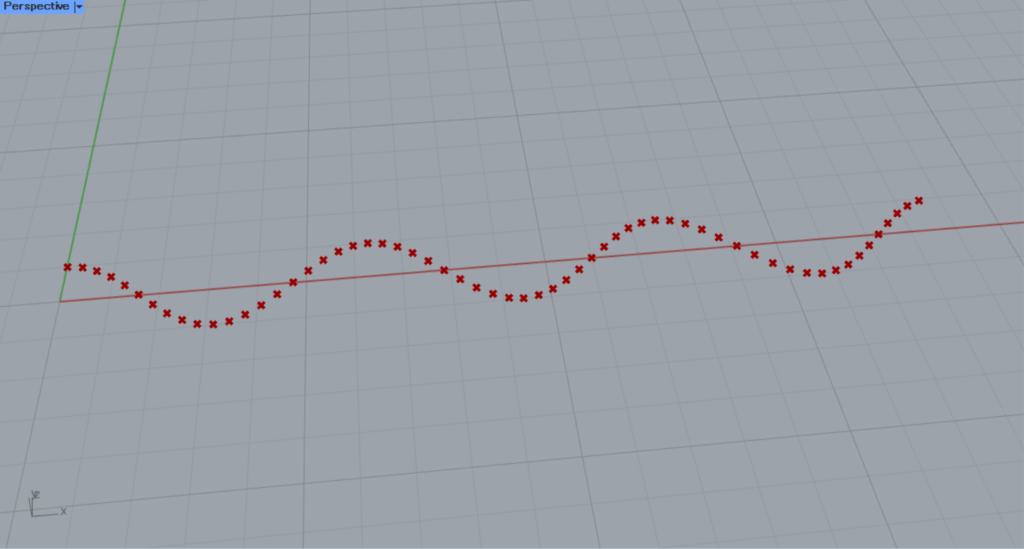
The result is a Cosine wave.
Usage Example 3
Next, let’s look at the Min function.
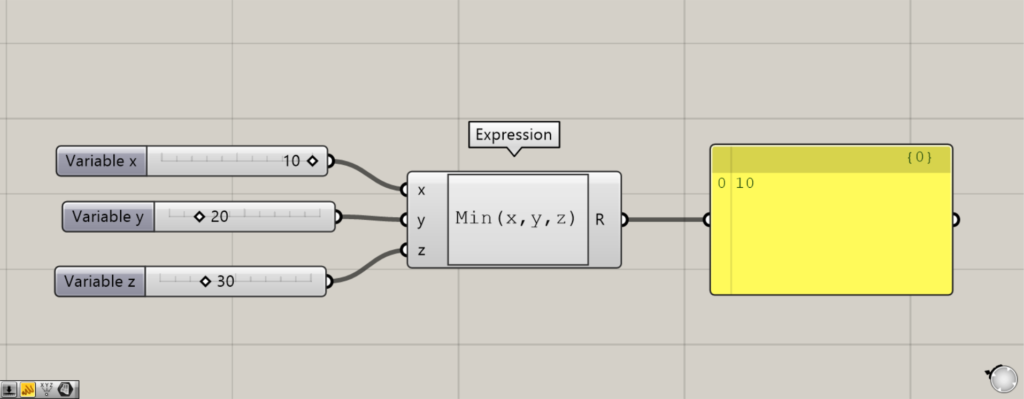
To use the Min function, enter Min(x,y,z) in Expression.
Using the Min function, only the smallest value among the values entered into the left terminal is output.
Usage Example 5
The last function is the sigma function.
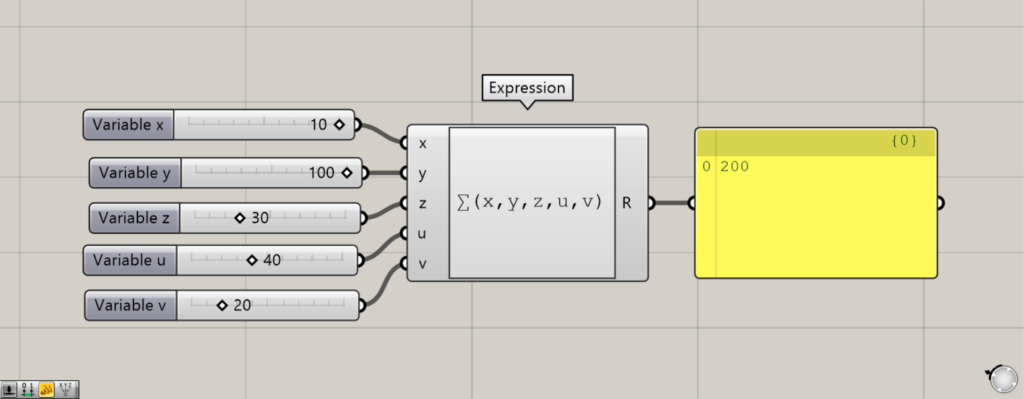
To use the sigma function, enter ∑(x,y,z,u,v…) in Expression.
The sigma function will output a number that is the sum of the numbers entered on the left side.
List of Grasshopper articles using Expression component↓

![[Grasshopper] How to use Expression to use mathematical expressions, formulas, and functions](https://iarchway.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/10/Expression.png)



Comment