数式や計算式、関数を使うことができる、Expressionの使い方について解説します。
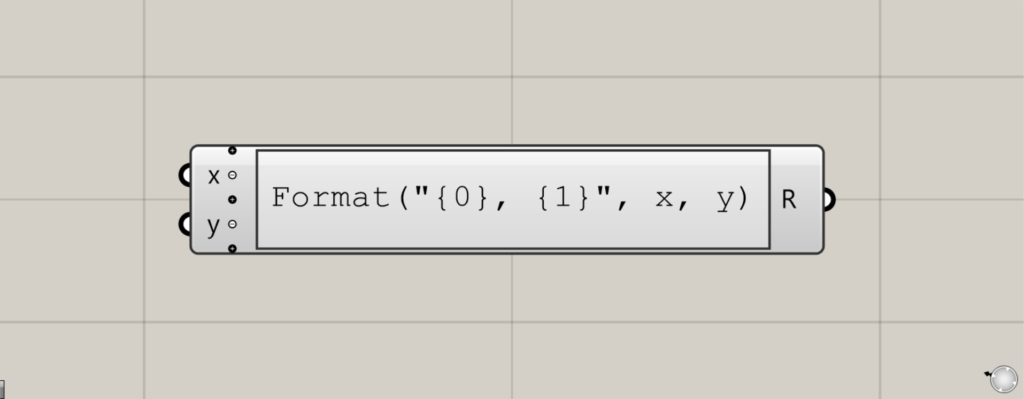
グラスホッパー上では上のように表されます。
数式や計算式を使う
Expressionを使うことで、数式や計算式を使うことができます。
Expressionの設定画面
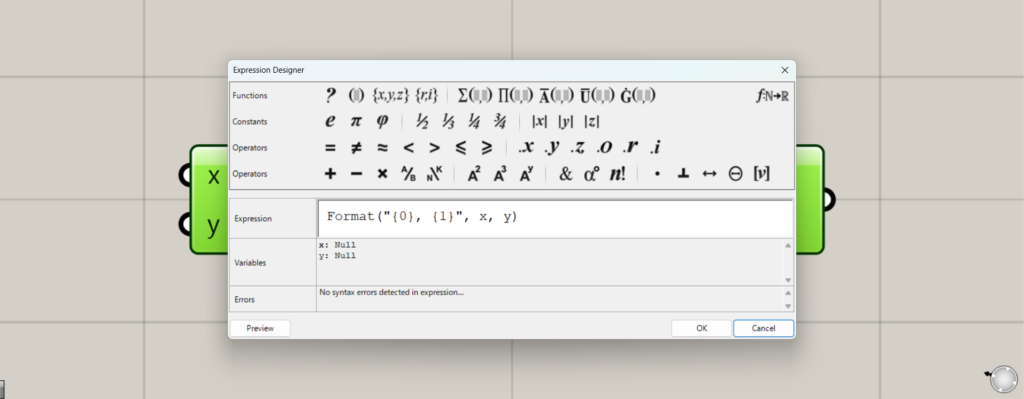
Expressionをダブルクリックすると、Expressionの設定画面が表示されます。
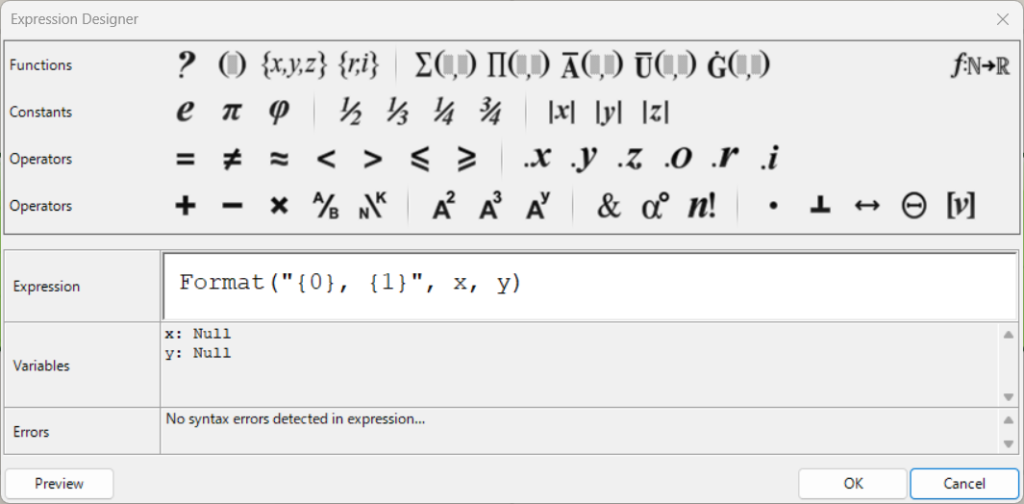
こちらが、Expressionの設定画面になります。
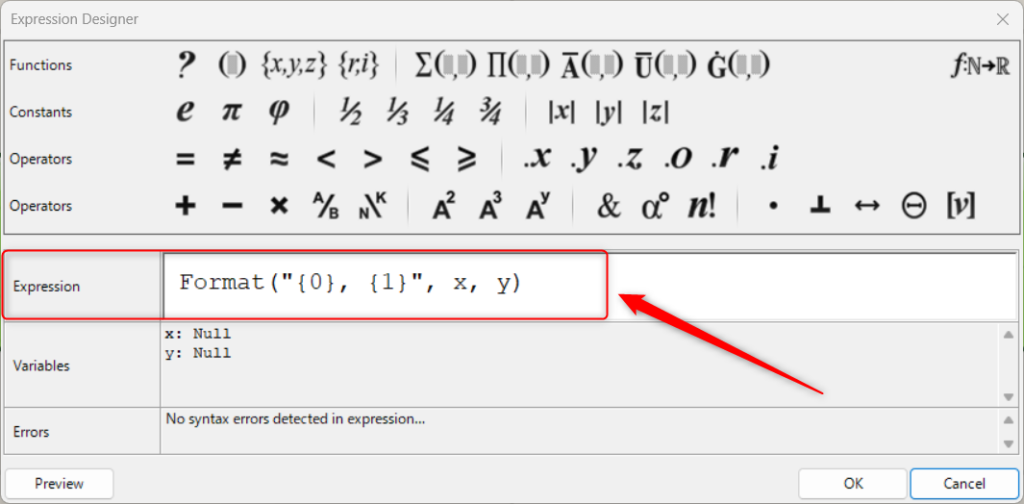
Expressionの部分を変えることで、任意の数式や計算式を作ることができます。
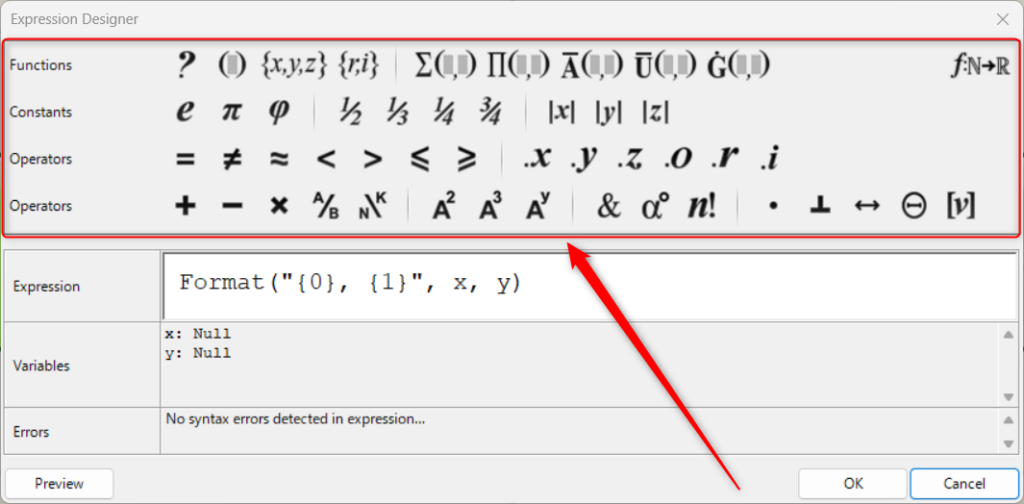
また、上のアイコンをクリックすることで、数式や計算式に記号や関数を追加することもできます。
数式や計算式を作る
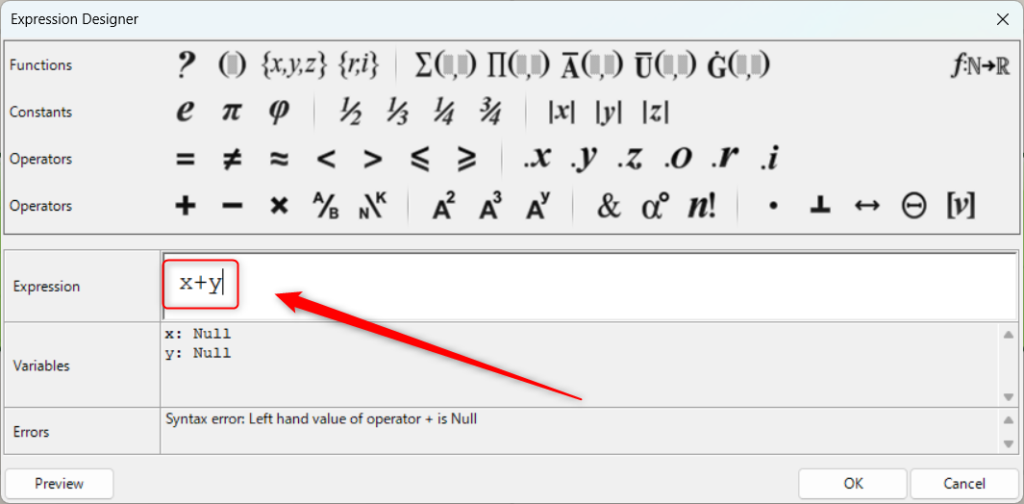
まずは簡単な計算をしてみます。
最初は、Expressionにx+yと入力しました。
その後、右下のOKを押します。
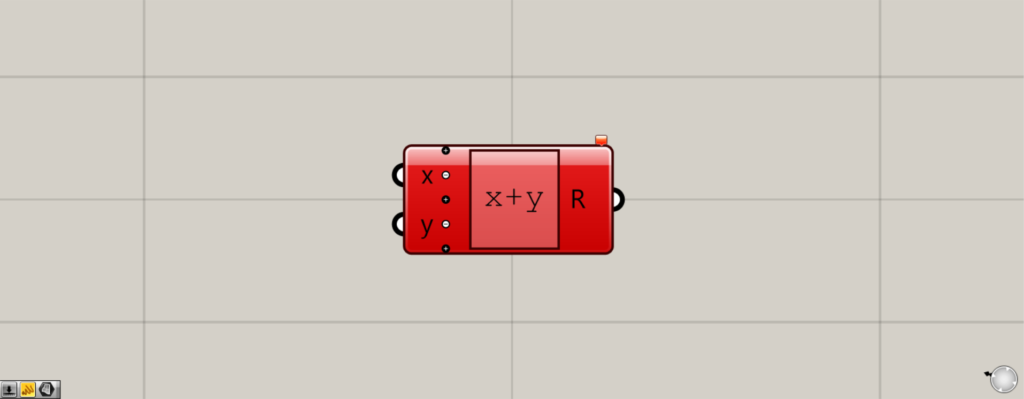
すると、上の画像のように赤くエラー表示されます。
しかし、このままでも問題ありません。
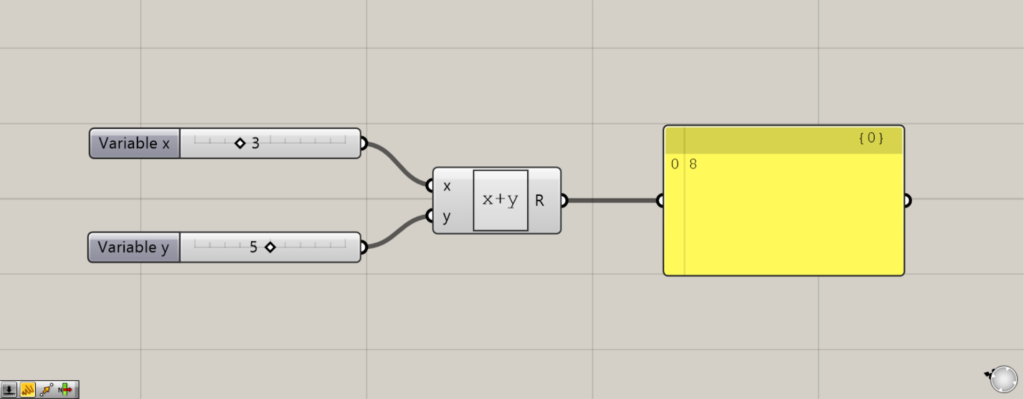
左側の端子に情報を入力します。
デフォルトでは、x端子とy端子があります。
今回は、x端子に3、y端子に5を入力しました。
すると、3+5の足し算が行われ、R端子から8が出力されました。
このように、左側の端子からは変数を入力します。
端子・変数の数を増やす
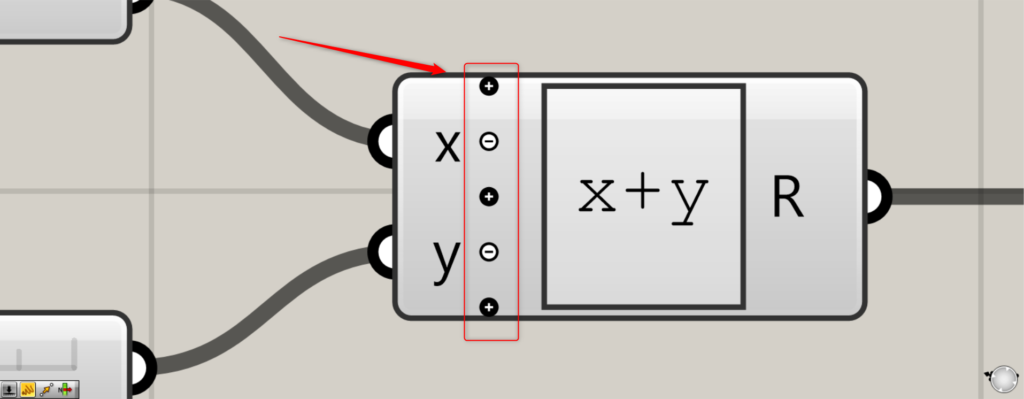
左側の端子の数を変えることもできます。
Expressionにズームすると、+と-のアイコンが表示されるようになります。
+のアイコンを押すと、その場所に端子が追加されます。
-のアイコンを押すと、その部分にある端子が消えます。
今回は、y端子の下の+を押しました。
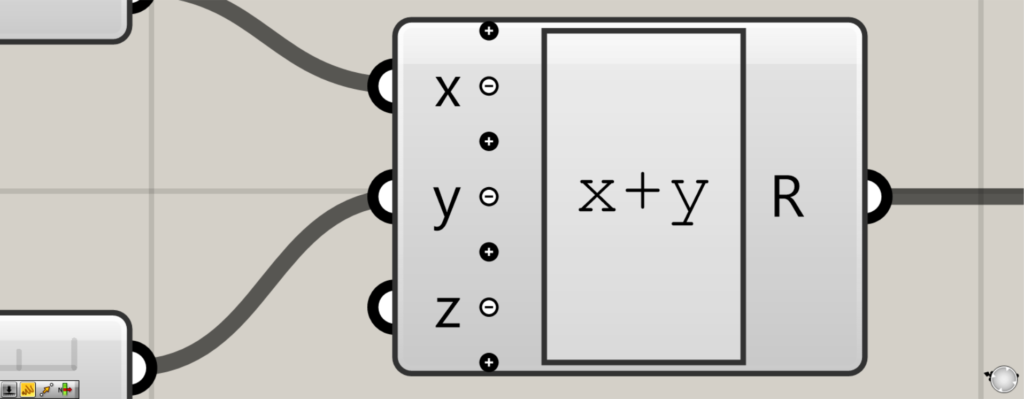
すると、新しくz端子が追加されました。
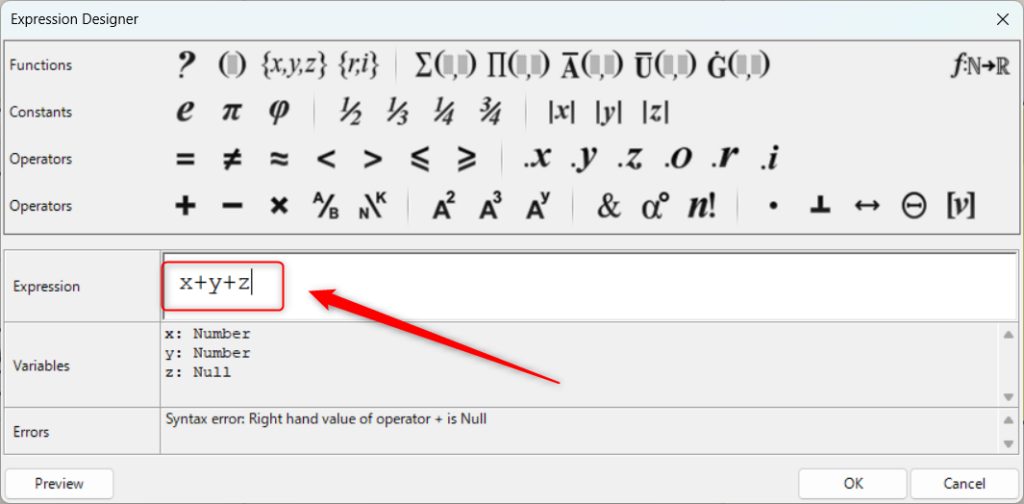
z端子ができたので、計算式を変えてx+y+zに変更しました。
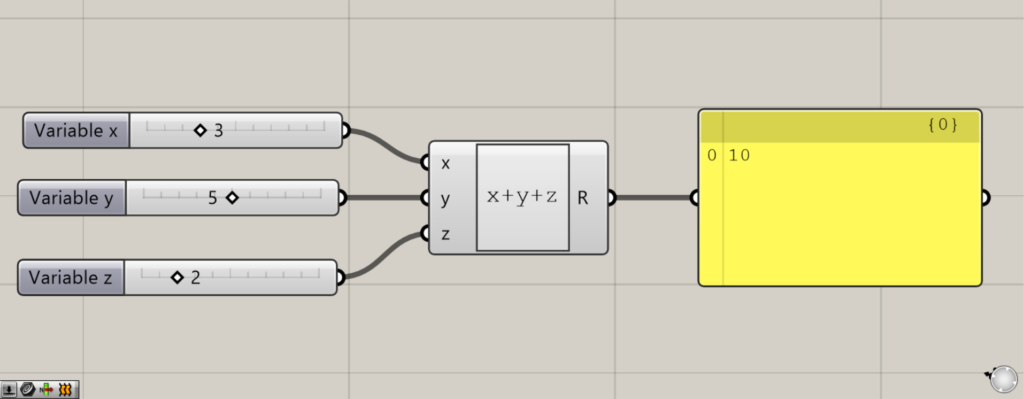
すると、このように3つの端子で計算できました。
このように、複数の端子で計算することもできます。
端子・変数名を変える
端子の名前を変えることで、変数名を変えることもできます。
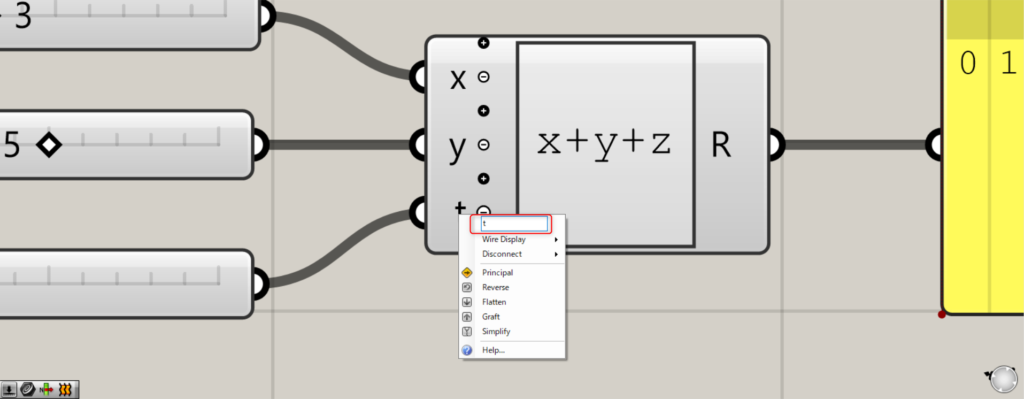
その場合、変更したい端子を右クリックします。
その後、端子名を変更します。
今回は、端子名をtにしました。
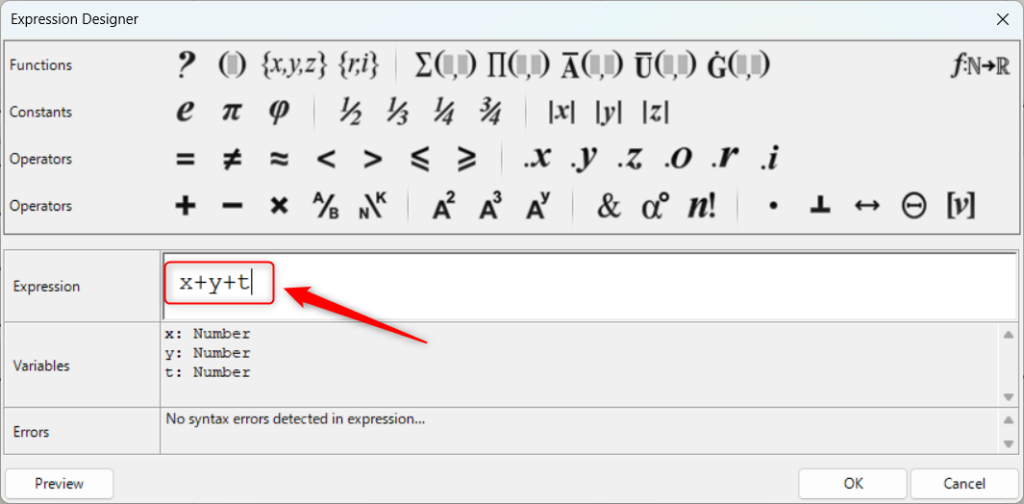
その場合、計算式の変数名も変えます。
今回は端子名をtにしたので、x+y+tにしました。
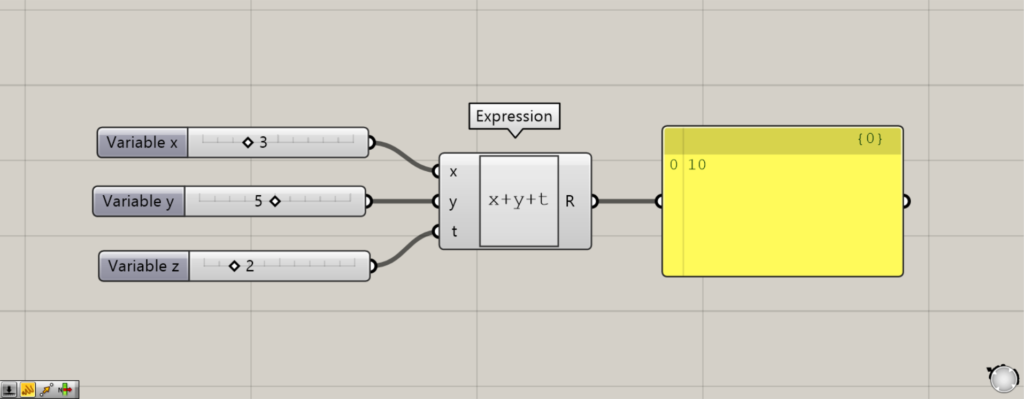
すると、このように変数名を変えて計算できました。
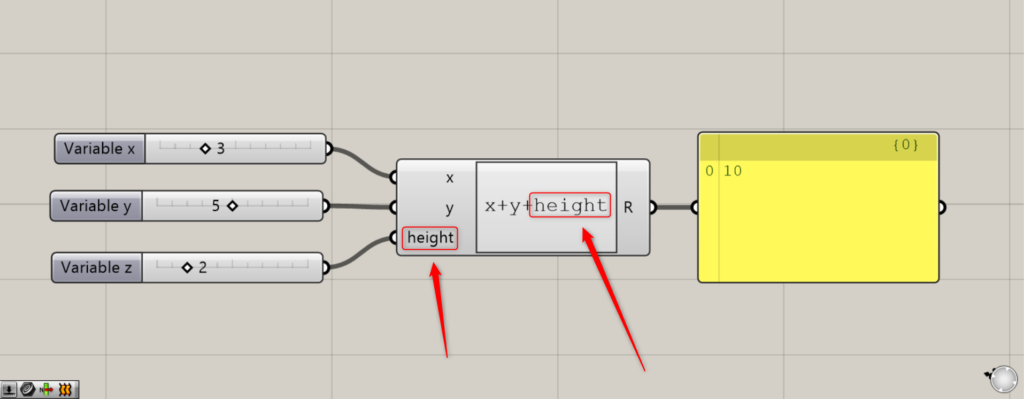
長い変数名は、上の画像のように長くすることもできます。
文字列として結合する
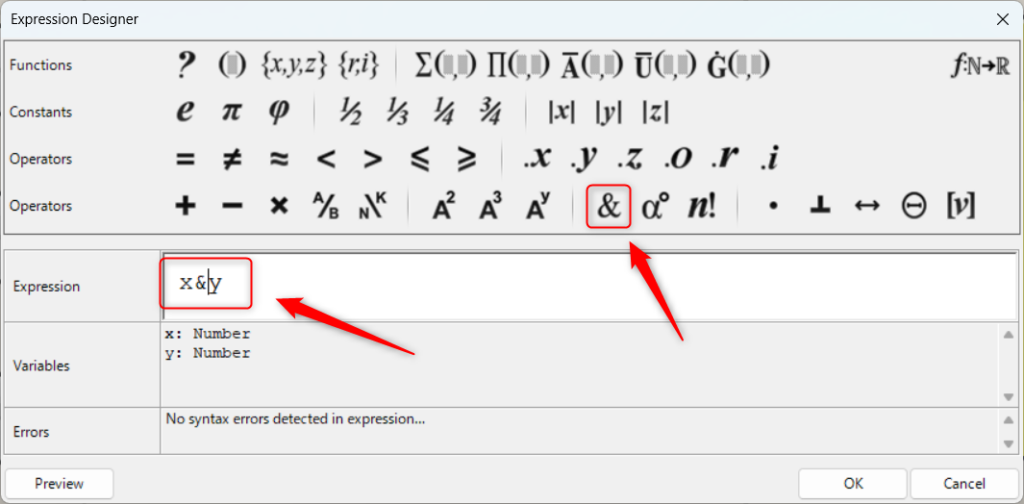
&を使うことで、入力した情報を文字列として結合させることもできます。
今回は、x&yをExpressionに入力しました。
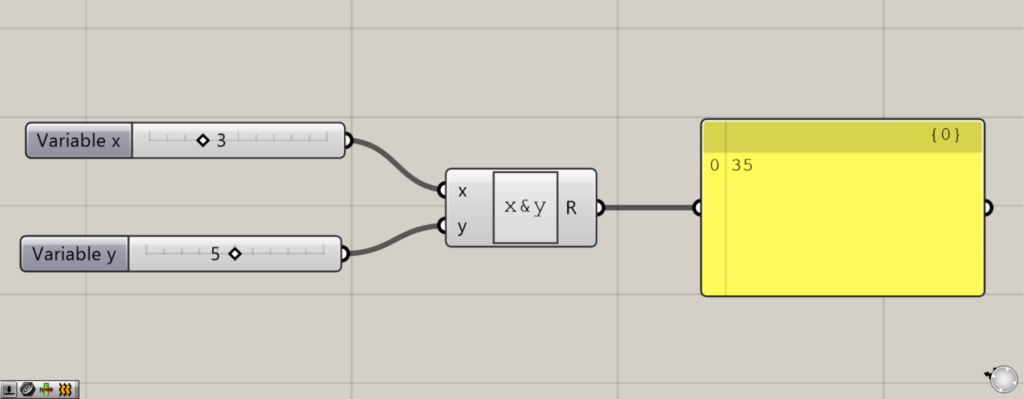
その後、左側の端子に情報を入力します。
最初は、x端子に3、y端子に5を入力しました。
すると、上の画像のように35と表示されました。
これは数値の35ではなく、3と5が文字として隣り合っている状態です。
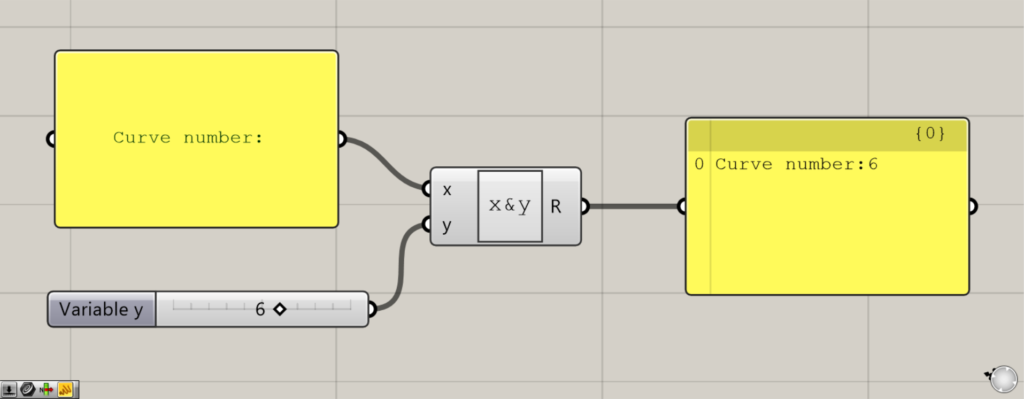
文字として扱うため上の画像のように、線の数:6のような使い方もできます。
座標を作成する
座標を作成することもできます。
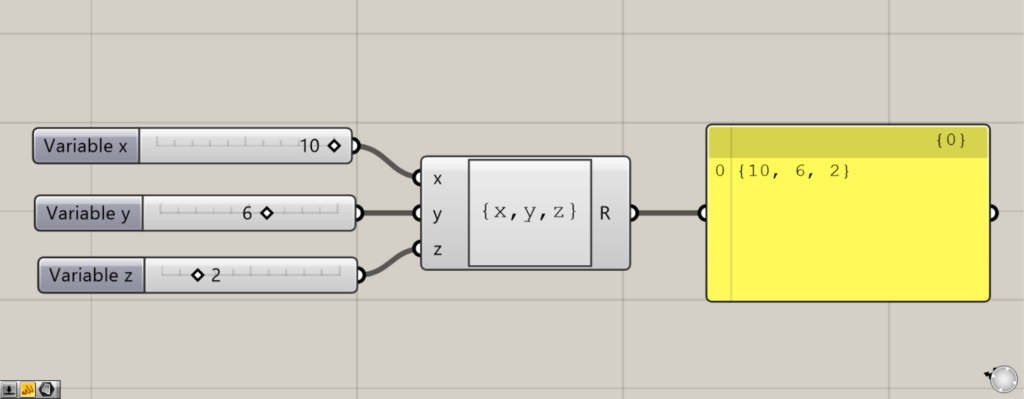
その場合、Expressionに{x,y,z}のように入力します。
その後、左側の端子にx、y、z座標のそれぞれの数値を入力します。
すると、座標データが作成されます。
ライノセラス上を見てみると、指定した座標に点が作成されていることが分かります。
関数を使う
次は、関数を使う方法を解説します。
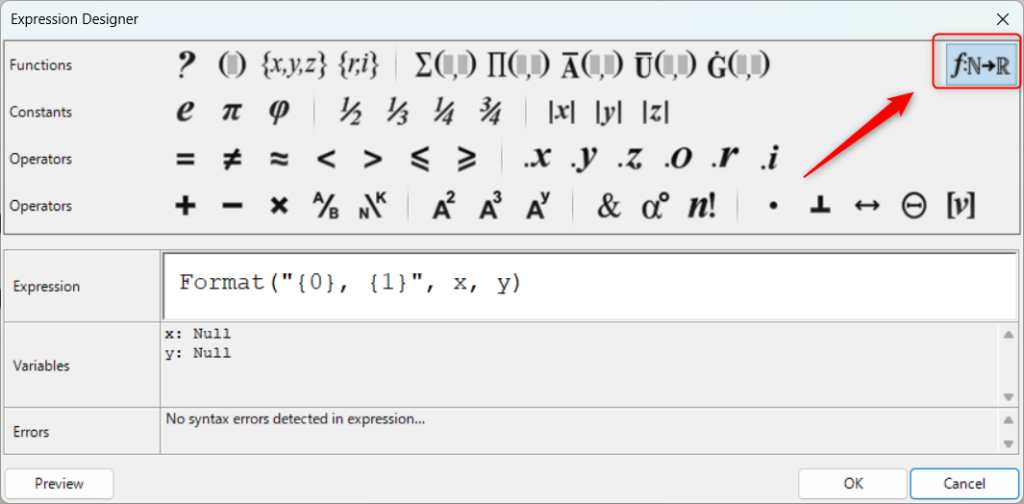
Expressionの設定画面で、一番右上の部分をクリックすると、使用できる関数を確認することができます。
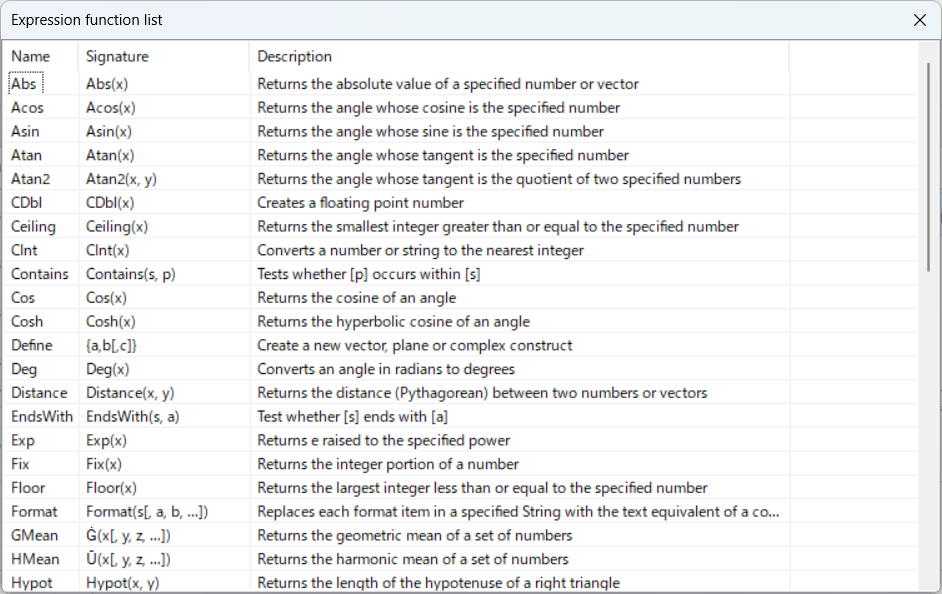
このように、関数一覧が表示されます。
以下に、使用できる関数を一覧でまとめました。
一番左のNameは関数名です。
真ん中のSignatureは、Expressionでの関数の入力方法です。
Descriptionは、関数の説明(英語)です。
| Name | Signature | Description |
| Abs | Abs(x) | Returns the absolute value of a specified number or vector |
| Acos | Acos(x) | Returns the angle whose cosine is the specified number |
| Asin | Asin(x) | Returns the angle whose sine is the specified number |
| Atan | Atan(x) | Returns the angle whose tangent is the specified number |
| Atan2 | Atan2(x, y) | Returns the angle whose tangent is the quotient of two specified numbers |
| CDbl | CDbl(x) | Creates a floating point number |
| Ceiling | Ceiling(x) | Returns the smallest integer greater than or equal to the specified number |
| Clnt | Clnt(x) | Converts a number or string to the nearest integer |
| Contains | Contains(s, p) | Tests whether [p] occurs within [s] |
| Cos | Cos(x) | Returns the cosine of an angle |
| Cosh | Cosh(x) | Returns the hyperbolic cosine of an angle |
| Define | {a,b[,c]} | Create a new vector, plane or complex construct |
| Deg | Deg(x) | Converts an angle in radians to degrees |
| Distance | Distance(x, y) | Returns the distance (Pythagorean) between two numbers or vectors |
| EndsWith | EndsWith(s, a) | Test whether [s] ends with [a] |
| Exp | Exp(x) | Returns e raised to the specified power |
| Fix | Fix(x) | Returns the integer portion of a number |
| Floor | Floor(x) | Returns the largest integer less than or equal to the specified number |
| Format | Format(s[, a, b, …]) | Replaces each format item in a specified String with the text equivalent of a corresponding value |
| GMean | Ġ(x[ y, z , …]) | Returns the geometric mean of a set of numbers |
| HMean | Ū(x[ y, z , …]) | Returns the harmonic mean of a set of numbers |
| Hypot | Hypot(x, y) | Returns the length of the hypotenuse of a right triangle |
| If | If(test, A, B) | Returns A if test is True, B if test is false |
| IndexOf | IndexOf(s, a[, i]) | Find the first character position of [a] within [s], starting the search at index [i] |
| Int | Int(x) | Returns the integer portion of a number |
| LCase | LCase(s) | Converts all characters in a string to their lower case equivalent |
| Left | Left(s, i) | Returns the [i] characters on the left hand side of the string |
| Length | Length(x) | Returns the magnitude of a vector or the number of characters in a string |
| Ln | Ln(x) | Returns the natural (base e) logarithm of a specified number |
| Log | Log(x[,b]) | Returns the base [b] logarithm of a specified number |
| Log10 | Log10(x) | Returns the base 10 logarithm of a specified number |
| Max | Max(x[ Z, …]) | Returns the maximum value in a set of numbers |
| Mean | A(x[, Z, …]) | Returns the mean (average) of a set of numbers, vectors or planes |
| Min | Min(x[, y, Z, …]) | Returns the minimum value in a set of numbers |
| MinkowskiDistance | MinkowskiDistance(x, y, p) | Returns the p-order Minkowski distance between two numbers or vectors |
| Pow | Pow(x, y) | Returns a specified number or vector raised to the specified power |
| Prod | Π(x[, y, z, …]) | Returns the product of a set of numbers |
| Rad | Rad(x) | Converts an angle in degrees to radians |
| Replace | Replace(s, a, b) | Replaces all occurrences of [a] in [s], with [b] |
| Right | Right(s) i) | Returns the [i] characters on the right hand side of the string |
| Round | Round(x[, d]) | Rounds a floating point number to the specific decimal places |
| Sin | Sin(x) | Returns the sine of an angle |
| Sinh | Sinh(x) | Returns the hyperbolic sine of an angle |
| Sqrt | Sqrt(x) | Returns the square root of a specified number |
| StartsWith | StartsWith(s, a) | Test whether [s] starts with [a] |
| SubString | SubString(s, i[ I]) | Returns a substring based on start char index and length |
| Sum | ∑(x[, y, z, …]) | Returns the sum of a set of numbers or vectors |
| Tan | Tan(x) | Returns the tangent of an angle |
| Tanh | Tanh(x) | Returns the hyperbolic cosine of an angle |
| UCase | UCase(s) | Converts all characters in a string to their upper case equivalent |
| Unitize | [v] | Returns a unit length vector |
関数の使用例
いくつかの関数の使用例を見てみましょう。
使用例1
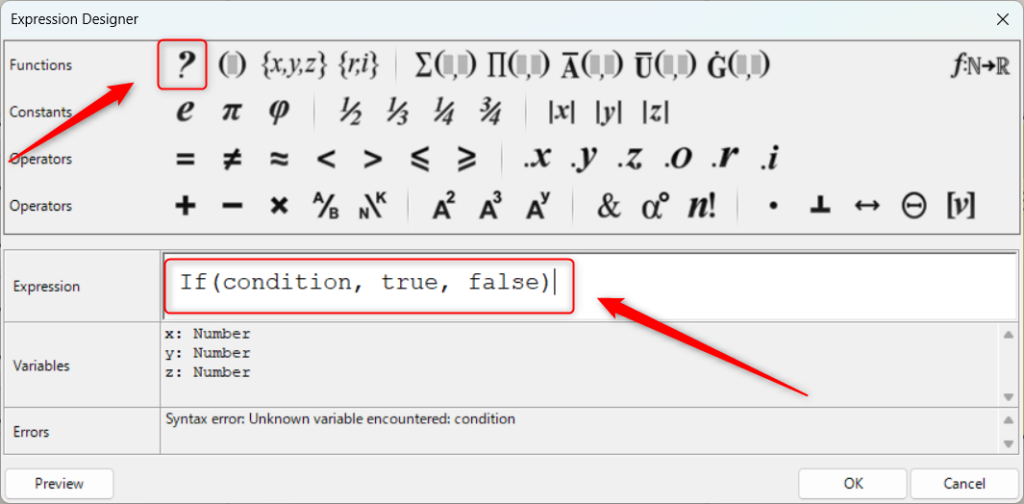
1つ目の例は、If関数です。
If関数は、Expressionの左上のアイコンをクリックすることでもできます。
If関数を使うには、If(条件, 真の場合, 偽の場合)のように入力します。
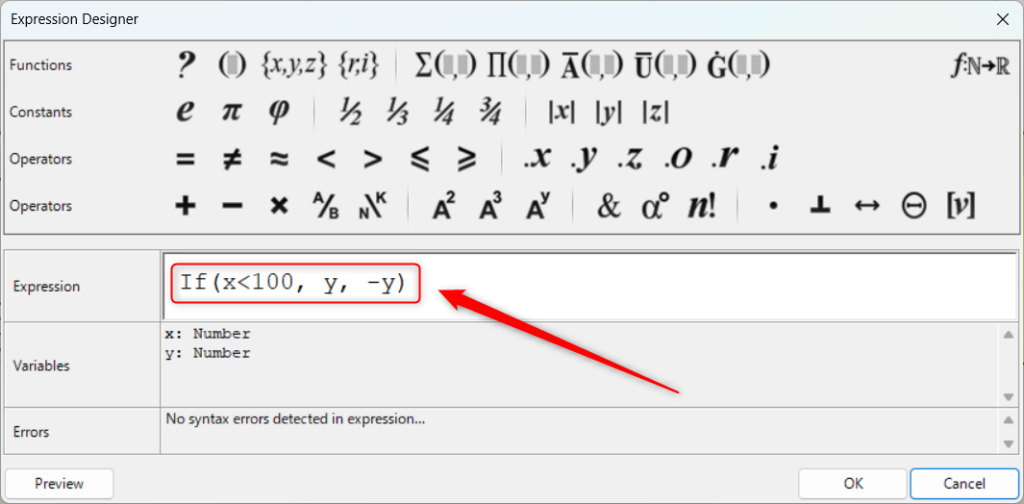
今回は、If(x<100, y, -y)と入力しました。
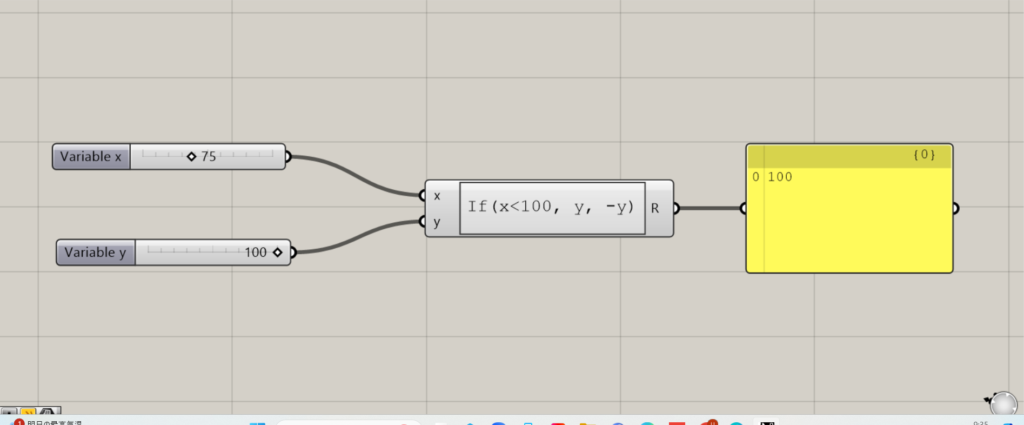
この場合、xが100未満の時、yは負の値になります。
今回の場合、xに入力した数値は75で100より小さいので、出力される数値は正の値です。
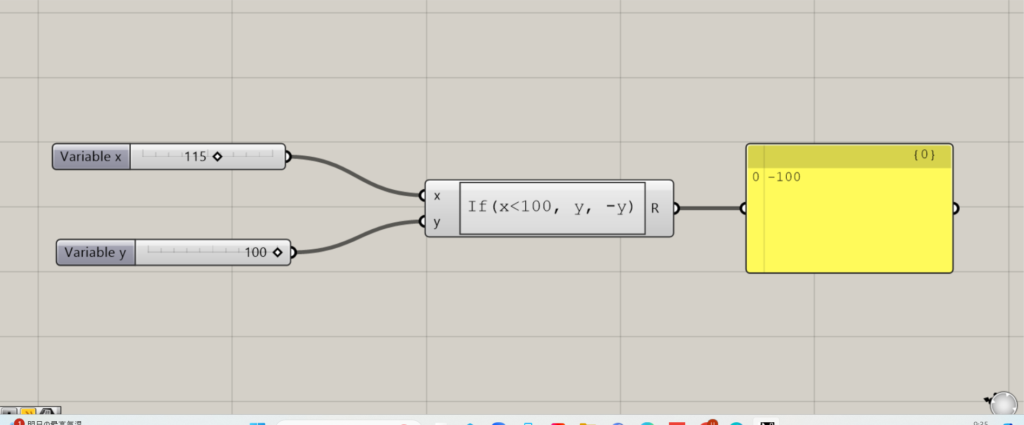
逆にxが100以上の時は、yは正の値になります。
今回の場合、xに入力した数値は115で100より大きいので、出力される数値は負の値です。
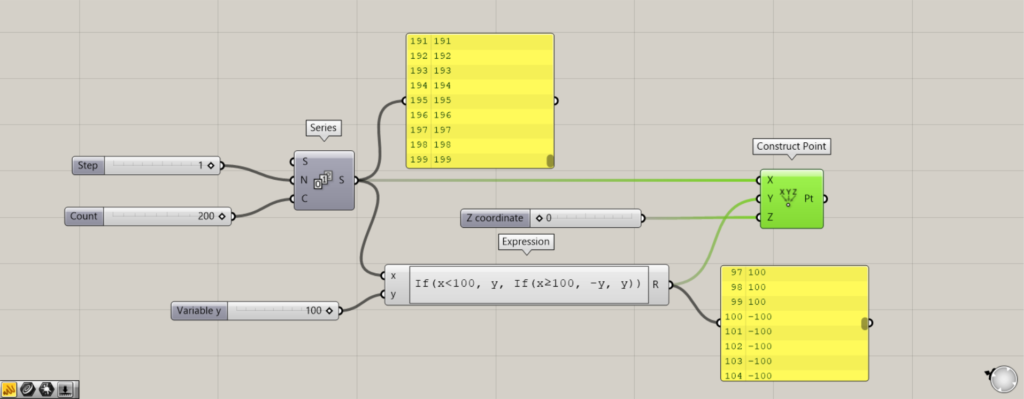
使用コンポーネント:①Series ②Expression ③Construct Point
上の例は、点を複数作成する例です。
先程の方法を応用して、ある一定の数値をxが超えた場合、負の数値になるので、点の位置が変わります。
SeriesのN端子に、増加数の1を入力します。
C端子に、作成する数値の個数の200を入力します。
すると、0~199の数値が作成されます。
その数値を、先程のExpressionのx端子につなげます。
その後、Construct PointのX端子に、Seriesをつなげます。
Y端子に、ExpressionのR端子をつなげます。
Z端子に、0をつなげます。
すると、X座標100で、生成される点のY座標が負の座標に来るようになりました。
使用例2
次の使用例は、Sin関数です。
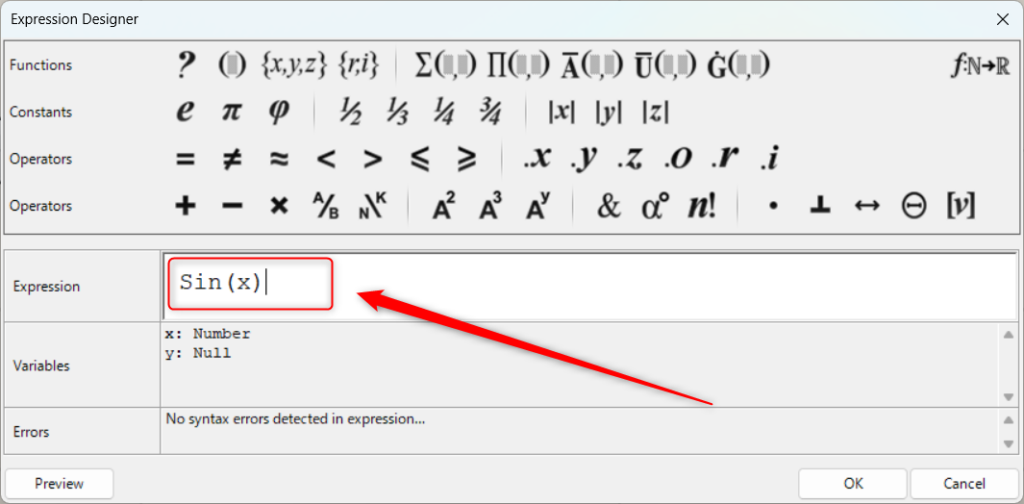
Sin関数を使うには、ExpressionでSin(x)と入力します。
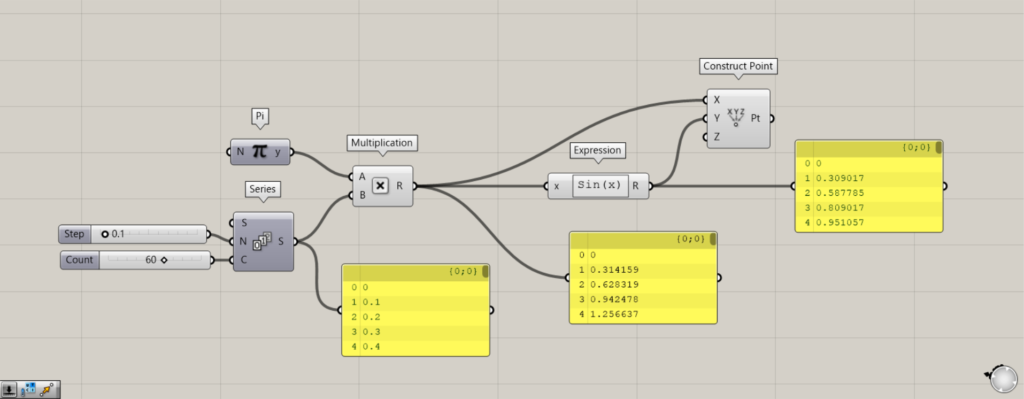
使用コンポーネント:①Pi ②Series ③Multiplication ④Expression ⑤Construct Point
Piを使うことで、円周率のπを使うことができるようになります。
0.1を、SeriesのN端子につなげます。
C端子に、作成する数値の個数を入力します。
その後、PiとSeriesをMultiplicationにつなげます。
さらに、MultiplicationをExpressionにつなげます。
Construct PointのX端子に、Multiplicationをつなげます。
Construct PointのY端子に、Expressionをつなげます。
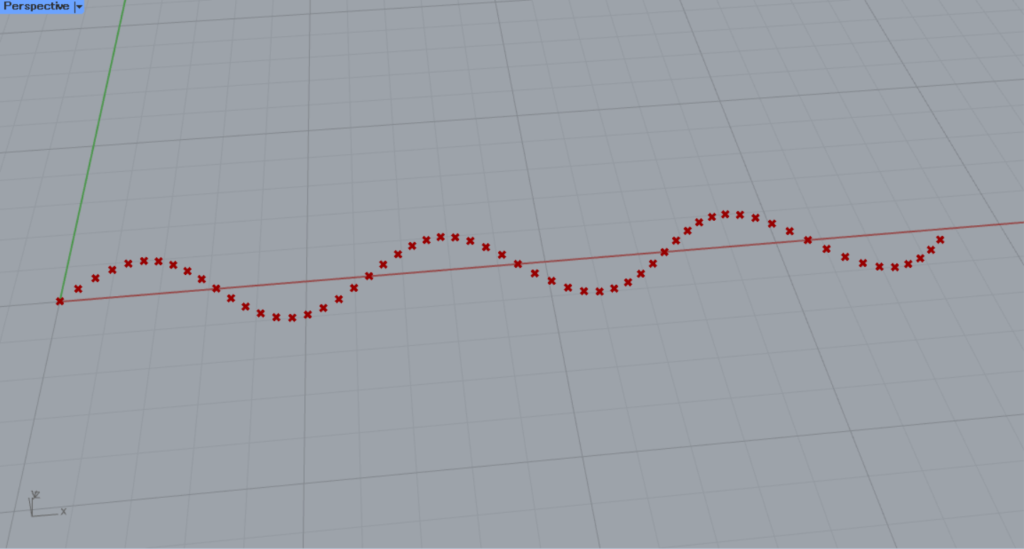
すると、このようにSin波を描くように点が作成されました。
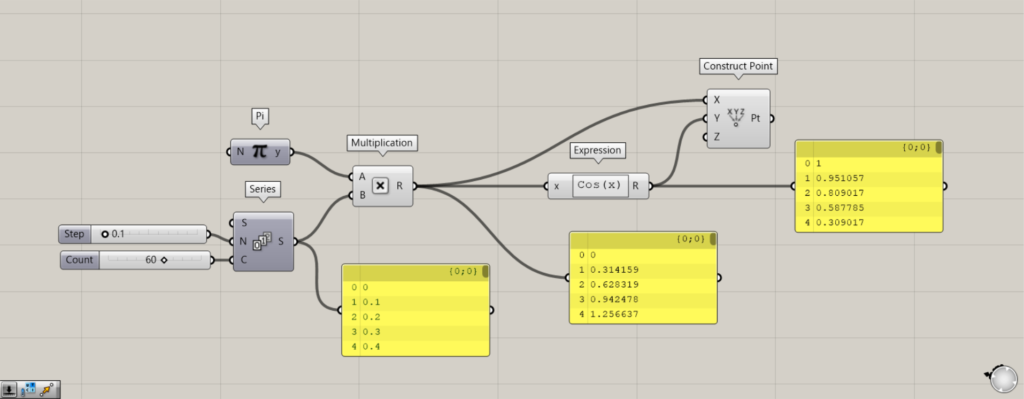
Cos関数に変えてみます。
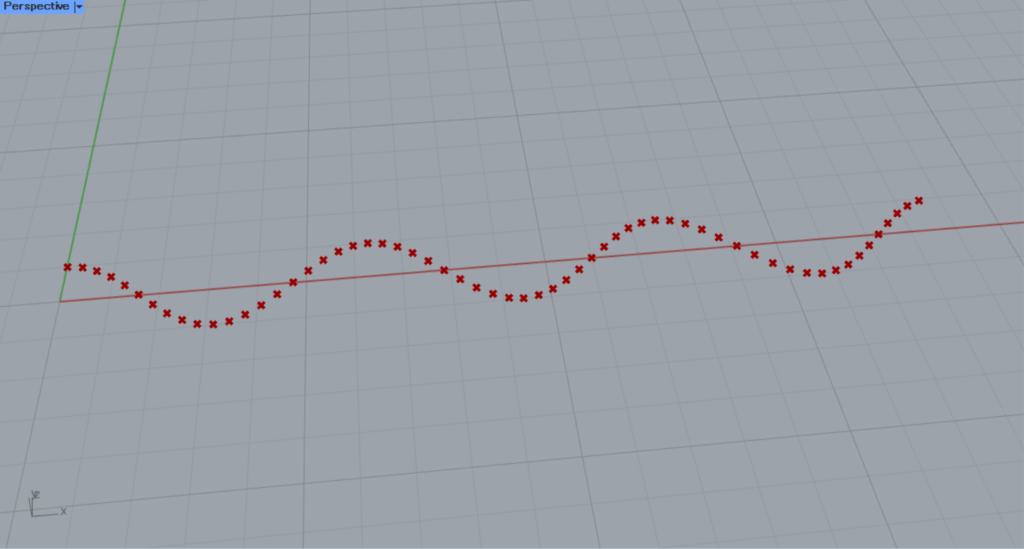
すると、Cosine波に変わりました。
使用例3
次は、Min関数です。
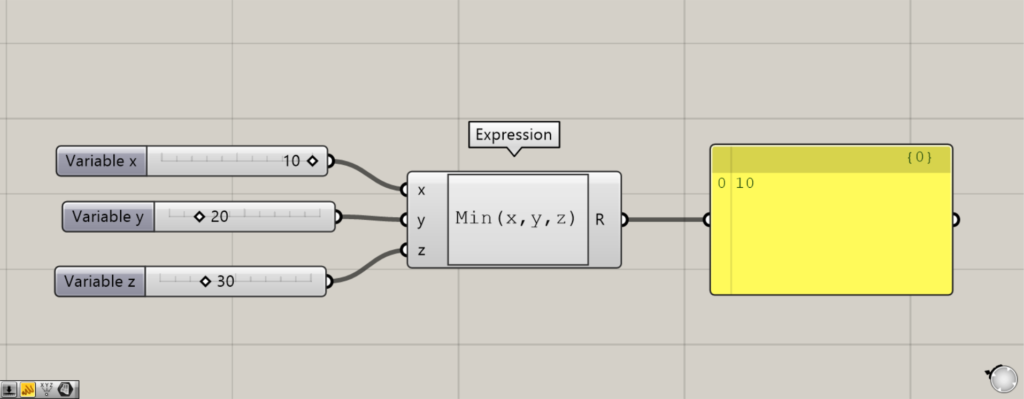
Min関数を使うには、ExpressionでMin(x,y,z)と入力します。
Min関数を使うと、左側の端子に入力した数値から、一番最小の数値のみを出力します。
使用例4
最後は、シグマ関数です。
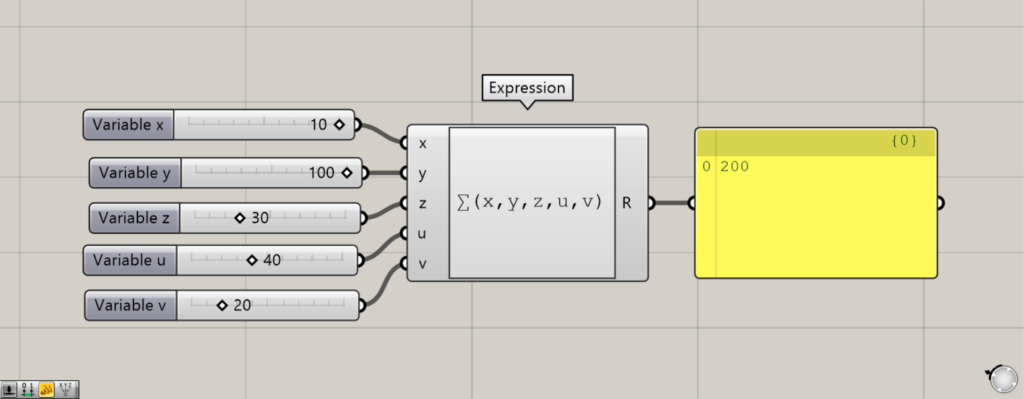
シグマ関数を使うには、Expressionで∑(x,y,z,u,v…)のように入力します。
シグマ関数を使うと、左側に入力した数値を合計した数値を出力します。
Expressionコンポーネントを使用しているグラスホッパー記事はこちら↓

![[Grasshopper]数式や計算式、関数を使うことができるExpressionの使い方](https://iarchway.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/09/eyecatch-4.png)




Comment