This section describes how to use the Remap Numbers component, which changes the numbers in a list by a newly specified range.
On the Grasshopper, it is represented by either of the two above.
To change the numbers in the list to a new specified range
By using Remap Numbers, you can change the numbers in the list within a newly specified range.
Components used: (1) Bounds (2) Remap Numbers
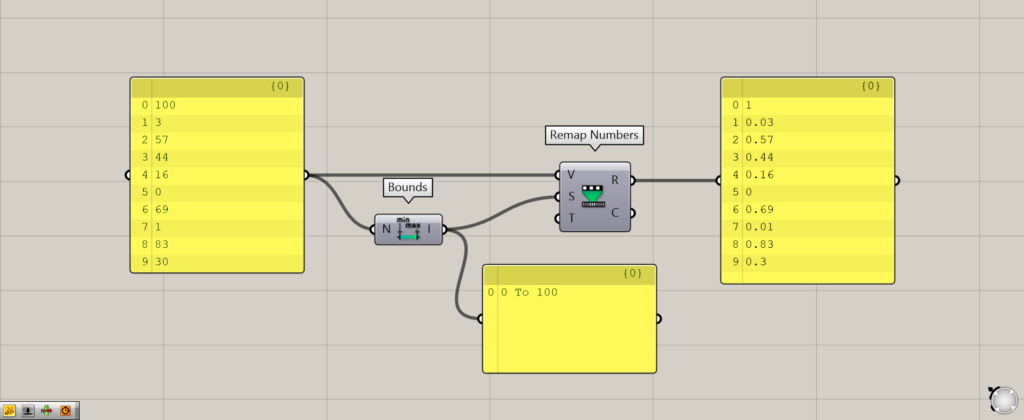
In the Remap Numbers(V), connect the numerical data in the list that you want to change.
In this case, random numbers between 0 and 100 are connected.
In the Remap Numbers(S), connect the domain range of the numbers in the list (the range consisting of the minimum and maximum values of the numbers).
This time, Bounds is used to create a domain range consisting of the minimum value of 0 and the maximum value of 100 from the original numerical values in the list, and is connected to the Remap Numbers(S).
Then, initially, the numbers were converted from the Remap Numbers(R) so that the maximum value of the numbers was 1.
In this case, the maximum value of 100 of the original numerical value is converted to 1 and accordingly to 0.57 for a numerical value of 57, and 0~1 for a numerical value of 57.
Additional Components: (1) Construct Domain
Initially, the maximum value was converted to 1. However, the minimum and maximum values to be converted can also be converted by setting the Remap Numbers(T).
The Remap Numbers(T) also specifies a domain range.
This domain range becomes the minimum and maximum values after conversion.
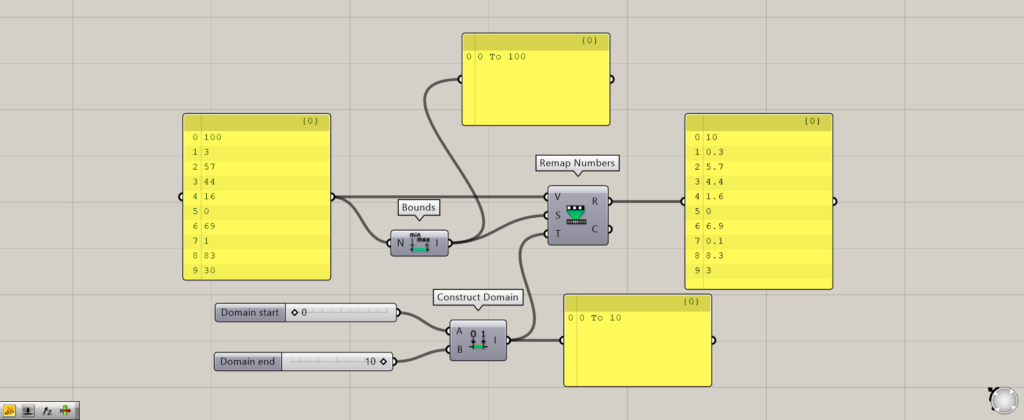
In this case, Construct Domain is used to create the domain range.
In this case, the minimum value of 0 is input to the Construct Domain(A) and the maximum value of 10 to the Construct Domain(B), creating a domain range of 0~10 and connecting it to the Remap Numbers(T).
Then, as shown in the image above, the original maximum value of 100 is output as 10, and other values are converted accordingly, such as 57 as 5.7 and 16 as 1.6.
Thus, the maximum and minimum values after conversion can be specified with the Remap Numbers(T).
Output Data
Remap Numbers outputs two sets of data, one on the Remap Numbers(R) and the other on the Remap Numbers(C).
The difference between the two appears when a number that exceeds the range specified by the S is connected to the V.
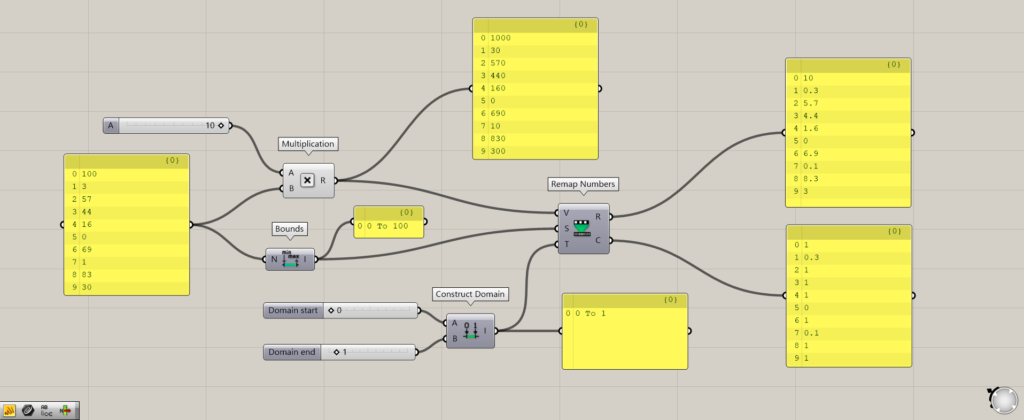
Additional Components: (1) Multiplication
In the image above, the Remap Numbers(S) is connected to a domain range of 0~100.
However, the Remap Numbers(V) is multiplied by 10 using Multiplication to the original values.
Therefore, all values are multiplied by 10, and some values exceed the 0~100 values specified on the Remap Numbers(S).
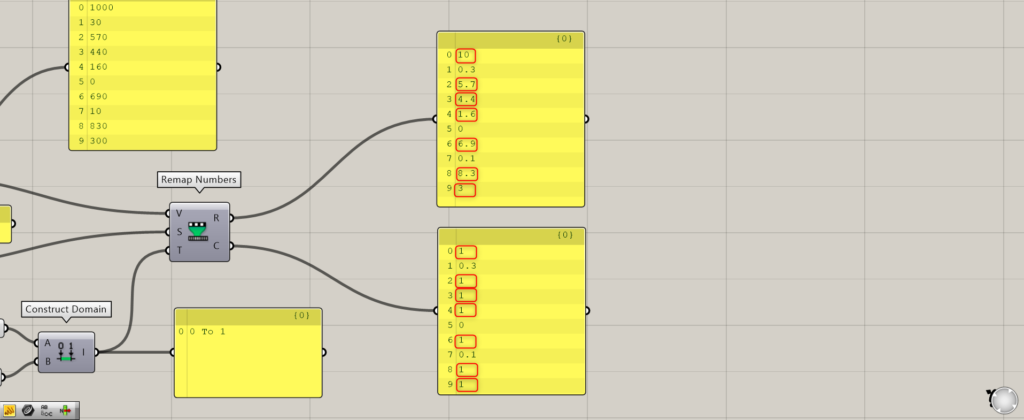
In this case, we have specified a domain range of 0~1 on the Remap Numbers(T), so that a numerical value of 100 would be 1, and a numerical value of 57 would be 0.57.
In the case of the Remap Numbers(R), the output is also a number greater than 1, 10 for a value of 1000 and 5.7 for a value of 570.
Since the numerical value of 100 is 1, 1000 is converted to 10, and so on.
However, for the Remap Numbers(C), both 1000 and 570 are converted to 1.
This means that any number that exceeds the 0~100 domain range of the Remap Numbers(S) in the original number, no matter how large, will be converted to the maximum value.
In this case, the number 1000 is outside the 0~100 range, so it becomes a number 100, which is then converted to a number 0~1 on the Remap Numbers(T), so it becomes 1.
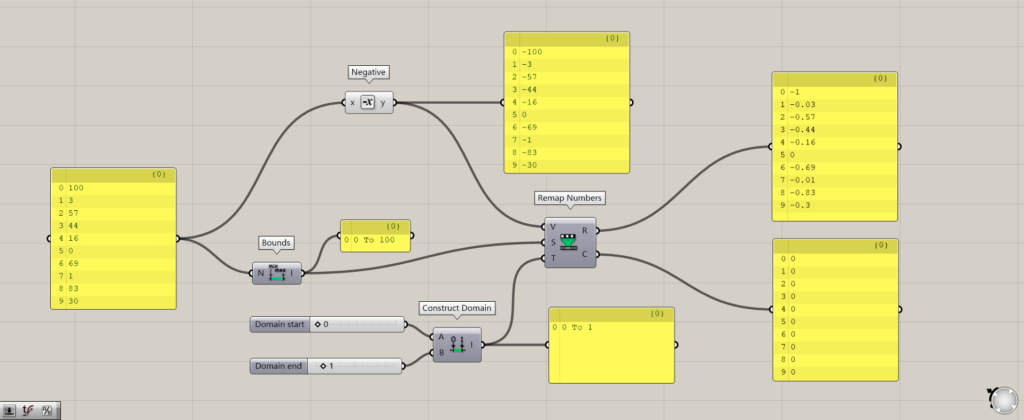
Additional components: (1) Negative
If the value is smaller than the minimum value, the Remap Numbers(C) is still forced to convert the value to the minimum value.
In this case, Negative is used to convert the original value to a negative value.
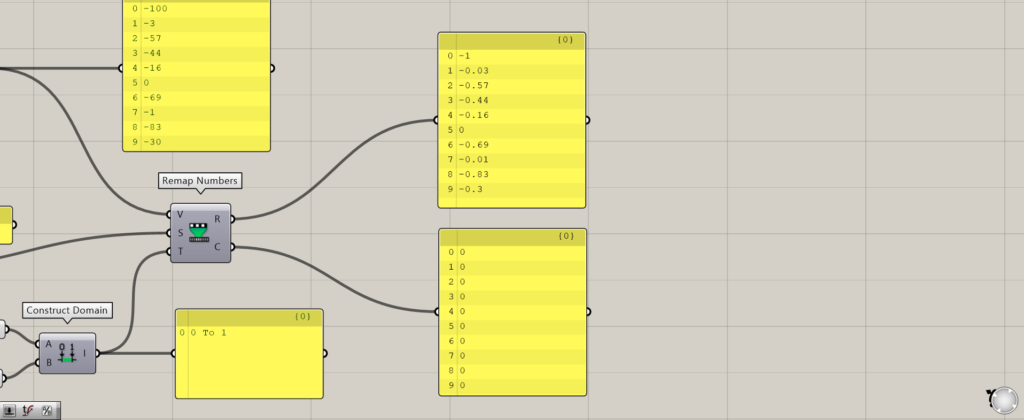
Looking at the Remap Numbers(C), the domain range specified by the Remap Numbers(S) is 0~100, so negative numbers below that range are converted to the minimum value of 0.
Thus, the Remap Numbers(C) forces any number that exceeds the maximum and minimum values to be converted to the maximum and minimum values.
List of Grasshopper articles using Remap Numbers component↓

![[Grasshopper] How to use Remap Numbers to change numbers in a new range](https://iarchway.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/09/Remap-Numbers.png)



Comment