This article explains how to use Surface Split to divide surfaces with curves.
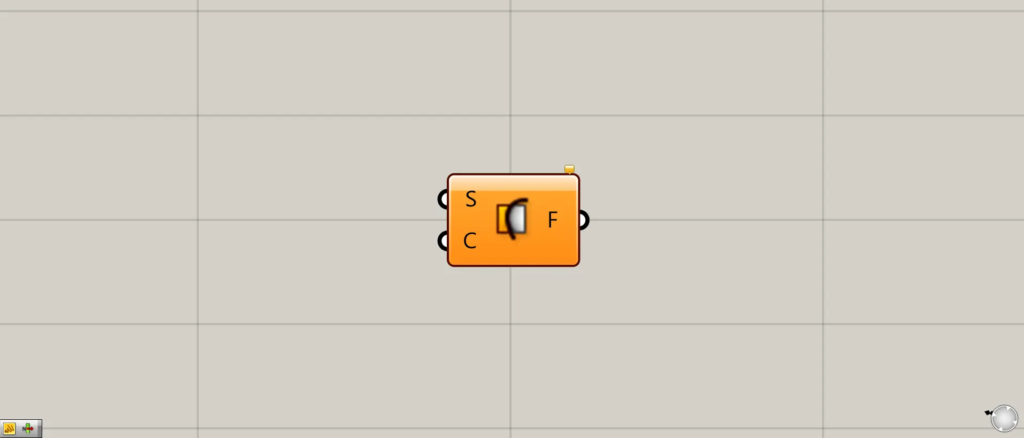

On the Grasshopper, it is represented by either of the two above.
Divide a surface with curves
Using Surface Split, you can divide a surface with curves.
In this case, please note that the operation will not execute correctly unless the surface data and curve data are not overlapping.
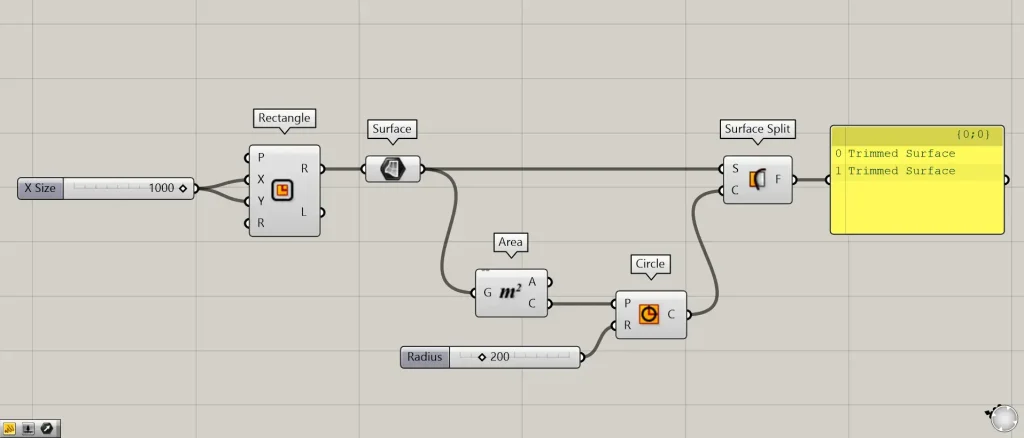
Components used: ① Rectangle ② Surface ③ Area ④ Circle ⑤ Surface Split
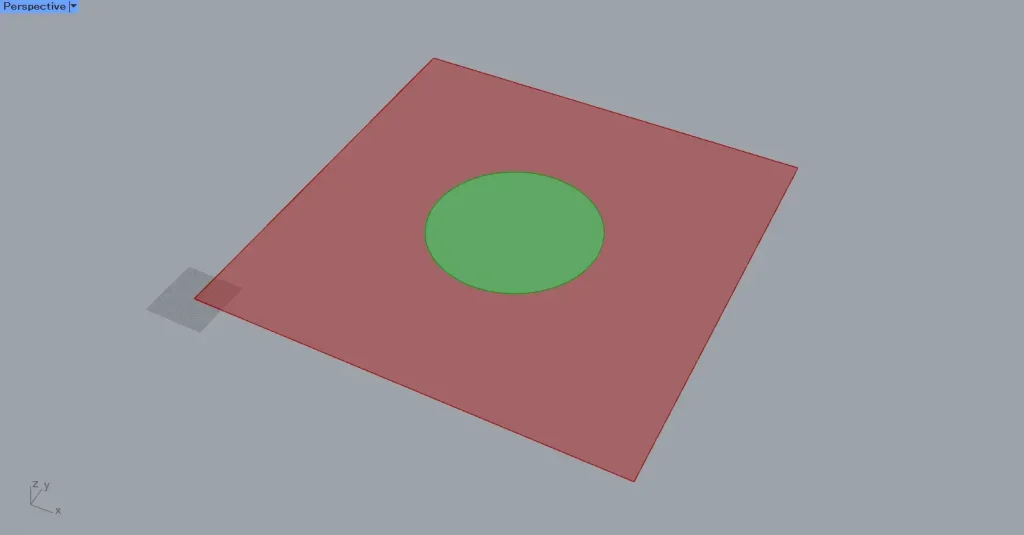
As an example this time, we’ll create a square surface and divide it using circular curve data.
First, enter the numerical value for the length of one side into the Rectangle(X and Y).
This time, 1000 has been entered in both fields.
Then, a 1000×1000 square line data set will be created.
Then, connect the Rectangle to the Surface.
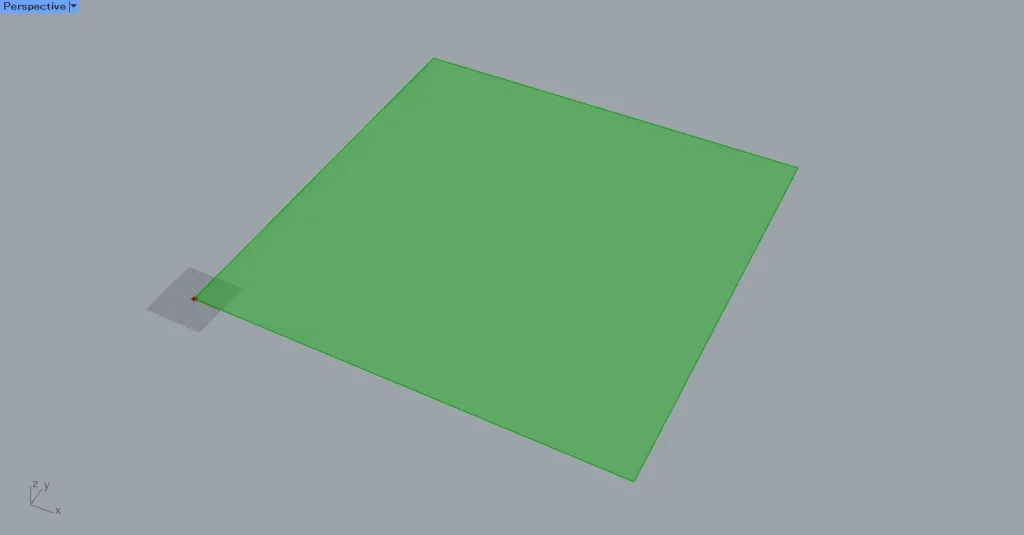
Then, as shown in the image above, a square surface was created.
Then connect the Surface to the Area.
Then, you can obtain the point data at the center of the square.
Next, connect the Area(C) to the Circle(P).
Additionally, enter the radius value into the Circle(R).
This time, enter 200.
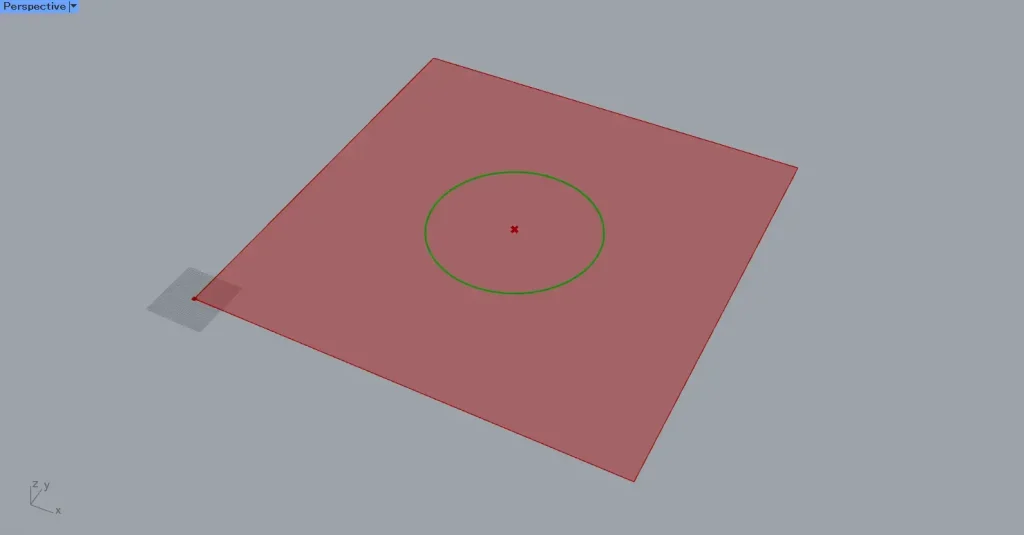
Then, a circle with a radius of 200 was created at the center of the square.
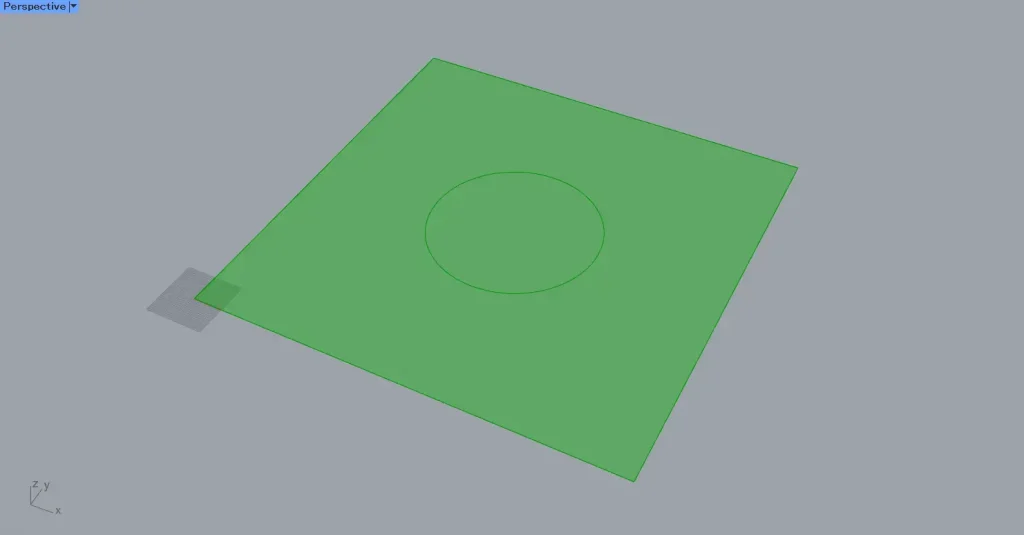
Next, connect the Surface to the Surface Split(S).
Also, connect the Circle to the Surface Split(C).
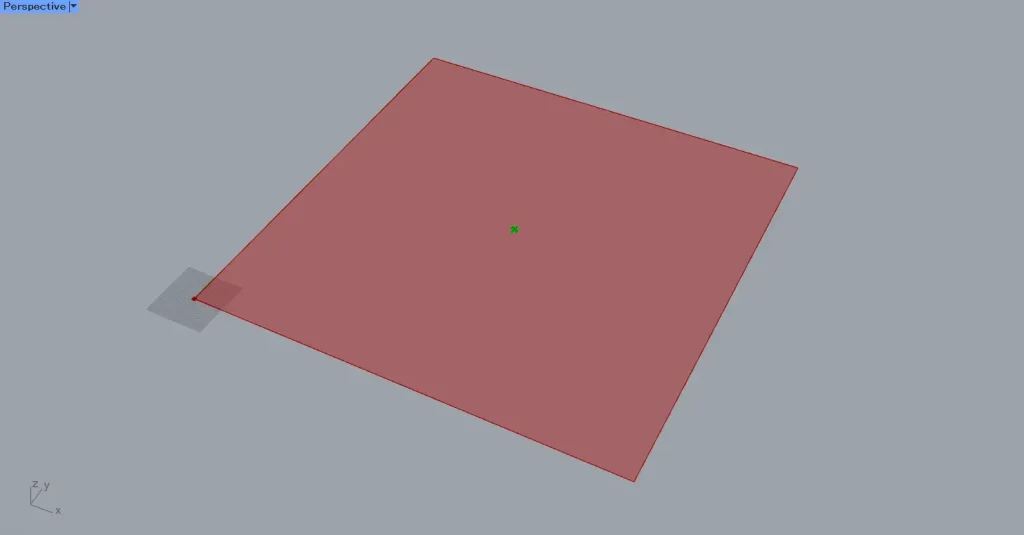
Then, the surface is divided using curve data.
However, since multiple surface data sets exist that have been split by Surface Split, both will be displayed.
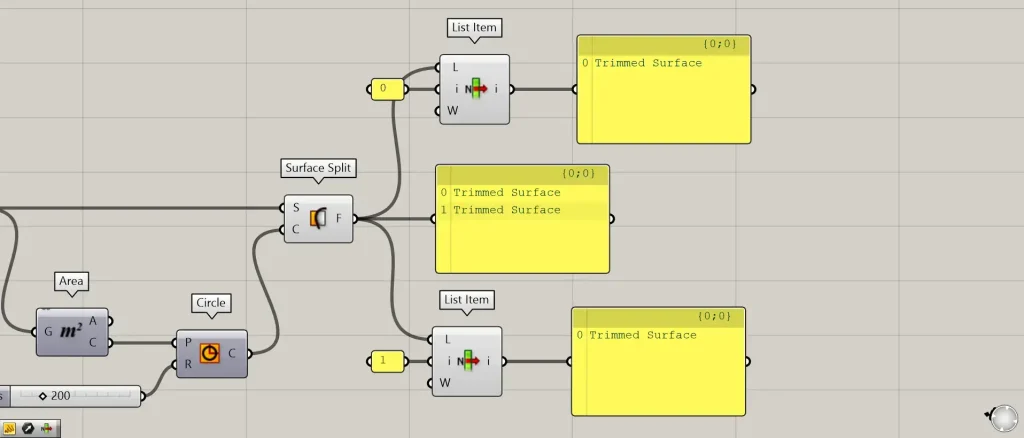
Additional Component: ①List Item
Let’s try acquiring each of the split surfaces.
Looking at the Surface Split data, you can see that it is split into two surfaces.
Prepare two List Item and connect the Surface Split to each List Item(L).
Then, enter 0 into the first List item(i).
Enter 1 into the other List Item(i).
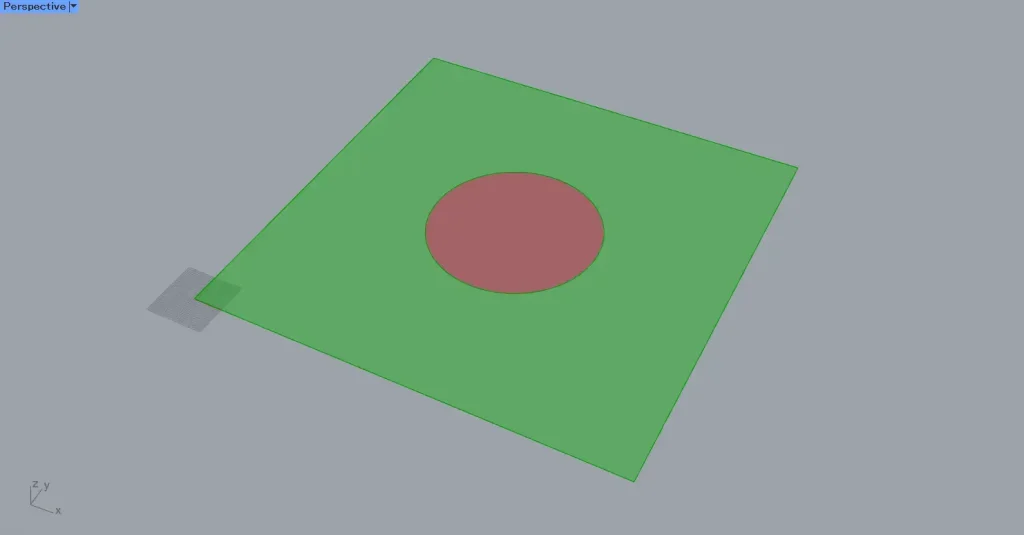
This allows you to obtain the surfaces with index numbers 0 and 1, as shown in the top two images.
In this way, when you want to obtain individual surfaces after splitting them with Surface Split, use List Item or Cull Index.
List of Grasshopper articles using Surface Split component↓

![[Grasshopper] How to use Surface Split to divide surfaces with curves](https://iarchway.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/01/Surface-Split.png)



Comment